Flux after tooth extraction: what to do for prevention
Flux, or scientifically odontogenic periostitis or gum abscess, is a purulent inflammation of the maxillary periosteum, the occurrence of which is predominantly associated with a diseased tooth.He has a kind of purulent abscess, which at untimely appeal to the dentist can lead to serious complications.
Causes of flux

the event of failure to the dentist inflammation can lead to serious complications
lateral abscess can occur for various reasons and factors such as:
- Caries - the most common cause of periostitis, as well as other dental diseases such as chronic periodontitis, alveolitis, periodontitis, suppuration of the cyst of the jaw or inflammation of the retinized( neprRezai) of teeth;
- damage to - traumatic periostitis is often observed after tooth extraction, surgical procedures, after jaw fracture and various dental injuries that lead to inflammation of the bone tissue;
- inflammatory process of in the gingival pocket, that is, the space between the gum and the tooth - the food that accumulates in these pockets can become a source of bacterial growth, which contributes to the occurrence of flux;
- a temporary filling of may cause a periostitis that has not been replaced by a permanent one;
- bacterial flora - streptococci, staphylococci, G + and G-sticks, putrefactive bacteria;
- in children periostitis often occurs after tonsillitis, angina, otitis, influenza, when there is a hematogenous or lymphogenic pathway of infection;
- is often tied with overcooling , stresses, physical overvoltages.
Flux types and symptoms accompanying it
The severity of the symptoms of the flux depends on the form, localization of the process and the patient's immunity. There are several types of odontogenic periostitis, namely:
- Serous is the easiest form of periostitis.Accompanied by edema of soft tissues, mucosal erythema, an increase of regional lymph nodes.Often the reaction is on the tooth, the patient pulpitis or periodontitis, or arises due to injury;

- Purulent form of - manifested by edema and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the mouth and soft tissues, the formation of a painful compaction with a purulent content, sometimes the swelling may have a zone of fluctuations in the middle( then it is an abscess).Common symptoms include weakness, decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, fever temperatures of 38-38.5 ° C.Patients complain of severe pain that can radiate to the temple, ear, orbit, neck and is amplified when the mouth is opened and jaw movements Visually, depending on the location of the flux, there is edema of the cheek, upper or lower lip, suborbital, parotid, or chin;.Painful sensations become less intense when a fistula is formed and pus flows from the flux into the oral cavity.
- diffuse form of periostitis - is characterized by the spread of edema to adjacent tissues.When the upper incisor is affected, the edema passes to the upper lip and nose region, with molars affected to the buccal and parotid region, premolars to the lower region of the cheek.There is also an increase in temperature, general weakness, decreased appetite;
- chronic periostitis - characterized by a prolonged course( about 4-8 months and more) with periodic exacerbations.It is accompanied by such symptoms as swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane, thickening of the bone at the site of the process, the formation of a dense infiltrate, entrainment of regional lymph nodes, a slight increase in body temperature during exacerbation.
When it is necessary to remove the tooth with the
flux Often the only solution is to remove the tooth with the flux.
This procedure is unavoidable in the following cases:
- if conducted conservative therapy did not produce the expected result;
- if the tooth has a large crack that can not be cured conservatively;
- in the presence of neglected diseases( caries, pulpitis, periodontitis), due to which the destruction of the dental tissue is so significant that conservative therapy or sealing is impossible;
- in the presence of an infectious process in the tissues of the tooth in the interzubesnev region.

In the first and last trimester of pregnancy, tooth extraction with flux
is contraindicated
Contraindications to tooth extraction with flux are:
- diseases in acute phase;
- first and last trimester of pregnancy;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- severe diseases of the nervous system;
- diabetes mellitus;
- disorders of the blood clotting system;
- post-auction period.
The process of tooth extraction with periostitis
Before deciding to remove the tooth with a flux, the dentist assigns a radiograph to the patient, which will show the degree of destruction in the bone tissue of the tooth and jaw.
In the preoperative period, the patient is drained with pus and is prescribed antibiotic therapy to reduce swelling and inflammation.At the first stage of the operation, the mucosal tissue that surrounds the periosteum is dissected, with the aim of accessing the root of the affected tooth.Then, the tooth itself is removed by parts using a laser or a special tooth file.When the tooth is removed, the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions and sutured.
Flux treatment after tooth extraction
Normally, the flux after tooth extraction should disappear within three to five days.If after tooth extraction the flux does not pass, you should immediately consult a doctor for adequate treatment.Independently anything to undertake categorically is not advised as it is possible only to worsen the state and complicate the process.If the flux is not large, the doctor can prescribe antibiotic therapy, which can be local in the form of ointments or general.
If conservative therapy does not give a positive effect to or if suppuration is too severe, surgical methods for removing the flux should be consulted.Local anesthesia is done, then a cut is made at the site of suppuration, all pus is removed and the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions.Pat by drainage for further possible outflow of pus.After the operation, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy to prevent the progression of inflammation.

Normally, the flux after tooth extraction should disappear within three to five days.
It also happens that the flux was formed immediately after the extraction of the tooth.The reason for this may be getting the infection during the operation or after because of non-observance of the doctor's recommendations.After the tooth extraction operation, it is advised to refrain from eating and drinking for a while, it is not recommended to smoke, and it is also necessary to conduct a more thorough oral hygiene.Failure to follow these recommendations can trigger the development of a new inflammation.What to do with the flux after tooth extraction?First of all, you need to see a doctor.After the examination, a decision is made about the method of therapy.
With conservative treatment, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs must be prescribed, as well as detoxification therapy.It is also recommended to rinse the mouth with chlorhexidine solution or other antiseptic solutions that fight bacteria and somewhat reduce toothache.If the patient's immunity is very weak, vitamins, immunomodulators are prescribed.Local therapy includes the use of Vishnevsky ointment, Metrogil denta, Levomekol.Ointments are superimposed on the outer part of the cheek in the projection of the abscess.If conservative therapy does not give the desired result, resort to surgical intervention.
Prevention of periostitis
In order to avoid such an unpleasant disease as periostitis, the following recommendations should be observed:
- visit the dentist regularly( at least once a year);
- observe the rules of oral hygiene( brush your teeth two times a day after meals, use dental floss after eating, use mouth rinses);
- use toothpastes based on medicinal plants( chamomile, calendula, etc.);
- timely treatment of dental diseases that can lead to periosteasis - dental caries, periodontitis, alveolitis, periodontitis, cyst of periosteum;
- immediately consult a doctor for any injuries to the teeth or jaws.
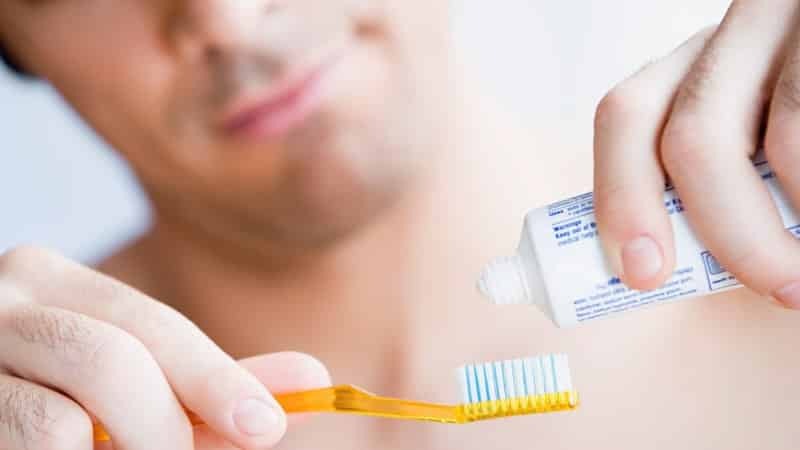
Prevention of periostitis consists in proper oral hygiene
Periostitis, also known as flux, is a rather unpleasant and dangerous disease.
For example, osteomyelitis of the jaw, phlegmon, upper mediastinitis and even sepsis.To avoid such an outcome, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms.He will prescribe the correct conservative therapy or surgical intervention, which consists in removing the tooth with the flux.But it happens that the tooth is removed, but the flux does not pass.Then the doctor again makes a decision about conservative therapy or the appointment of an operation to cut the abscess.
In order to prevent the occurrence of flux, preventive measures must be taken.After all, any disease is easier to prevent than treat.



