What is dangerous Gilbert syndrome?
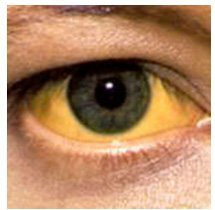 The appearance of a yellow shade of the skin or eyes after a feast with a wide variety of food and alcoholic beverages can be found by the person himself or by the help of others.Such a phenomenon, most likely, will be a symptom of a sufficiently unpleasant and dangerous disease - Gilbert's syndrome.
The appearance of a yellow shade of the skin or eyes after a feast with a wide variety of food and alcoholic beverages can be found by the person himself or by the help of others.Such a phenomenon, most likely, will be a symptom of a sufficiently unpleasant and dangerous disease - Gilbert's syndrome.
This pathology can also be suspected by the doctor( moreover, any specialization) if a patient with a yellowish tinge of the skin came to him at the reception, or when he passed the examination, he took the tests "liver tests".
Table of contents: What is Gilbert's syndrome? Causes of Gilbert's syndrome Classification Clinical picture How is Gilbert syndrome diagnosed? Gilbert syndrome treatmentWhat is Gilbert's syndrome
We recommend:This disease is a chronic hepatic pathology of benign nature that is accompanied by a periodicStaining the skin and sclera of the eyes in yellow and other symptoms.The course of the disease is wavy in nature - for a certain period of time a person generally does not feel any deterioration in health, and sometimes all symptoms of pathological changes in the liver are manifested - this usually happens with the regular use of fatty, sharp, salty, smoked foods and alcoholic beverages.
Gilbert syndrome is associated with a gene defect that is transmitted from parents to children.In general, this disease does not lead to severe changes in the structure of the liver, as, for example, with progressive cirrhosis, but it can be complicated by the formation of gallstones or inflammatory processes in the bile ducts.
There are specialists who do not consider Gilbert's syndrome a disease at all, but this is somewhat erroneous.The fact is that with this pathology there is a violation of the synthesis of the enzyme involved in the detoxification of toxins.If an organ loses some of its functions, then this condition in medicine is called a disease.

Yellow in Gilbert's syndrome is the action of bilirubin, which is formed from hemoglobin.This substance is quite toxic and the liver, under normal functioning, simply destroys it, removes it from the body.In the case of the progression of Gilbert's syndrome, bilirubin does not filter, it enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.And, getting into internal organs, it is able to change their structure, which leads to dysfunctionality.Especially dangerous if bilirubin "gets" to the brain - a person simply loses some of the functions.We hasten to reassure - at the considered disease such a phenomenon is never observed at all, but if it is complicated by any other pathology of the liver, then it is practically impossible to foresee the "way" of bilirubin in the blood.
Gilbert syndrome is a fairly common disease.According to statistics, this pathology is more often diagnosed in men, and the disease begins in adolescence and middle age - 12-30 years.
Causes of Gilbert's syndrome
This syndrome is present only in people who from both parents have inherited the defect of the second chromosome in the locus responsible for the formation of one of the liver enzymes.Such a defect makes the percentage of the content of this enzyme 80% less, therefore, it simply can not cope with its task( the conversion of indirect bilirubin to the brain fraction).
 It is noteworthy that such genetic defect can be different - in the location there is always an insert of two extra amino acids, but there can be several such insertions - the severity of the Gilbert syndrome depends on their number.
It is noteworthy that such genetic defect can be different - in the location there is always an insert of two extra amino acids, but there can be several such insertions - the severity of the Gilbert syndrome depends on their number.
The synthesis of the liver enzyme is greatly influenced by the male hormone androgen, so the first signs of the disease appear in adolescence, when puberty occurs, hormonal restructuring.By the way, it is because of the effect on the enzyme androgen that Gilbert syndrome is more often diagnosed in men.
An interesting fact - the disease in question does not manifest "from scratch", it is necessary to stimulate the appearance of symptoms. And such provoking factors may be:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages often or in large doses;
- regular intake of certain drugs - streptomycin, aspirin, paracetamol, rifampicin;
- recently conducted operative interventions for any reason;
- frequent stress, chronic fatigue, neurosis, depression;
- treatment of glucocorticosteroid-based drugs;
- frequent consumption of fatty foods;
- long-term use of anabolic drugs;
- excessive physical activity;
- fasting( even conducted for medical purposes).
Note: , these factors can trigger the development of Gilbert's syndrome, but may also affect the severity of the course of the disease.
Classification
Gilbert's syndrome in medicine is classified as follows:
- The presence of hemolysis is an additional destruction of red blood cells.If the disease undergoes simultaneous with hemolysis, the level of bilirubin will be increased initially, although this is not typical for the syndrome.
- The presence of viral hepatitis.If a person with two defective chromosomes tolerates viral hepatitis, the symptoms of Gilbert's syndrome will appear up to 13 years.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of the disease under consideration are divided into two groups - mandatory and conditional. The mandatory manifestations of Gilbert's syndrome include:
- appearing from time to time skin areas of a yellow hue, if bilirubin decreases after an exacerbation, then the sclera of the eyes begin to yellow;
- general weakness and rapid fatigue for no apparent reason;
- in the eyelid region forms yellow plaques;
- is broken sleep - it becomes shallow, intermittent;
- decreased appetite.Conditional symptoms, which may not be present:
- in the right upper quadrant, the severity is felt, regardless of the food intake;
During the remission of Gilbert's syndrome, some of the conditional symptoms may be absent altogether, and in a third of patients with the underlying disease they are absent even during periods of exacerbation.
How to diagnose Gilbert's syndrome
Of course, the doctor will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis, but even with external changes in the skin, Gilbert's syndrome can be expected.Confirm the diagnosis can blood test for bilirubin level - it will be elevated.And against the background of such an increase, all other analyzes of liver functions will be within normal limits - albumin level, alkaline phosphatase, enzymes that talk about liver tissue damage.
Gilbert syndrome does not suffer from other internal organs - this is also indicated by the indices of urea, creatinine and amylase.In the urine there are no bile pigments, there will be no changes in the electrolyte balance.
The physician can and indirectly confirm the diagnosis with specific tests:
- Phenobarbital assay;
- test with fasting;
- test with nicotinic acid.
The final diagnosis is made based on the results of the Gilbert syndrome analysis - the patient's DNA is examined by .But even after that the doctor conducts some more tests:
-
 Ultrasound examination of of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.The doctor determines the size of the liver, the condition of its surface, reveals or refutes the presence of structural changes, checks for inflammation in the bile duct, excludes or confirms inflammation of the gallbladder.
Ultrasound examination of of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.The doctor determines the size of the liver, the condition of its surface, reveals or refutes the presence of structural changes, checks for inflammation in the bile duct, excludes or confirms inflammation of the gallbladder. - Study of hepatic tissue with the radioisotope method .Such an examination will indicate a violation of the absorptive and excretory functions of the liver, which is inherent just for Gilbert's syndrome.
- Liver biopsy .Histological examination of the patient's hepatic tissue sample allows to deny inflammation, cirrhosis and oncological changes in the organ and to detect a decrease in the level of the enzyme, which is responsible for protecting the brain from the harmful effects of bilirubin.
Treatment of Gilbert's syndrome
Whether the treatment should be treated at all in the case of the disease under consideration, the attending physician will decide - it all depends on the general condition of the patient, on the frequency of the periods of exacerbations, on the duration of the remission stages and other factors.A very important point is the level of bilirubin in the blood.
Up to 60 μmol / l
If at this level of bilirubin the patient feels within normal limits, there is no increased fatigue and drowsiness, and only a slight icterus of the skin is noted, then no medication is prescribed. But doctors can recommend the following procedures:
-
 reception of sorbents - activated carbon, polysorb;
reception of sorbents - activated carbon, polysorb; - phototherapy - exposure to the skin with blue light makes it possible to remove excess bilirubin from the body;
- diet therapy - from the diet excluded fatty foods, alcoholic beverages and specific foods that are identified as provocative.
Above 80 μmol / l
In this case, the patient is given Phenobarbital at a dose of 50-200 mg per day for 2-3 weeks.Given the fact that this drug has a hypnotic effect, a ban is imposed on the patient to drive the car and visit the work.Doctors can recommend and medicines Barboval or Valocordin - they contain phenobarbital in small doses, so they have not so much hypnotic effect.
Mandatory for bilirubin in the blood above 80 μmol / l in the diagnosed Gilbert syndrome is prescribed a strict diet. For food it is allowed to use:
- fermented milk products and cottage cheese with low fat content;
- skinny fish and lean meat;
- non-acidic juices;
- biscuit cookies;
- vegetables and fruits in fresh, baked or boiled form;
- dried bread;
- sweet tea and fruit drinks.
It is strictly forbidden to enter in the menu chocolate, cocoa, buttery pastries, spicy, fatty, smoked and pickled products, any alcoholic beverages and coffee.
Inpatient treatment
If, in the two cases described above, treatment of a patient with Gilbert's syndrome is performed under outpatient conditions under the supervision of a doctor, then if hospital bilirubin is too high, insomnia, decreased appetite, nausea, hospitalization will be required. The bilirubin in the hospital is reduced by the following methods:
-
 introduction of intravenous polyionic solutions;
introduction of intravenous polyionic solutions; - reception of sorbents under the individual scheme;
- administration of lactulose preparations - Normase or Dufalac;
- the appointment of hepatoprotectors of the latest generation;
- blood transfusion;
- administration of albumin.
The patient's diet is corrected drastically - animal proteins( meat products, eggs, cottage cheese, offal, fish), vegetables, fruits and berries in fresh form and fats are completely excluded from the menu.It is allowed to eat only soups without roasting, bananas, sour-milk products with a minimum level of fat content, baked apples, biscuit biscuits.
Remission of
Even if there is remission, patients should never be "relaxed" - it is necessary to take care that there is not another exacerbation of Gilbert's syndrome.
First, you need to protect the biliary tract - this will prevent stagnation of bile and the formation of stones in the gallbladder.A good choice for such a procedure will be choleretic herbs, drugs Urocholum, Gepabene or Ursofalk.Once a week, the patient should do "blind probing" - fasting should be done with xylitol or sorbitol, then you need to lie on your right side and warm up the anatomical location of the gall bladder with a warmer for half an hour.
Secondly, you need to choose a literate diet.For example, it is necessary to exclude from the menu products that act as a provoking factor in case of aggravation of Gilbert's syndrome.Each patient has such a set of products is individual.
Forecasts of doctors
In general, Gilbert's syndrome is quite safe and does not cause the patient's death.Of course, some changes will be - for example, with frequent exacerbations the inflammatory process in the bile ducts can develop, stones in the gallbladder can form.This affects the ability to work in a negative way, but it is not the reason for disability registration.
If a child with a Gilbert syndrome is born in the family, then the parents must undergo a genetic examination before the next pregnancy.The same tests need to pass the pair in the event that one of the spouses has this diagnosis, or there are obvious symptoms of it.
Gilbert Syndrome and Army Service
As for military service, Gilbert's syndrome is not a reason for receiving a deferment or a ban on urgent service.The only warning is that a young man should not physically overexert himself, starve, work with toxic substances.But if the patient is going to build a professional military career, then it is not allowed to him - he just will not pass medical check-through commission.
Preventative measures
It is impossible to prevent the development of Gilbert's syndrome somehow - this disease occurs at the level of genetic abnormalities.But you can take preventive measures in relation to the frequency of exacerbations and the intensity of manifestations of the disease. These measures include the following expert advice:
-
 adjust diet and eat more plant foods;
adjust diet and eat more plant foods; - avoid excessive physical exertion, if necessary - change the type of work;
- to avoid frequent infection with viral infections - for example, you can and should be hardened, strengthen the immune system;
- to exclude injecting drugs, unprotected sex acts - these factors can lead to infection with viral hepatitis;
- try to be less exposed to direct sunlight.
Gilbert syndrome - the disease is not dangerous, but requires some restrictions.Patients must always be under the supervision of a doctor, regularly undergo examinations and comply with all medications and recommendations of specialists.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category