Antibiotics for cholecystitis: what drugs can be taken
Damage to the gallbladder is a common chronic disease that is combined with dysfunction of the biliary system. If pathogenic microflora is detected, antibiotic treatment will be required for cholecystitis.
Content
- 1 Disease types
- 2 The basics of antibiotic therapy
- 3 What antibiotics are needed for cholecystitis
- 4 Contraindications
Disease types
The available classification makes it possible to determine the type of disease and select the most effective treatment regimen. More than 90% of all diseases occur in calculus view. It is characterized by the appearance of calculi, but is asymptomatic for a long time. In the future, there are attacks of biliary colic.
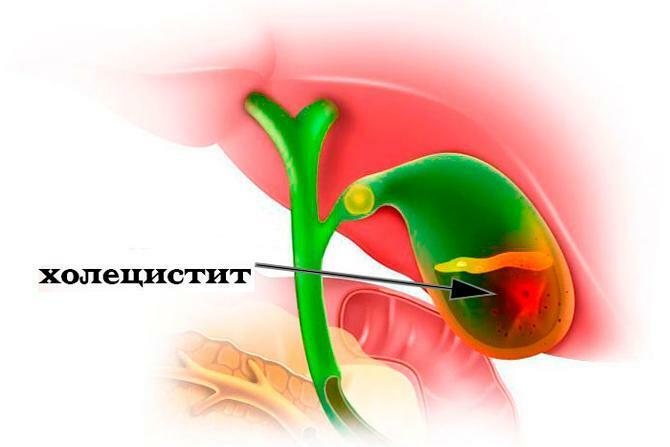
Noncalculous the view is associated with nutritional errors. Differs in a favorable course, the absence of stones, rarely occurring exacerbations.
Depending on the etiology, the following types of cholecystitis are distinguished:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- parasitic;
- post-traumatic;
- aseptic;
- allergic;
- enzymatic.
According to the symptoms and type of destructive changes in the bladder, acute and
chronic cholecystitis. The disease can be mild, moderate and severe. The course of the disease can be monotonous, without pronounced remissions and exacerbations. With an intermittent course, the manifestations are poorly expressed, exacerbations occur periodically. The recurrent type is characterized by severe exacerbations, alternating with a state of complete remission.The basics of antibiotic therapy
The acute and chronic form of calculous cholecystitis is treated with antibiotics in order to destroy the infection as much as possible and prevent complications. Most often, enterococci, Escherichia coli become the causative agent. Staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, from a chronic focus in the body can enter the gallbladder. Less often, bacteroids and clostridia penetrate into the bladder.
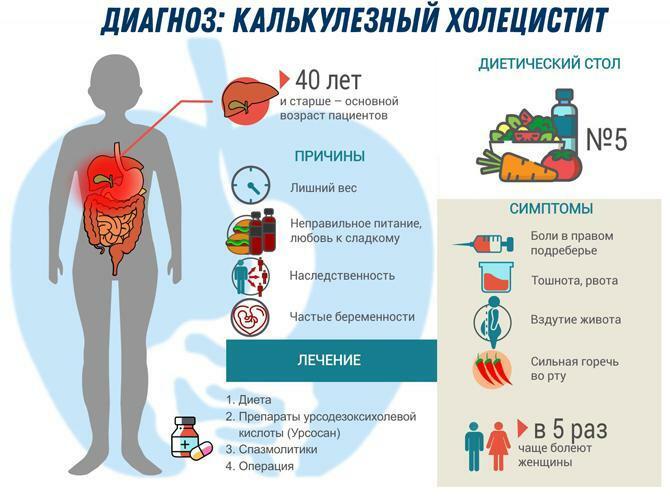
One tenth of patients are infected with hepatitis B and C viruses. Parasitic infection occurs with roundworms, opisthorchiasis. Rare pathogens include typhoid and paratyphoid bacilli, proteus, fungi of the genus Candida.
The doctor decides whether to use an antibiotic. They are prescribed for severe right pain in the hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting, colic in the intestines and loose stools. This raises the temperature. In the blood there is a high ESR, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
The doctor selects the dose, frequency of use, duration of the course, method of administration of the drug, based on the age and weight of the patient. As a rule, the treatment is calculated for 7-10 days. The advantage is given to the intravenous and intramuscular route of administration. Pre-check the reaction of the body with an intradermal test. Tablets are not prescribed if there is vomiting and diarrhea.
Before determining the sensitivity of the pathogen, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed, then it is replaced based on the bacterial culture data. With mixed flora, a combination of drugs is prescribed. To enhance the anti-inflammatory effect, vitamins of group B and C are added.
Important: the infectious process in the gallbladder is not treated with folk remedies. At best, they can stimulate the flow of bile.
Antibiotic treatment is not required for enzymatic cholecystitis. In this case, non-bacterial inflammation of the gallbladder is associated with the reflux of pancreatic enzymes, with insufficient closure sphincter of Oddi. Antibiotics are not needed in aseptic and allergic form.
What antibiotics are needed for cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gland is primarily associated with stagnation of bile. Violation of the outflow leads to an increase in the amount of lysolecithin, which damages the mucous membrane of the organ. The attachment of the pathogen causes an infectious and inflammatory process.
For treatment, the doctor selects a medicine that penetrates the gallbladder and can accumulate in the bile. And also the most sensitive drug to the detected microflora. Antibacterial agents for the treatment of cholecystitis are divided into the following groups:
- inhibitor-protected penicillins and cephalosporins;
- fluoroquinolones;
- macrolides;
- lincosamines;
- tetracyclines;
- derivatives of nitroimidazole.
The inflammatory process of the gallbladder is a serious illness. Self-medication is not only unacceptable here, but also dangerous. There are standard protocols that guide the doctor when prescribing antibiotic therapy. There are a number of the most effective drugs included in the treatment complex.
"Ampicillin"
Semisynthetic agent of the penicillin series. Accumulates in bile. It is active against staphylococci, streptococci, salmonella, Escherichia coli and enterococci. Destroys the cell membrane, inhibits the synthesis of bacteria. Applied in combination with Oxacillin, as the drug "Oxamp".
Among the disadvantages - it is destroyed by enzymes, therefore, a protected version of the inhibitor is used - "Ampisid", "Sulbatsin", "Unazin". It is prescribed with caution to patients with bronchial asthma, pregnant and lactating. Forbidden for renal failure, mononucleosis, colitis.
"Cefazolin"
The drug belongs to the first generation cephalosporins. Has a wide range of effects. Affects almost all major causative agents of cholecystitis. Release form - powder for injection. Contraindicated in hepatic and renal failure, enterocolitis, pregnant women and newborns.
"Ciprofloxacin"
The drug is a representative of the 2 generation fluoroquinolone group. It accumulates in bile to high concentrations. It is active against all types of bacteria, prevents their growth and division. Not prescribed for children under 18 years of age, pregnant and lactating. Use with caution in mental disorders, in patients with atherosclerosis, in renal and hepatic insufficiency.
"Amoxiclav"
It is an antibacterial agent and an immunostimulant. The medicine contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Works against E. coli and haemophilus influenzae streptococcus.
"Gentamicin"
The drug is effective for cholecystitis caused by Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella and Shigella. Belongs to the group of aminoglycosides. It does not accumulate in bile, therefore it is used in combination with other antibiotics. It has a negative effect on the kidneys and the nervous system.
"Metronidazole"
The medicine is prescribed as an adjunct to the main antibiotic if mixed anaerobic-aerobic infection is present. The remedy is perfectly combined with cephalosporins. The following combination is possible: "Ampicillin" + "Gentamicin" + "Metronidazole". If necessary, "Gentamicin" can be replaced with Sisomycin.
Less commonly used antibiotics such as "Erythromycin", "Levomycetin", "Trichopol".
Each organism is individual, which helps one patient, it is contraindicated for another. Various complications can occur during antibiotic treatment:
- allergies - from urticaria, up to anaphylactic shock;
- asthma attacks;
- decreased immunity;
- dysbiosis - bloating, loose stools;
- the appearance of a fungal infection.
During the period of treatment, it is necessary to adhere to a diet, exclude alcohol. In parallel, the intake of probiotics is prescribed. To reduce pain, antispasmodics and analgesics "Duspatalin", "No-shpa". Hepatoprotective drugs: Ursofalk, Essentiale, Gepabene.
Choleretic agents such as Allohol, Hofitol, and enzymes - Pancreatin, Mezim.
Contraindications
There are many antibiotics, and they all have one side effect or another. When treating cholecystitis, all contraindications are considered relative. T. That is, if the patient is not allowed to take this drug, the doctor must select an alternative treatment option. These can be such situations:
- a history of antibiotic or other drug allergy;
- all periods of pregnancy;
- breastfeeding the baby;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- severe illness in the stage of decompensation.
Those who are strictly prohibited from antibiotics can use sulfa drugs. These are "Sulfadimethoxin", "Phtalazol", "Sulfadimezin". They are not as effective, but less toxic, have a relatively low price, and can be used for children.
When treating, it is important to adhere to the doctor's recommendations. You cannot change the dosage at your own discretion, skip taking the drug, reduce or increase the course of treatment. Before using the medication, you should carefully read the instructions.
For methods of treating cholecystitis, see the thematic video:
Read also: Cholesterosis of the walls of the gallbladder
Sources:
- https://kardiobit.ru/pochki/holetsistit/kakie-antibiotiki-naznachayut-pri-holetsistite
- https://vrbiz.ru/medikamenty/antibiotikami-holecistite#toc-4
- https://tden.ru/health/antibiotiki-ot-holetsistita
- https://lifetab.ru/4-samyih-effektivnyih-antibiotika-pri-lechenii-holetsistita-vospaleniya-zhelchnogo-puzyirya/#i-2



