Details on the removal of the bladder: surgery, consequences and complications
Bladder Removal( Cystectomy) The is a dangerous and difficult operation. It requires great professionalism of the surgeon, careful preoperative examination of the patient and a long rehabilitation period. Since this type of intervention is very traumatic, it is performed strictly according to indications, when there is no other way out. This is the most radical way of therapy. According to statistics, cystectomy is not required as often as once again, in favor of the fact that an operation to remove the bladder is an extreme measure.
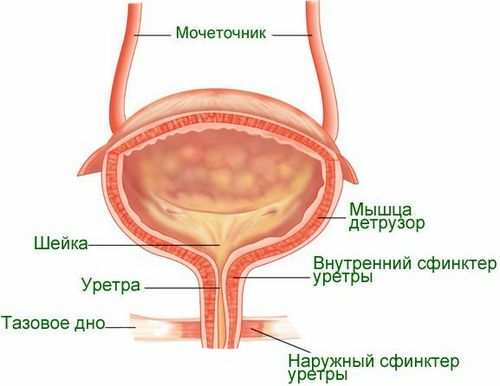
The structure of the bladder
In medical practice, two types of such intervention are distinguished:
- Removal of the bladder, during which the resection of the organ is performed.
- Total or radical cystectomy when a man removes regional lymph nodes, seminal vesicles and, in some cases, part of the intestine and prostate, in addition to the organ.
It's about disabling manipulation. What is cystectomy?
Contents
- 1 Indications for operation
- 2 Contraindications
- 3 Preoperative preparation
- 3.1 Studies and analyzes
- 3.2 Direct preparation
- 4 Intervention procedures
- 5 Complications after operation
- 6 Recovery after intervention
- 7 Is there life after cystectomy?
Indications for operation
Because of the hardest interventions, the list of indications is exhaustive and includes:
- Neoplastic processes of the bladder of malignant character in 3-4 stages( see Bladder cancer).Removal of the organ is indicated only in the case where there are no metastases to the surrounding organs, but the tumor has begun to germinate into nearby anatomical structures. This is an opportunity to save the patient's life.
- Wrinkling of the bladder( microcyst).In this case, massive fibrous( cicatricial) changes from the side of the hollow organ are observed. As a result of the course of the pathology, the bladder is unable to stretch because of decreased elasticity. This is fraught with its rupture and the development of peritonitis. The disease is formed as a result of the course of interstitial cystitis or tuberculosis.
- Developed papillomatosis of the bladder. Especially the diffuse form. The disease is characterized by the development of a number of benign lesions( papillomas) scattered throughout the surface of the bladder. For internal papillomatosis, a high risk of malignant transformation of tumors is typical.
- Malignant neoplasms of the bladder that have single metastases to regional lymph nodes. In this situation, the organ is removed along with the affected lymphatic structures.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications, on the contrary, is approximate. As it is a question of a severe and prolonged operation, not everyone is able to endure such a test. It is impossible to perform the operation:
- To persons of elderly and senile age due to the need for prolonged anesthesia.
- People in serious condition.
- Patients with infectious inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract in the acute phase. Great risk of becoming sepsis.
- Patients with low blood coagulability.
The first two indications are absolute. The following are relative and require correction of the state.
Preoperative preparation
It is required to carefully examine the patient in order to reduce the risk of death and postoperative complications. The activities are typical for preparation for any operative intervention, however there is a specificity.
Research & Analysis
-

Recommendations for necessary research, analysis and preparation for surgery are given only by the attending physician!
General and biochemical blood tests. They provide an opportunity to identify infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Determination of the concentration of sugar( glucose) in the capillary blood.
- ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, radiography of the lungs.
- Coagulogram. Gives an opportunity to assess blood coagulability.
- Cystoscopy. It is indicated for staging the process and indicating the nature of the surgical procedure.
Direct preparation of
- for two weeks requires the discontinuation of some medicines: Aspirin and others;
- a week before surgery, the patient is transferred to a diet low in fiber;
- is prohibited from eating for two days and is recommended to drink more;
- the hygienic treatment of the groin area is mandatory;
- for a day appointed cleansing enema and taking diuretics, in order to "expel" excess fluid from the body;
- for 12 hours is prohibited from smoking, drinking alcohol;
- from the evening before the operation you can not drink liquid.
This does not end with the preparation. Almost for two weeks the doctor appoints a man a course of antibiotics to prevent secondary infection and prebiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora. In addition, such measures are necessary to prepare the gastrointestinal tract: it is possible to use its part for urinary diversion.
Intervention Techniques
The most common method of cystectomy is as follows:
- The patient is placed on the operating table. Process the place of the proposed cut with antiseptic solutions, designate the line of excision. A urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder. In men, the urethra is long and narrow, and there are anatomical curves that prevent the catheter from entering normally. Therefore, the specialist should be careful not to damage the walls of the urethra.
- Next, an arc incision is made of the tissues two or three fingers above the pubis to expose the organ.
- Bubble is excised, the doctor examines the hollow organ.
- The walls of the organ are fixed, the prostate gland is additionally fixed( in the case of a radical operation).
- The doctor performs excision of the ureters, binds the vas deferens, mobilizes the organs of the urinary system, cutting the ligaments.
- Secondary catheterization for urinary diversion is performed.
- The bladder itself is removed.
- Through the hole in the abdominal cavity, the surgeon inserts a special reservoir for temporary collection of urine.
- The doctor sutures the wound.
Urinary diversion methods are very variable:
- Creation of a wet stoma, when the urinary canal is formed from the part of the ileum( constant wearing of the urine collection is required).
- Formation of an ostomy from other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Finally, the most modern method of postoperative recovery of normal urinary function is prosthetics - replacing the bladder with an artificial one.
Complications after surgery
Classical effects include bleeding and secondary infection of the wound surface. However, the following conditions are of great danger:
-

After surgery, acute urinary retention
may occur with acute urinary retention due to ureteral occlusion;
- kidney failure;
- inflammation of the urinary tract;
- when replacing an artificial organ for several months, urinary incontinence is observed;
- increases the risk of urolithiasis and pyelonephritis;
- there is a periodic blockage of the stoma.
This, however, solves the problem.
Recovery after intervention
The course of rehabilitation lasts from half a year to year .It requires careful compliance with a diet low in fiber. The diet should be sufficiently vitaminized( vegetables and fruits will help, but not too acidic).At the same time, the amount of liquid consumed should be reduced to a liter per day. Reduced physical activity, including sexual activity, is shown. The patient learns to empty the urinary tract again, with prosthetics this period can last up to 12 months.
Man is a creature possessing immense adaptive capabilities. If all the recommendations of a specialist are observed, the patient can live a long and quite qualitative life. Sexual activity is also rarely disturbed to the extent that the sexual function is completely lost. It is necessary to overcome the physical and psychological discomfort of using urinals or temporary incontinence in prosthetics. Provided that it is not a question of neglected oncology, the life of patients is tens of years. Life after cystectomy is. And its quality depends on the psychological mood of the person.
Removal of the bladder is a serious intervention designed to save the patient's life. It is carried out only on indications, but often there are no alternatives to cystectomy. In this case, the patient can only learn to live in new conditions.
Recommended for viewing: