Enterocolitis: symptoms and treatment
 Enteritis - an inflammatory lesion of the small intestine, inflammation of the large intestine is called colitis. If the patient has an inflammatory process that affects the entire intestine, talk about enterocolitis. Enterocolitis is not a separate disease - it is a syndrome that can develop against the background of infections, systemic autoimmune and allergic reactions, and exposure to the digestive tract of toxic substances.
Enteritis - an inflammatory lesion of the small intestine, inflammation of the large intestine is called colitis. If the patient has an inflammatory process that affects the entire intestine, talk about enterocolitis. Enterocolitis is not a separate disease - it is a syndrome that can develop against the background of infections, systemic autoimmune and allergic reactions, and exposure to the digestive tract of toxic substances.
What happens in the intestines with enterocolitis?
When the enterocolitis is inflamed the intestinal mucosa. At the initial stages of the disease, these pathological changes are reversed and completely disappear after treatment.However, the longer the pathological process lasts, the more inflammation spreads.Therefore, in neglected cases, the intestinal mucosa in the lesions completely loses its normal morphology and ceases to perform functions, including digestive-absorbing and barrier.That is, the eaten food is not digested normally, the nutrients necessary for the body are not absorbed into the blood, but the toxins of bacteria, on the contrary, begin to penetrate into the bloodstream causing the patient to become highly intoxicated.
If destruction of the mucous membrane progresses and results in damage to small blood vessels, the patient may develop latent intestinal bleeding. It can be detected using endoscopic examination methods and a test for latent blood.
Varieties and causes of enterocolitis
Enterocolitis is acute and chronic .In acute inflammation of the intestine, only the upper layers of the mucous membrane( epithelium) are initially affected.But chronic enterocolitis almost always proceeds with the defeat of deeper layers of the intestinal wall.The development of chronic enterocolitis is usually associated with inadequate treatment of the acute form of pathology.
Depending on the cause of development, enterocolitis is divided into:
-
 Infectious. Many bacteria( Salmonella, Yersinia, pathogenic E. coli, Shigella, Proteus) and viruses( rotaviruses, enteroviruses) can be an etiological factor.This group of enterocolitis occurs most often and is almost always acute.
Infectious. Many bacteria( Salmonella, Yersinia, pathogenic E. coli, Shigella, Proteus) and viruses( rotaviruses, enteroviruses) can be an etiological factor.This group of enterocolitis occurs most often and is almost always acute. - Parasitic. Helminths and protozoa can cause enterocolitis.
- Almentary. Irregular intake of food, poor-quality products, excess in the diet of fatty, spicy dishes, addiction to alcohol - all these factors can contribute to the development of an inflammatory reaction in the intestine.
- Toxic - associated with ingestion of household chemicals, surrogate alcohol, large doses of medicines, etc.
- Mechanical. Enterocolitis can develop against a background of chronic constipation.Solid feces have a mechanical damaging effect on the delicate mucous membrane of the intestine, causing its damage and inflammation.
- Autoimmune and allergic .The most striking example is ulcerative colitis.
- Stressful .When stress worsens blood supply and innervation of the intestinal wall, which can become a trigger mechanism for the development of enterocolitis.
- Secondary - caused by diseases of other digestive organs.
Symptoms of enterocolitis
Acute enterocolitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
-
 Severe distended pain in the abdomen.When the small intestine is affected, it is localized around the navel, when involved in the pathological process of the large intestine - in the lateral and lower abdomen.
Severe distended pain in the abdomen.When the small intestine is affected, it is localized around the navel, when involved in the pathological process of the large intestine - in the lateral and lower abdomen. - Bloating, constant rumbling.
- Nausea, repeated vomiting.
- Diarrhea.In stool, there may be a noticeable admixture of blood, mucus, slices of food.
If the nature of enterocolitis is infectious, the patient will have signs of general intoxication and fever. In addition, with acute enterocolitis accompanied by severe diarrhea, dehydration may develop.Its manifestations are dry skin and mucous membranes, severe thirst, a significant decrease in the number of urination, a headache.
There are usually no bright clinical pictures for chronic enterocolitis, but the patients are still concerned:
- Periodic pain in the abdomen.They increase markedly after eating and almost completely pass after going to the toilet.Alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- .
- Weight loss.
In the remission phase, the patient can feel completely normal.But the aggravation of the disease can proceed according to the type of acute enterocolitis.
Diagnostics of enterocolitis
The main task for enterocolitis is to determine precisely the cause of inflammation of the intestine, to carry out treatment and to prevent the pathological process from passing into a chronic form. For this, patients with symptoms of enterocolitis must undergo a comprehensive examination, including:
- Bacteriological examination of stool. Sowing the patient's feces on special nutrient media allows to identify "bad" microorganisms and assess the condition of "good" microorganisms.Usually, such a study is supplemented by the determination of the sensitivity of the sown pathogens to antibiotics, which helps doctors in choosing the drugs for treatment.
- Coprological analysis. Shows how fully the digestion of food takes place, how long it lingers in the intestinal tract, whether there is inflammation.
- Colonoscopy - endoscopic examination of the intestine with the possibility of sampling the material for subsequent histological analysis.
- Parasitologic examination of stool.
- General clinical and biochemical blood tests.
Treatment of enterocolitis
The tactics of treatment of enterocolitis are determined by the cause of the inflammatory process in the intestine.However, there are general recommendations:
-
 In acute enterocolitis in the early days a strict diet is shown( in fact, this is fasting).In the future, the patient's diet can be expanded at the expense of mucous porridges, vegetable grinded soups, kissels.
In acute enterocolitis in the early days a strict diet is shown( in fact, this is fasting).In the future, the patient's diet can be expanded at the expense of mucous porridges, vegetable grinded soups, kissels. - Rehydration is performed to normalize the body's water balance.If there is no vomiting, the patient is prescribed a copious drink, if there is vomiting, rehydration is performed by intravenous infusion of special solutions.
- To reduce pain, use antispasmodics.
For bacterial enterocolitis, antibiotics form the basis of therapy. After such a course of treatment, patients are shown restoration of the normoflora of the intestine, which can last several months.Why is it important to restore normal intestinal biocenosis?Intestinal bacilli, bifido- and lactobacilli, which are the main inhabitants of the intestine, play the role of defenders - they do not allow activating opportunistic microorganisms and develop pathogenic bacteria.In addition, the process of digestion in the intestine depends on the state of the microflora.If everything is in order, the food will be properly digested, if not, the processes of fermentation and putrefaction will begin.
With chronic enterocolitis, it is very important not only to influence the cause of inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, but to restore the digestive process. For this, patients need to follow a diet and, if there are indications, take enzyme preparations that will help the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the food you eat.
Principles of dietary nutrition with enterocolitis
Enterocolitis impairs the absorption of nutrients in the intestine, so if the patient is sick for a long time, his body begins to suffer from a lack of proteins, minerals and vitamins.In extreme cases, depletion may develop.In addition, chronic enterocolitis is almost always accompanied by a disorder of stools like constipation or diarrhea, as well as fermentation or putrefactive processes.The patient may have diseases of other digestive organs( for example, the pancreas, which plays an important fermentosynthesizing role). All these factors must be taken into account in the preparation of a therapeutic diet, which ideally should: provide the patient with a sufficient number of nutrient connections;
- ;
- restore the frustrated functioning of the intestines and other digestive organs;
- eliminate the resulting exchange disturbances;
- to create conditions for the speedy extinction of the inflammatory process in the intestinal tract.
So, with acute enterocolitis, the intestine needs maximum mechanical and chemical shudder .Therefore, patients in the first days of the disease are allowed to drink only warm and slightly sweet tea, rice broth, blueberry jelly, etc.When the condition improves a little, grated or cooked steamed dishes from vegetables and low-fat meat are introduced into the diet.Gradually, the degree of grinding food is reduced and thus make the digestive tract work fully.The same tactic of diet therapy should be applied and with exacerbation of chronic enterocolitis .
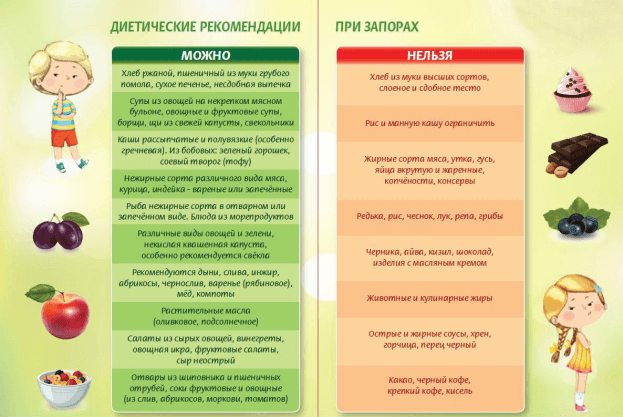
When the phenomena of inflammation in the intestines die away ( when chronic enterocolitis passes into the stage of remission), the patient is transferred to a diet with increased content of proteins, lipotropic substances, vitamins, and chemical elements involved in hematopoiesis.If there are constipation, stimulant products of intestinal peristalsis are introduced into the diet.If the patient suffers from diarrhea - food that slows the progress of feces through the intestinal tract.If diarrhea alternates with constipation - dishes that have little effect on peristalsis.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist-doctor



