Staphylococcus aureus
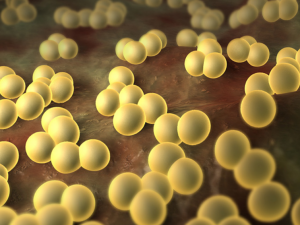 Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical frame positive bacterium, which is often found on the skin and in the nose of people. About 20% of the world's population is a constant carrier of this bacterium from the genus Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical frame positive bacterium, which is often found on the skin and in the nose of people. About 20% of the world's population is a constant carrier of this bacterium from the genus Staphylococcus aureus.
The name of its bacterium is due to the appearance, which is distinguishable only under the microscope: unlike many bacteria, which are mostly colorless, S. aureus is due to the pigments from the group of carotenoids - golden color.
The bacterium of the golden staphylococcus is commensal, it colonizes on the surface of mucous membranes and skin. Staphylococcus aureus: symptoms and treatment is exactly what will be discussed below.
Symptoms of the disease
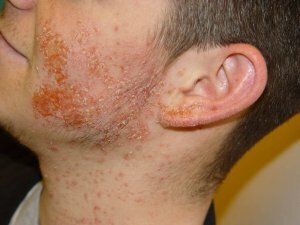 In humans, staphylococci cause various lesions - abscesses, sycosis, hydroadenitis, dermatitis, carbuncles, eczema, periostitis, panaritium, osteomyelitis, blepharitis, folliculitis, furuncles, pyoderma, pneumonia, meningitis, peritonitis, cholecystitis, appendicitis.
In humans, staphylococci cause various lesions - abscesses, sycosis, hydroadenitis, dermatitis, carbuncles, eczema, periostitis, panaritium, osteomyelitis, blepharitis, folliculitis, furuncles, pyoderma, pneumonia, meningitis, peritonitis, cholecystitis, appendicitis.
The development of secondary diseases causes staphylococci in smallpox, wound infections, influenza, postoperative suppuration.
In children, staphylococcal pneumonia and sepsis are formidable diseases.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus
Modern approaches in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus include the following directions:
- Optimization of the hormonal status and metabolism of the body with food additives( such as chitosan and cordyceps), various mineral preparations and vitamins.
- Surgical methods;
- Use of antimicrobials and antibiotics;
- Methods of immunomodulation;
Use in the treatment of vitamin-mineral preparations
 The reason for the decrease in immunity and frequent recurrence of infections is the lack of minerals and vitamins in the body.
The reason for the decrease in immunity and frequent recurrence of infections is the lack of minerals and vitamins in the body.
Vitamin-mineral preparations are very successfully used for the treatment and prevention of staphylococcal infections. It is also justified to use these drugs in the presence of a shortage of vitamins in the off-season. The beginning of the use of food additives and vitamin preparations should be discussed with the attending physician, it is necessary to understand the appropriateness of this treatment and the consequences and risks associated with it.
Treatment with antimicrobials and antibiotics
The invention of antibiotics has expanded the capabilities of medicine for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. To date, a lot of antibiotics are known, which indicate the features and indications for use and describes possible side effects.
For microbes from the group of Staphylococcus aureus, it is peculiar to differ by rapid adaptation to various antibiotics, great resistance. Therefore, in connection with this, the process of treatment with antibiotics against staphylococcal infection becomes quite problematic. At present, there has been an increase in cases of "hospital infections".This means that in patients who are on treatment, an infectious process may occur. Such bacteria that contribute to the disease can have high resistance and endurance to many antibiotics, they are not amenable to treatment, they require the appointment of expensive and potent drugs.
Surgical methods for the treatment of staphylococcus aids
When a doctor identifies staphylococcus aureus, the treatment is prescribed using a surgical technique. Surgical methods of treatment are used in cases when there are purulent forms of staphylococcal infection. Such purulent forms can not be treated by methods other than surgical ones. In any case, they threaten serious complications.
Methods of immunomodulation
Immunomodulating agents and their purpose in the treatment and prevention of staph infections have become more popular. This is due to the fact that treatment acts directly - stops the decrease in immunity, immunomodulation does not use dangerous to health and toxic drugs. In addition, the normalization of the functionality of the immune system helps reduce the risk of not only infections of Staphylococcus aureus, but also a number of other diseases.
When using herbal natural immunostimulants, which are very reliable and effective drugs for the process of improving the body's immunity, the problem of resuming the disease with staphylococcal infection is eliminated. Previously, such drugs have been used in alternative medicine, but now plant remedies have been used in scientific medicine all over the world. So, the receipt of natural immunostimulants has assumed a high-scale character, the preparations are obtained from the plants of Cordyceps, Ginseng, Eleutherococcus, Pantocrin, Roscorps, Rhodiola rosea, Echinacea purpurea, Schisandra Chinese. In addition, Chitosan has a very active effect.
Autohemotherapy is the process of transfusion of the patient's blood to the patient himself. Such therapy involves taking blood from a vein in a patient with the introduction of this blood to the same patient by intramuscular injection. So, as a result of this procedure, the blood that was injected intramuscularly is destroyed. Thus, the decay products or biologically active substances released at the same time begin to stimulate immunity. This method of treatment is used to treat the chronic form of the disease.
Consequences of Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus diseases are divided into two types - infections and intoxications.
In infections, the causative agent of Staphylococcus aureus invades the tissues of the macroorganism, multiplies and in most cases destroys them. The ability of the causative agent to cause infection is due to the presence of virulence factors in it( these are substances that facilitate survival and promote further propagation of the pathogen in the microorganism).
To be honest, the effects of Staphylococcus aureus are unpredictable. This type of staphylococcus can cause various diseases that pass into the future in chronic forms. More often it's all kinds of purulent formations and food poisoning. There are cases of extremely severe and life-threatening illnesses caused by golden Staphylococcus aureus.