Balantidiasis
 Balantidiasis is a rare parasitic disease in which the large intestine is affected by ulcers. Symptoms of the disease are difficult, so if you do not start treatment in time, the sick person will die. To protect yourself from this disease, you need to know about it as much as possible: about the methods of infection, about the symptoms, and also about treatment and prevention.
Balantidiasis is a rare parasitic disease in which the large intestine is affected by ulcers. Symptoms of the disease are difficult, so if you do not start treatment in time, the sick person will die. To protect yourself from this disease, you need to know about it as much as possible: about the methods of infection, about the symptoms, and also about treatment and prevention.
What causes the disease?
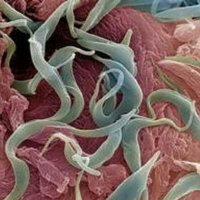
Balantiadiasis provokes the causative agent - infusoria. The first mention of this infusoria was mentioned in the works of the Swedish scientist Malmsteen in 1857.In 1901, scientist S. Soloviev proved that this infusoria can cause a disease in a person. The causative agent is the largest among intestinal microorganisms. In the external environment, the bacterium retains its viability for three to four weeks. Scientists believe that one type of balantidium parasitizes a pig and a human.
The disease is diagnosed very rarely. But at the same time, the population's infection can be high. Most often, people who live in rural areas - about 5%.The greatest risk is to those people who are in contact with pigs. The thing is that pigs are a natural carrier of the disease. Infected with balanty, a person can infect other people in contact with him.
What happens when a disease occurs?
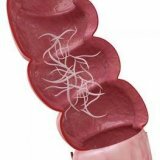
As mentioned above, the pigs are carriers of the disease. A person becomes infected when he gets balantidia in the digestive tract. The danger lies in the fact that the pathogen can not manifest a pathogenic effect for a long time, being in the intestine. As a rule, the pathogen lives in the lower parts of the small intestine.
Most often affected are straight, sigmoid and cecum. Initially, on the folds of the mucous membranes, edema and hyperthermia develop, then erosion occurs. The causative agent penetrates into the thickness of the tissues and causes foci of necrosis and hemorrhage. After the rejection of necrotic masses takes place, there remains a cavity that connects with the gut lumen. Ulcers have rugged and thickened edges, uneven bottom, which is covered with a purulent-bloody touch. Sometimes ulcers lead to the development of peritonitis.
Symptoms of the disease
A pathological process occurs as a result of active multiplication of parasites in the tissues of the colon or in the distal part of the small intestine. Because of active multiplication of parasites ulcers are formed. Doctors distinguish acute and chronic balantidiasis. Both forms of the disease can occur in the form of dysentery, in which malodorous blood-mucous diarrhea develops. It is also possible the occurrence of colitis with semi-fluid masses( with mucus, but without blood).
In chronic form, the disease can proceed exactly as in acute form. However, there can be no diarrhea at all. In acute forms of balantid dysentery, the percentage of deaths is very high due to late treatment. If balantidiasis is not complicated by a bacterial infection, the body temperature may not rise. As a rule, this disease affects only the intestine.
The incubation period lasts about fifteen days. In addition to acute and chronic balantidiasis, latent is isolated. Acute forms of the disease resemble in their symptoms colitis or enterocolitis. The patient has symptoms of general intoxication of the body: severe weakness, decreased appetite, headache, fever with chills. Simultaneously with these symptoms, there are abdominal pains, meteorisms, diarrhea. In fecal masses there may be impurities of blood and mucus. Often, patients complain of dry mouth, soreness and cramping in the colon. Upon examination, the doctor discovers an enlarged liver. With sigmoidoscopy, a focal ulcerative process is detected. The analysis of blood reveals a moderate anemia, a decrease in protein and albumins, eosinophilia. In acute balantidiasis, symptoms are pronounced. The stool can occur up to twenty times a day with impurities of blood and mucus and with putrefactive odor. Patients lose weight sharply.
Chronic balantidiasis is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication, fever, signs of intestinal damage( diarrhea, abdominal pain, false urges to defecate, flatulence).Often there are spasms in the intestines. With latent form, the symptoms of intoxication are poorly expressed, the body temperature is normal, and the stool occurs up to three times a day. The patient complains of pain in the region of the blind and ascending colon. Parasites are found in stool.
Diagnosis of the disease
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient passes the analysis of feces. Also, doctors do scraping from the affected areas of the intestinal mucosa. Due to mobility, large size and characteristic form, bacteria are easily recognized.
Often doctors are interested in the place of residence and about possible contact of the patient with pigs. It has already been said above that most often this disease people who live in rural areas and who are in close contact with pigs - carriers of bacteria.
In a native smear, the doctor can detect vegetative forms of bacteria, whose length is on average 75 microns and the width is 40 microns. Bacteria move quickly and easily change the shape of the body. Therefore, to detect them, it is best to use a small magnification of the microscope.
How baldatidiasis is treated
The sooner the doctor begins to treat the patient, the higher the chances of recovery. With timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable, but without the use of special antiparasitic therapy, mortality occurs in 12% of cases.
Special anti-parasitic drugs are used for treatment. The course of treatment is two to three five-day cycles. Most often, doctors prescribe to patients with balantidiasis such drugs: monomycin( 0.15 g four times a day), oxytetracycline( 0.4 g four times a day) and metronidazalone( 0.5 g three times a day).
To date, there is no vaccination that would protect against this disease. Therefore, for the prevention of the disease, every person who lives in the countryside and contacts pigs must follow simple rules. The most important rule is to adhere to all hygiene standards when caring for pigs. It is equally important to find out the symptoms of the disease in time and consult a doctor. General measures to prevent balantidiasis are the same as in dysentery.
If you notice symptoms similar to the symptoms of this disease, you should contact an infectious disease specialist or parasitologist. If these doctors are not in your clinic, then you need to see a therapist. He will examine you and provide first aid. After that, the therapist is obliged to give a referral to blood and stool tests, and also to give you an additional examination that will help to identify the disease. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor should refer you to other specialists who will further treat the disease.