Traumatic shock: causes, clinical picture, emergency care
 One of the worst complications of massive injuries is traumatic shock.Due to the influence of many factors, among which the leading place is the decrease in the volume of circulating blood, changes in the body are increasing, which without assistance quickly lead to the death of the victim.
One of the worst complications of massive injuries is traumatic shock.Due to the influence of many factors, among which the leading place is the decrease in the volume of circulating blood, changes in the body are increasing, which without assistance quickly lead to the death of the victim.
Causes of traumatic shock
Even recently, even health workers used the term "pain shock".His existence was associated with an erroneous theory, according to which the main "trigger" of the disease was severe pain.There were even conducted studies allegedly proving the correctness of this hypothesis.
However, the "painful" theory did not explain the absence of shock in women giving birth( readers can paint colorfully about extreme pain during labor) or the ability of a person to fight even during a war, even after a serious injury.Therefore, the first place was put forward the theory of hypovolemia.
According to her, the main cause of development of traumatic shock is acute massive blood loss due to:- fractures;
- extensive injuries of soft tissues;
- burns;
- frostbite;
- ruptures of internal organs, etc.
In this case the body mobilizes absolutely all its forces in order to save the main organs - the heart, brain, kidneys, lungs.As a result of a cascade of neurohumoral reactions, all peripheral vessels contract, and almost all available blood is sent to these organs.This is achieved primarily through the development of catecholamines - adrenaline and norepinephrine, as well as hormones of the adrenal cortex.
However, saving the "commanders", the body begins to lose "simple fighters".Cells of peripheral tissues( skin, muscles, internal organs) experience oxygen starvation and switch to the anoxic type of metabolism, in which lactic acid and other harmful decomposition products accumulate in them.These toxins poison the body, contributing to a worsening of metabolism and aggravating the course of the shock.

In contrast to hemorrhagic shock, in the case of traumatic an important role is played by the pain component.Because of the powerful signals coming from the nerve receptors, the body reacts excessively sharply, resulting in a traumatic shock in its severity ahead of hemorrhagic.
Clinical picture of traumatic shock
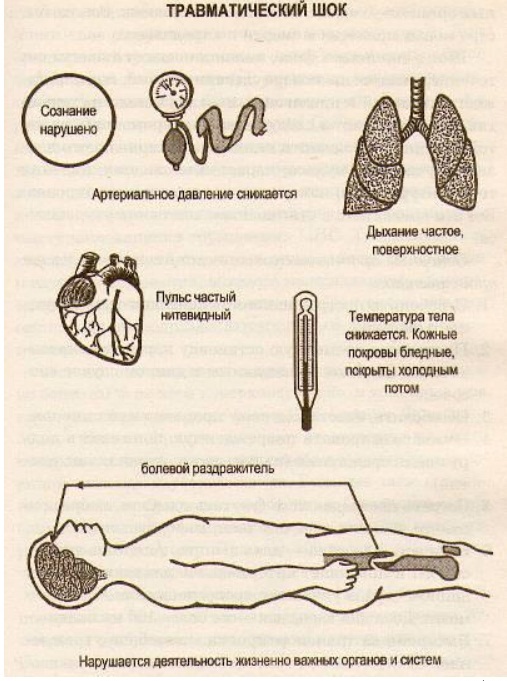 There is a clinical classification of traumatic shock, based on the magnitude of falling blood pressure, heart rate, state of consciousness and laboratory data.However, it is interesting first of all to doctors, who on its basis make a decision about the methods of treatment.
There is a clinical classification of traumatic shock, based on the magnitude of falling blood pressure, heart rate, state of consciousness and laboratory data.However, it is interesting first of all to doctors, who on its basis make a decision about the methods of treatment.
For us, the other classification is very important, very simple. According to her traumatic shock is divided into two phases:
- Erectile, in which a person is under the influence of "horse" doses of stress hormones.In this phase the patient is excited, rushes, breaks somewhere to run.Because of the massive release of catecholamines, blood pressure can be normal even with severe blood loss, but paleness of the skin and mucous membranes due to spasm of small vessels, and tachycardia for compensating for missing fluid in the bloodstream are noted.
- The torpid phase occurs quickly enough and the more rapidly, the higher the degree of fluid loss.In this phase, the person becomes inhibited, sluggish.The arterial pressure begins to fall, the pulse becomes even more frequent, breathing becomes more frequent, urine production stops, a cold sweat appears - a threatening sign of a critical violation of the blood supply of tissues.
In the absence of medical care or untimely and poor quality of its provision, the situation rapidly deteriorates, the shock goes to the terminal state, which almost always ends with the death of the patient due to severe hemostasis disorders, stopping nutrition and supplying oxygen to the cells of vital organs, accumulation of tissue decay products.
First aid for traumatic shock
It is possible to say without embarrassment that every minute of delay with rendering assistance to a person in a state of shock takes ten years of life from him: this phrase accurately reflects the criticality of the situation.
Traumatic shock is a condition that almost never occurs in a hospital, where there are all the necessary specialists, equipment and medicines, where a person has maximum chances of survival.Usually injuries are received by the victim on the road, when falling from a height, during explosions in military and peacetime, at home.That is why the first aid in case of traumatic shock should be rendered by the person who found it.
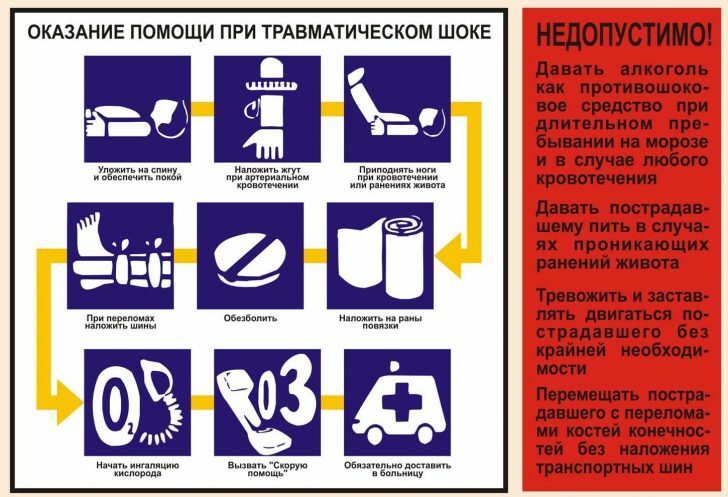
First of all, anyone who is injured in an accident or falls from a height as a person with a spinal fracture should be evaluated.It can not be lifted, moved and even shaken - this can aggravate the course of the shock, and the possible displacement of the vertebrae will certainly make a person disabled even if he survives.
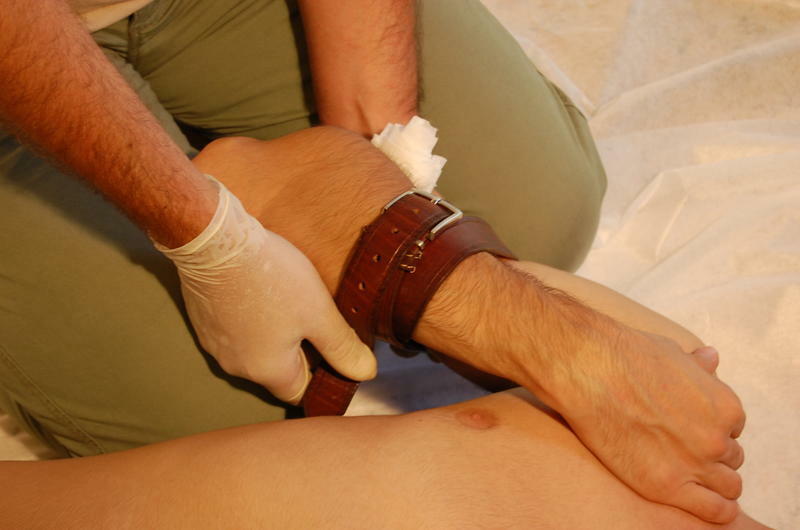 The first stage of medical care is to stop bleeding.To do this, in the "field" conditions, you can use any clean rag( of course, it is desirable to use a sterile bandage!), Which tightly bandages the affected limb or, twisting it in a ball, clamp the wound.In some cases it is necessary to apply a hemostatic tourniquet.Stopping bleeding turns off the main cause of the shock and gives a short but valuable time span to provide other types of help and call an ambulance.
The first stage of medical care is to stop bleeding.To do this, in the "field" conditions, you can use any clean rag( of course, it is desirable to use a sterile bandage!), Which tightly bandages the affected limb or, twisting it in a ball, clamp the wound.In some cases it is necessary to apply a hemostatic tourniquet.Stopping bleeding turns off the main cause of the shock and gives a short but valuable time span to provide other types of help and call an ambulance.
Breathing is another important task.It is necessary to release the oral cavity from foreign bodies and prevent their entry in the future.
The next step is to anesthetize any analgesic, preferably stronger and preferably - an injection form.Do not give the pill to a person without consciousness - he can not swallow it, but can choke it.It is better not to anesthetize at all, especially since the unconscious patient already does not feel the pain.
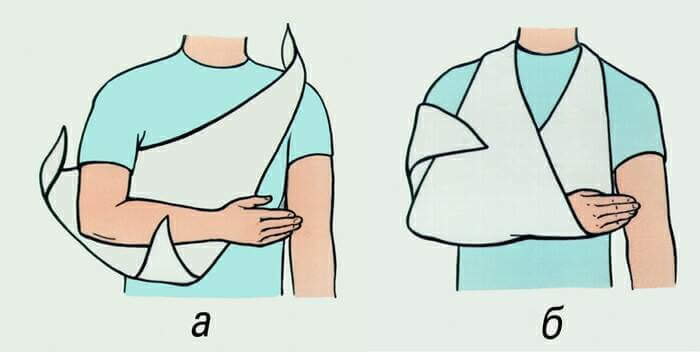
Providing immobilization( complete immobility) of the affected limbs is an integral part of first aid.Due to it the intensity of pain sensations decreases and it also increases the chances of the survivor.Immobilization is made using any improvised means - sticks, boards, even rolled up in a tube of glossy magazines.
- connects the system for intravenous infusion of blood substitution solutions;
- uses pressure-enhancing drugs;
- introduces strong painkillers, including drugs;
- provides oxygen inhalation and, if necessary, artificial ventilation.
Important : after the first medical assistance and stabilization of vital signs( and only after stabilization!) The victim is immediately taken to the nearest hospital.When trying to transport a person with unstable pressure and pulse, with uncontaminated blood loss, he almost certainly perishes.That is why the ambulance does not immediately move from its place, no matter how much the demands from doctors about it.
Complex contra-shock measures continue in the hospital, surgeons perform the final stop of bleeding( with internal injuries surgery is required), finally stabilize the pressure, pulse and respiration parameters, inject glucocorticoid hormones that support myocardial contractility, eliminate vasospasm and improve tissue respiration.
The main criterion for recovering from shock is the restoration of kidney function, which begins to excrete urine.This sign may appear even earlier than normal blood pressure.It is at this point that we can say that the crisis has passed, although remote complications still threaten the patient's life.
Complications of traumatic shock
In shock, one of the main mechanisms that make it worse is thrombosis.The body during blood loss activates all its protective systems, and often they start to work not only in the place of injury, but also in very remote organs. Severe complications due to this develop in the lungs, where there may be:
- thromboembolism( blockage of the branches of the pulmonary artery);
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome( switching off lung tissue from gas exchange) is a deadly complication with 90% mortality;
- focal pneumonia;
- swelling of the lung, almost always ending sadly.
Relatively long existence of body tissues in conditions of oxygen starvation can lead to the development of microcirculation necrosis, which become a favorable environment for infection.The most common complication of traumatic shock is infectious and inflammatory diseases of almost any organ - spleen, liver, kidneys, intestines, subcutaneous fat, muscle, etc.
Traumatic shock is an extremely serious disease with high mortality and from the timeliness of treatmentAlmost everything depends here.Knowledge of his basic symptoms and methods of first aid will allow a person to avoid death, and in many cases - to prevent the development of complications.
We recommend to watch:
Bozbey Gennady, medical reviewer, ambulance doctor