Pain in the neck and lower back with osteochondrosis
 Pain in the neck and lower back is most often a consequence of osteochondrosis - a disease of the spine that results from a disruption in the structure of the intervertebral discs.According to statistics, every second inhabitant of the planet during his life experiences characteristic pain in the back.And approximately in 95% of cases they are caused by an osteochondrosis of various localization.
Pain in the neck and lower back is most often a consequence of osteochondrosis - a disease of the spine that results from a disruption in the structure of the intervertebral discs.According to statistics, every second inhabitant of the planet during his life experiences characteristic pain in the back.And approximately in 95% of cases they are caused by an osteochondrosis of various localization.
Anatomical and physiological features of the spine in people
In the human spine, there are 33-34 vertebrae separated from each otherAnother intervertebral disc.Because of the erection, several bends appeared in it - cervical and lumbar lordosis and thoracic and sacral kyphosis.They serve to amortize vertical loads.
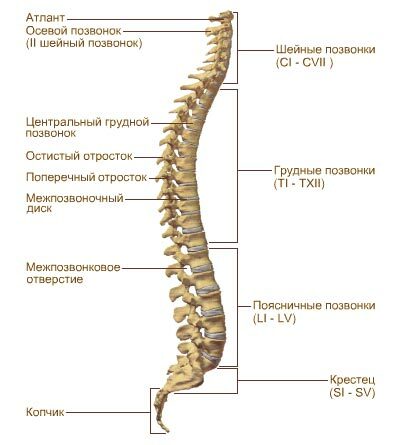
Elasticity and elasticity, as well as mobility and the ability to resist even significant loads, the spine is attached to the intervertebral discs - special cartilaginous structures consisting of: two solid cartilaginous plates adjacent to the bodies of adjacent vertebrae,
- ;
- pulp kernel located between them;
- consisting of a fibrous cartilage of the fibrous ring surrounding the pulpous nucleus outside.
The main role in the development of osteochondrosis is played by the fibrous ring.With a decrease in its elasticity, it loses its ability to withstand loads.When the spine is bent, the pulpous nucleus begins to protrude through the wall of the fibrous ring, causing neurologic symptoms( all known radiculitis, which is called discogenic radiculopathy in medicine).
Causes of osteochondrosis
Recent theories of scientists in the first place among the causes of osteochondrosis put upright.For a relatively short( by historical standards), a man from a four-legged creature turned into a biped.This time, the spine did not have enough to adapt to the changed conditions of functioning.
The human skeleton designed to work horizontally has become vertical.The unusual direction of the loads, coupled with age-related changes in intervertebral discs, genetic disorders, environmental factors, and lead to partial destruction of the cartilaginous parts of the spine.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
There are several options for classifying osteochondrosis based on various key criteria.Until recently, a gradation based on the degree of destruction of the intervertebral disc was adopted in our country:
1 degree - painless stage.In this case, the pulpous nucleus, when moving in the spine, presses on the fibrous ring.A defect in the ring is not yet available.
2nd degree - stage of instability.Due to the partial loss of the ability to fix the vertebrae by the fibrous ring, they lose their stability.This is what the people call "displacement of the vertebrae," that "treat" the bone-smelters.At this stage, there are already various symptoms, the brightness of which, however, rarely reaches a maximum.
3 degree - herniated intervertebral disc.At the same time, a rupture occurs in the fibrous ring, through which the pulpous nucleus extends beyond the disk.This causes periodic intolerable pain in the affected segment of the body, hard to stop even when using strong analgesics.

4 degree is characterized by the defeat of extra-disk structures - vertebrae, ligaments, muscles, nerves, blood vessels.
Currently, another classification is used:
1 degree - dysfunction characterized by impaired intervertebral disk function without its persistent organic changes;
2 degree - instability, in which there is a disturbance of functions, coupled with frequent displacements of the vertebrae and hernias;
3 degree - restabilization, when the vertebrae assume a new position due to fibrosis of the disc( germination with its coarse connective tissue);This is not a recovery, but rather a complication of osteochondrosis.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Symptomatic disease is directly dependent on the degree of changes occurring in the structures of the intervertebral disc.And to cause the emergence of certain clinical signs can not only hernia, but also bony proliferation of vertebral bodies.
For quite a long time, destructive processes do not manifest themselves in any way, however, when the changes increase, the symptomatology of the disease also becomes brighter.Pain is the symptom that, first and foremost, causes the patient to seek help or to start any action for the treatment of the disease.Pain can be localized both in the area of the disc and in the zones innervated by the squeezed spinal cord.For example, with osteochondrosis of the cervical region, the hand can hurt, and with lesions of the lumbar intervertebral discs, pain occurs in the thigh, lower leg and even the foot.
Pain sensations are of a permanent nature, amplified by movements of the body, limbs.They can be extremely intense, so much that they deprive the patient of the ability to move and even get out of bed.Taking pain medication only brings a short incomplete relief.
The second symptom of osteochondrosis is a violation of limb functions. Due to the deterioration of the innervation of the hands or feet, movements in them become inadequate.A person feels a muscle weakness, an inability to perform the usual amount of work so far, the limb quickly becomes tired and takes a long enough time to recover.
The third symptom is a sensitivity disorder. It is expressed in the numbness of the corresponding area of the skin, the appearance of paresthesias( sensation of "goosebumps"), hyperesthesia( increased tactile sensitivity).To less bright symptoms include increased sweating and the appearance of red spots on the skin.However, usually patients do not pay attention to such "trifles" and only a very attentive doctor can identify these important clinical signs.More in detail about the general symptoms of osteochondrosis and diagnosis of this disease - in the video review:
Features of the symptomatology in the defeat of various parts of the spine
Because each department of the spine has its anatomical structures, the symptoms of osteochondrosis can vary significantly.
Pain in cervical osteochondrosis
The following syndromes can occur when this spine is injured:
-
 Spinal.In this case, the structures of the altered vertebrae squeeze the spinal cord, causing various violations of the type of paralysis or paresis.
Spinal.In this case, the structures of the altered vertebrae squeeze the spinal cord, causing various violations of the type of paralysis or paresis. - .There is a symptomatology of squeezing the corresponding spinal cord - a severe pain that prevents active( and often passive!) Movements of the head, as well as violations of skin sensitivity in the affected nerve segment of the body.
- Vertebral artery.In this case, the altered structures of the spine compress the vertebral artery feeding the brain. Reducing blood flow to the brain structures leads to very vivid symptoms:
- headache in one half of the head( migraine-like);
- sensation of "goose bumps" also in the half of the head;
- pain in the neck and occiput, intensifying when bending or bending the neck;
- drop-attacks - attacks of complete paralysis that occur without loss of consciousness( falling attacks);While the person after a sudden turn of the head suddenly loses all his strength and falls.
Pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The lesion of the thoracic spine also manifests itself in a number of characteristic symptoms:
- The main symptom is a marked pain that increases with the act of breathing( especially with deep inspiration), corners of the body, coughing andSneezing;
- is possible and such a sign as pain in the heart, often taken for a heart attack;
- possible pain in the right or left hypochondrium, the upper abdomen;Such a localization of sensations very much complicates the diagnosis, since even experienced doctors can confuse chest osteochondrosis with cholecystitis, pancreatitis, acute abdomen or angina pectoris;
- neurologic disorders are manifested in the form of sensitivity disorders of various kinds - paresthesias( sensation of "goosebumps"), increase or decrease of skin sensitivity.
Pain in osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
The most vivid and familiar, perhaps, all symptom is a pain in the lower back, often giving up the areas of the buttocks, the hip joint or lower limbs.Sometimes it arises suddenly after a sharp physical strain( lumbago), in other cases it increases gradually( lumbalgia).Most patients note the appearance of paresthesias, burning or pain in the legs, lack of freedom of movement( stiffness) in the lower back.Pain can increase dramatically when trying to overcome this stiffness.
When a lesion of the lumbar region is often the appearance of a pain syndrome precedes a kind of aura:
- fatigue;
- unpleasant sensations in the gluteal region;
- instantly arising and immediately passing pains in the lower back with awkward movements, corners of the body.
Doctors note a clear relationship between dynamic and static loads on the spine on one side and the intensity of pain sensations on the other.

In addition to pain in lumbar osteochondrosis, as with lesions of other localizations, there are impaired sensitivities, and in some cases, signs of spinal cord injury.These symptoms are more typical for the already formed hernia of the intervertebral disc, although they can be caused by spondyloarthrosis and other causes similar to hernia.
Diagnosis of vertebral osteochondrosis
Despite the fairly vivid symptomatology, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis is made only after an accurate confirmation of degenerative processes in the spine.To determine the possible tactics of treatment, a physician should pay attention not only to the data obtained from the patient, but also to the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
The second place after studying the history of the disease is radiation diagnostic methods, which include:
- radiograph of the spinal column;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
In principle, to obtain sufficient confidence in the diagnosis of an experienced orthopedist, only the results of an X-ray examination using functional samples and contrasting subarachnoid space are sufficient.In many situations, it is precisely these physicians that are limited, given the ubiquitous prevalence of the method and its relative cheapness.
Axial computed tomography( ACT) is considered a more informative way of obtaining data.With its help, it is possible to obtain all the data on: the
- state of the vertebral bodies and their processes;
- topography of the spinal canal;
- channel sizes at different levels;
- localization and size of hernial protrusion.
Sometimes a contrast medium is introduced into the spinal canal, which allows us to refine the data obtained before. Nevertheless, the most informative method of radiation diagnosis is MRI.Magnetic resonance tomography has several advantages over the usual "X-ray" or ACT:
- the ability to scan the entire vertebra at once;
- allows you to explore an object in any plane;
- allows you to see even small formations, and not only bones but also soft tissues are visualized;
- study completely safe, since there is no ionizing radiation.
 MRI has the maximum resolution of all diagnostic methods and helps not only to establish an accurate diagnosis, but also to determine adequate surgical intervention tactics.
MRI has the maximum resolution of all diagnostic methods and helps not only to establish an accurate diagnosis, but also to determine adequate surgical intervention tactics.
Treatment of osteochondrosis pain
There is no consensus on the tactics of treating osteochondrosis.In different periods, the disease is treated both by neuropathologists, manual therapists, homeopaths, reflexologists, surgeons and orthopedists.This is due to the fact that the causes of the onset of degenerative processes in intervertebral discs are unknown.
Complete recovery of osteochondrosis using modern medicine to achieve, alas, impossible.All the efforts of specialists are aimed at suppressing acute phenomena and the earliest restoration of the patient's capacity for work. Measures to combat disease pathology can be divided into three parts:
- non-pharmacological treatment;
- medication;
- surgical treatment.
For acute pain, the patient is prescribed a bed rest and complete elimination of any physical activity.It is recommended that avoiding sharp slopes and taking poses that aggravate pain.Muscular relaxation is facilitated by lying on a hard surface( shield under the mattress). For osteochondrosis, drugs from groups of analgesics are used:
- indomethacin;
- diclofenac;
- ibuprofen;
- nimesulide;
- ketorolac;
- meloxicam;
and muscle relaxants: - Tolperisone;
- tizanidine.
These drugs eliminate pain, suppress the inflammatory reaction and relieve muscle spasm, which in itself can enhance the symptoms of the disease.Often, along with the administration of these medicines, the physician prescribes physiotherapeutic analgesic procedures, rubbing ointments with analgesics, compresses with novocaine.
If the drug therapy is ineffective, Novocain blockade can be recommended.After abating acute pain the patient is allowed to get up, walk, gradually increase physical activity.
Important: : Long sitting position is not recommended, carrying heavy loads for up to 8 weeks.
Sometimes, for a short period of time, a doctor can recommend wearing a cervical collar or a lumbar lumbar belt.This allows to relieve the affected area of the spine and accelerate recovery.
Please note: Prolonged wearing of these devices is not recommended, since it leads to weakening of the back muscles and increasing the load on the spine itself.
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis should be resorted to only as a last resort.Operations are subjected to patients with hernias compressing the spinal cord or its roots.In this case, usually remove the affected disc and connect the adjacent vertebrae by various methods.Thus, the very basis for the appearance of neurological symptoms is eliminated.You can get more information about the treatment methods by watching the video:
Prevention of osteochondrosis
Due to the fact that the causes of the disease have not been studied in part, and partly are unrecoverable( eg genetic predisposition), it is impossible to prevent the development of the disease. Nevertheless, if several simple rules are observed, the frequency of exacerbations of the disease can be significantly reduced.And for this you need:
- to strengthen the muscles of the back, as they take on a significant share of the load;
- avoid hypothermia;
- to avoid lifting weights, and if this is not possible, then at least raise them without bending the spine;
- sleep on a relatively hard surface;
- use orthopedic pillow and orthopedic mattresses;
- with the slightest discomfort in the back to consult a doctor.
Osteochondrosis is not cure, but its manifestations can be weakened if it is responsive to your own health and not to engage in self-medication.
Volkov Gennady Gennadievich, medical reviewer, ambulance doctor.