Diphtheria: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
In vaccinated people, diphtheria can flow imperceptibly, according to the type of ARI - with a low temperature, swelling and reddening of the throat, moderate intoxication.Therefore, often such cases are not recorded as diphtheria.
toxic diphtheria is more rare and predominant in unvaccinated people, the symptoms of this form of ailment are predetermined by how much toxin the corynebacterium has isolated: the more toxin, the heavier the patient's condition. The toxic diphtheria manifests itself with the following symptoms of :
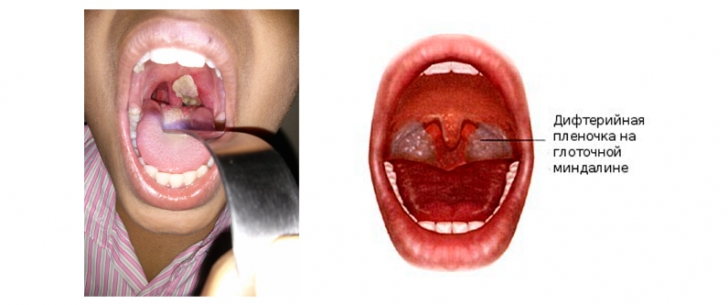
- with extensive film deposits( the pharynx can be completely invisible beyond the greatly enlarged tonsils and the films passing to the soft palate);
- very high temperature;
- with the strongest intoxication;
- neck edema.
Separately describe the symptoms of diphtheria croup - a specific lesion of the larynx.Such diphtheria in children can very quickly end in suffocation and death( the child's larynx itself is narrower, so it quickly overlaps due to swelling and films).
To suspect the development of diphtheria croup is possible by the following features :- hoarseness;
- noisy and difficult breathing( especially on inspiration);
- barking cough;
- pale gray skin color.
Diphtheria of other localizations also form specific films( conjunctiva, mucous genitalia, in wounds) and swelling of the tissues, symptoms of intoxication appear.
Complications of diphtheria
The occurrence of complications of diphtheria is mainly due to the effect on the nervous system, kidneys, heart and other organs of toxins of the causative agent of the disease. If the patient does not receive assistance in time, he or she may develop:
- Infectious-toxic shock.
- DIC-syndrome( severe disruption in the blood coagulation system).
- Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, which leads to heart dysfunction.
- Nephrozonephritis - damage by toxins of the kidney parenchyma.
- Polyneuritis, reversible paresis and paralysis.
Diagnosis of diphtheria

The data obtained during the examination of the patient and the results of laboratory tests( bacterioscopy and bacteriological culture of the material taken from the patient's throat, serological tests) serve as the basis for the diagnosis of diphtheria.However, the patient can be hospitalized even before the diagnosis is made, since the abnormality counts for hours in this pathology.
In addition, in order not to miss diphtheria, hiding under the "mask" of other diseases, all patients with symptoms of angina also take smears from the pharynx.
Treatment of diphtheria
Note: treatment of diphtheria patients, regardless of the severity of the disease, is performed in an infectious disease hospital.
These patients are prescribed:
- Diet and bed rest.
- Antiphlogistic serum( PDS), which inactivates the toxin released by the pathogen.The sooner this drug is introduced, the lower the risk of complications and the best prognosis for the patient.
- Antibiotics to which the corynebacteria are sensitive.Antibacterial therapy helps to reduce the number of pathogens and, accordingly, the toxin they release, and also prevents the long stay of the corynebacteria in the nasopharynx of the person and the infection of other people.As a rule, doctors give preference to penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins.The duration of such treatment is 7-10 days.
- Detoxication therapy.
- According to indications, hormones( prednisolone), antihistamines.
- Local antibacterial treatment.
- Vitamins.
Severe toxic diphtheria, diphtheria croup, infectious-toxic shock and other dangerous complications of the disease are indications for the hospitalization of a patient in the intensive care unit.
Diphtheria prophylaxis
Recommended to read:Diphtheria refers to infectious diseases that can be controlled by vaccination, so vaccination against diphtheria is the main measure of prevention for this infection.Equally important in preventing the spread of diphtheria is the implementation by the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service of a number of anti-epidemiological measures: examination and, if necessary, immunization of persons who have been in contact with a patient or carrier of toxic corynebacteria, disinfection in the home and places visited by the patient( garden, school), compulsory treatmentCarriers of infection( they are prescribed antibiotics), etc.
Vaccination against diphtheria
 Vaccination from diphtheria is carried out with diphtheria toxoid( inactivated toxin).This substance stimulates the synthesis of antitoxic immunoglobulins in the body.Usually, a complex preparation is used to immunize children, which in addition to the diphtheria component( it is designated by the letter "D"), has tetanus( "C"), and pertussis( "K").This vaccine is called DPT , and if it lacks the pertussis component - ADS( vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus without pertussis component is administered to adolescents and adults).In addition, there is also an isolated antidiphtheria vaccine - AD, which is used according to the indications.Vaccines with a reduced amount of antigens( ADS-M, AD-M) can also be used for routine revaccination of adults.
Vaccination from diphtheria is carried out with diphtheria toxoid( inactivated toxin).This substance stimulates the synthesis of antitoxic immunoglobulins in the body.Usually, a complex preparation is used to immunize children, which in addition to the diphtheria component( it is designated by the letter "D"), has tetanus( "C"), and pertussis( "K").This vaccine is called DPT , and if it lacks the pertussis component - ADS( vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus without pertussis component is administered to adolescents and adults).In addition, there is also an isolated antidiphtheria vaccine - AD, which is used according to the indications.Vaccines with a reduced amount of antigens( ADS-M, AD-M) can also be used for routine revaccination of adults.
About the vaccination of DTP in this video review tells the pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky:
For children, adolescents and young people, the vaccination against diphtheria in Russia is carried out according to the following scheme : 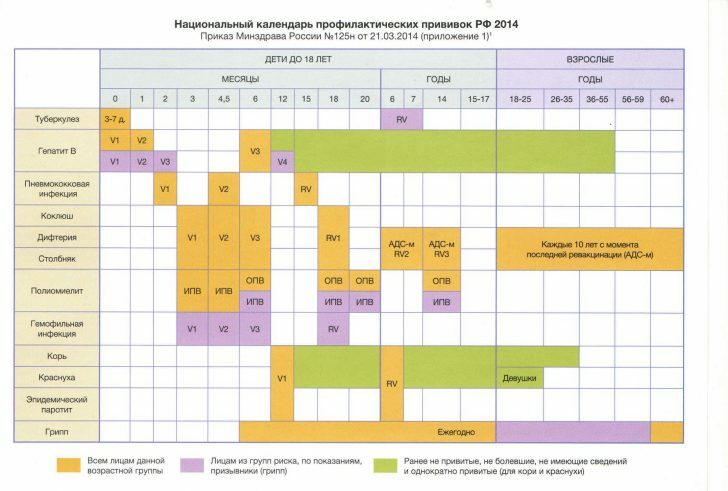 It is also worth noting that adults need vaccination against diphtheria,Than children, since post-vaccinating immunity "suffices" only for 10 years.Therefore, parents should be revaccinated on a regular basis so as not to fall sick and not endanger their children.
It is also worth noting that adults need vaccination against diphtheria,Than children, since post-vaccinating immunity "suffices" only for 10 years.Therefore, parents should be revaccinated on a regular basis so as not to fall sick and not endanger their children.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist doctor