Rubella in children: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
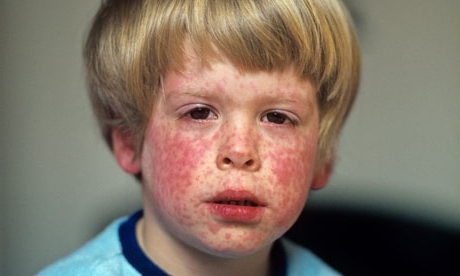 Rubella is an infectious disease of viral origin, which has a very high level of contagiousness, that is, infectiousness.Its main signs are the appearance of typical rubella elements on the skin, symptoms of intoxication of the organism of moderate severity, a change in the pattern of blood and an increase in regional lymph nodes.
Rubella is an infectious disease of viral origin, which has a very high level of contagiousness, that is, infectiousness.Its main signs are the appearance of typical rubella elements on the skin, symptoms of intoxication of the organism of moderate severity, a change in the pattern of blood and an increase in regional lymph nodes.
Rubella Transmission Routes
Rubella Forms:
- acquired when a healthy child becomes infected;
- is congenital - with it a sick child gets the virus in utero from the mother and allocates it within 12-24 months after birth.
Rubella in children can occur in mild forms and with complications, more often neurological( rubella encephalitis, arthritis, meningitis, pneumonia, etc.).The disease is quite common, its outbreaks are fixed every 4-5 years in children's and adults' groups.It is also characterized by seasonality, and the peak of activity falls on the winter.The child's organism is very susceptible to the rubella virus, especially at the age of 1 year to 7-10 years.Breasts up to 12 months of age have innate immunity.Those who have already been ill with this disease have a lasting immunity for the rest of their lives.
Rubella infection occurs from a sick person who is the source of a viral infection.
The disease is transmitted in the following ways:
- airborne( kiss, conversation);
- vertical route of infection( transplacental) - from a sick mother to a fetus;
- pin - when using general toys, personal care items.
In total, the patient is contagious to others for 21-28 days.
Please note: should take into account that a person with rubella is contagious both in the incubation period - 7-10 days before the rash, and after the appearance of symptoms - about 3 weeks.
The carriers of the disease can also be virus carriers that do not show signs of disease and are healthy.
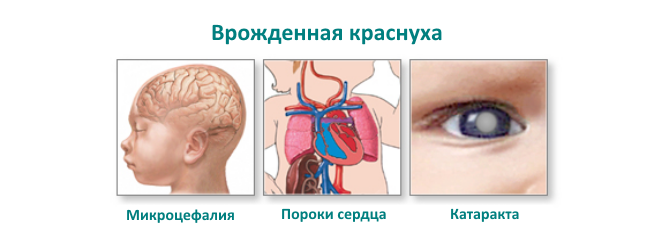
Important : This disease has a particular risk during pregnancy in the first trimester.Rubella causes the fetus during this period to congenital malformations of a severe form, up to its death.
Pathogenesis of
Rubella enters the healthy body through penetration through the respiratory tract and mucous membranes.Hematogenously, the virus spreads and also enters the lymphatic system, where it multiplies in the lymph nodes for about 7 days.Clinically, this is manifested by lymphadenopathy - a noticeable increase in the size of the nodes themselves.Also can be observed catarrhal phenomena - rhinitis, perspiration in the throat, dry unproductive cough, lacrimation.Against the background of the subfebrile condition, a rash starts appearing, which looks like small oval or round spots of pink-red color.In childhood, this disease is much easier than in the adult.
Note: in laboratory tests of blood and swab from the nasopharynx virus can be detected even 8 days before the appearance of the rash.After the rash, the virus is diagnosed by its isolation from the analysis of feces or urine.
Causes of the disease
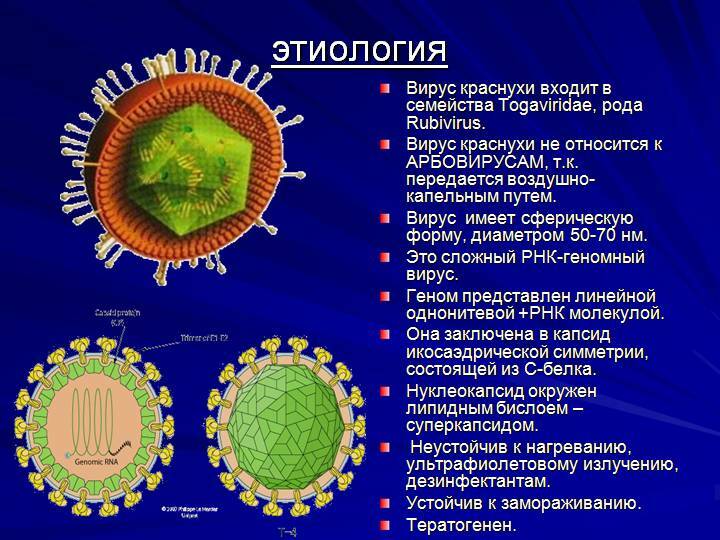
Calls the rubella RNA virus of the genus Rubivirus, which belongs to the family Togaviridae.Particles of the virus containing pathogenic RNA have a very small size - 60-70 nm.Rubella eradicator at a temperature exceeding 56 ° C for 60 minutes, but in a frozen state can live many years.Getting on the mucous membranes or damaged skin, the virus begins to rapidly multiply in favorable conditions.It accumulates in the lymph nodes, with blood spread to all organs and systems, eventually settling in the skin.
Rubella: symptoms
Rubella in children is much easier than in adults.The disease occurs in 4 stages:
- incubation period - takes on average 7 to 21 days;
- period of catarrhal phenomena - with it often there are no pronounced symptoms of rubella, but there may be a runny nose, reddening of the mountain, enlarged lymph nodes( this period lasts 1-3 days, no longer);
- is the height of the disease - at this time, exanthema and rashes( small, pink or red, with clear and even edges) begin to appear, in some cases it can merge, which often happens in children.
- period of convalescence( recovery).
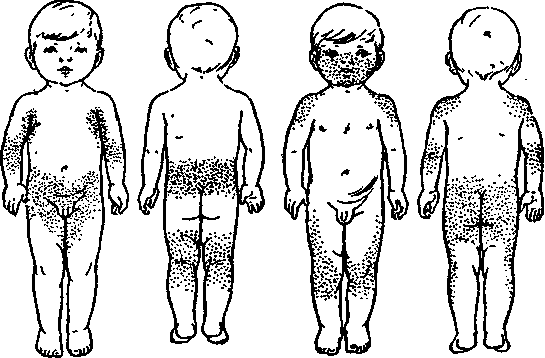
It is worthwhile to clarify the localization and the type of rash with rubella, as these are its characteristic features.When differentiating the disease, attention is drawn to the following moments of :
- for rubella skin rash are located in the zone of the back, face, buttocks, neck, on the scalp, the inner flexion surface of the knees and elbows, behind the ears; and the

 .
. - for rubella there is no rash on the feet and palms;
- rash has the appearance of round elements with a diameter of up to 5 mm;
- the body is covered with a rash within 24 hours;
- does not exclude elements on the oral mucosa;
- 3-5 days after the onset, the rash disappears and leaves no traces on the skin;
- peeling or pigmentation after rubella does not remain.
On examination, the doctor notices the enlarged lymph nodes of such groups: mid-tine, occipital, zadnesheynye.Their size is approximately like a large pea, and they remain so even when the rash descends.
The general condition of the child is slightly impaired, parents can observe lethargy and malaise.The body temperature does not usually exceed 38 ° C and is kept at 37-37.5 ° C.Older children with rubella complain of pain in the joints, muscles, headache.In parallel with the rash, mild conjunctivitis, rhinitis and cough may develop.Most often, when examining the oral cavity, there is a looseness of the tonsils and exanthem on the soft palate mucosa( pale pink spots).
Note: In , in some cases rubella rubella symptoms occur when the signs of the disease are very poorly expressed.In this case, the laboratory diagnosis will help to diagnose correctly.
Diagnosis
Sometimes it is difficult to confirm the diagnosis of "rubella".In some cases, it is confused with scarlet fever or measles.That is why it is important to visit a doctor who will conduct an objective examination.If the pediatrician or infectiologist doubts the correctness of the diagnosis, then additional tests are prescribed.
The rubella examination consists of the following items:
- Inspection.The doctor will notice on the skin of the child a characteristic rash with rubella, which almost instantaneously spreads throughout the body, enlarged lymph nodes and catarrhal phenomena.
- Laboratory tests:
- Urinalysis.There is a large number of white blood cells.
- Blood test.With rubella there is a rise in ESR, a level of monocytes and leukocytes, and sometimes the appearance of plasma cells.
- Immunoenzymatic analysis.His task is to determine the stage of rubella and the presence of antibodies in the blood to her.
Important: doctors prescribe additional studies to differentiate rubella from enterovirus exanthema, measles and allergies to medications.
Complications for rubella
In fact, with rubella complications are quite rare, and they usually occur in children who suffer from immunodeficiency.
Among the possible manifestations of such pathologies are:
- Otitis;
- pneumonia;
- sore throat;
- encephalitis;
- eustachaite;
- male infertility;
- arthritis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- meningoencephalitis;
- sinusitis;
- orchitis.
The cause of complications is a severe rubella, absence of treatment, non-compliance with medical prescriptions, attachment of a secondary bacterial infection against a background of reduced immunity.
Separately identify complications of rubella in pregnancy.The disease mainly affects the fetus, causing various malformations, sometimes - incompatible with life.The mother's body does not suffer from this, but the virus overcomes the placental barrier and provokes spontaneous abortion, fetal malformations.
Treatment of rubella in children

Treatment for rubella is symptomatic, since there is no specific rubella.If there is no critical elevation of body temperature, hospitalization is not required, and the patient is treated at home with the permission of the doctor, but subject to bed rest.
Treatment of rubella includes:
- antibiotics when attaching a secondary bacterial infection;
- vitamin and mineral complexes for the maintenance of the body during the period of illness;
- antihistamines are prescribed if there is severe rash, itching and there is pain syndrome;
- with conjunctivitis apply albucid;
- physiotherapy in the form of UHF and dry heat is prescribed in case of painful and enlarged lymph nodes;
- it is important to maximally limit the load on the child's vision, that is, to minimize the stay in front of the monitor, watching TV, computer games, reading;
- antipyretic is required only in case of exceeding the temperature to the level of 38 ° C, which is extremely rare with rubella;
- from throat pain locally use sprays;
- the stuffy nose is treated by rinsing with saline solutions and using nasal drops;
- phytotherapy is recommended only with the permission of the doctor( raspberry at a temperature, rose hips and calendula for a restorative effect, etc.).
Treatment of congenital rubella in children involves the use of etiotropic agents in the form of recombinant interferon.With her usually appointed Re-afferon, Viferon.If meningoencephalitis develops in parallel, corticosteroid hormones are also shown.Interferon has a powerful antiviral effect and activates reduced immunity.At the cellular level, it increases the phagocytosis of macrophages that successfully fight the virus.Rubella is a systemic viral pathology, therefore it requires the administration of interferon both parenterally and orally up to 3 times a day.This is due to the fact that these drugs penetrate the body at the tissue level and are then rapidly inactivated.
Rubella prophylaxis
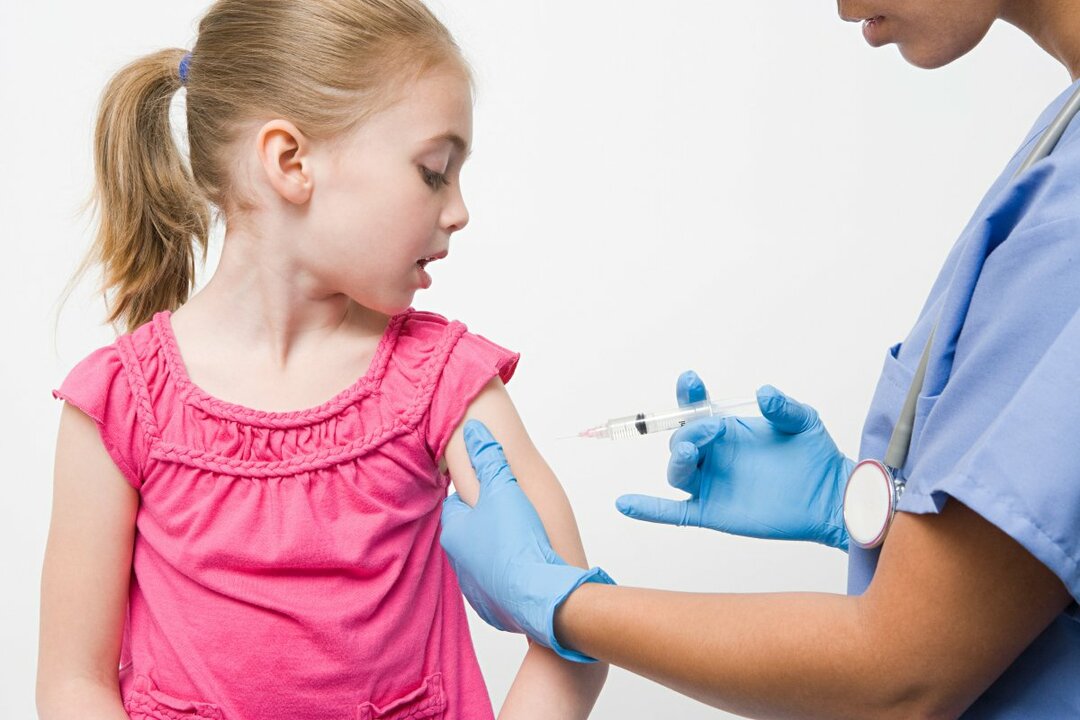 The main prevention of this disease is vaccination.It is necessary to pass it not only to children, but also to those women who reached childbearing age, but did not have rubella before.Especially if they are planning a pregnancy in the near future.To prevent the spread of the virus, a child with rubella should be isolated for up to 7 days after the appearance of rashes.Quarantine in a children's team, which a sick child visited, is not taken.In this case, it is necessary to protect the patient's contact with pregnant women.
The main prevention of this disease is vaccination.It is necessary to pass it not only to children, but also to those women who reached childbearing age, but did not have rubella before.Especially if they are planning a pregnancy in the near future.To prevent the spread of the virus, a child with rubella should be isolated for up to 7 days after the appearance of rashes.Quarantine in a children's team, which a sick child visited, is not taken.In this case, it is necessary to protect the patient's contact with pregnant women.
From rubella vaccine is given to all children according to the vaccination calendar.It is done in the form of intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.Vaccination after 15-20 days forms a stable immunity in the child, which remains active for more than 20 years.
You can get more information about the symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment of rubella by viewing this video review:
Viktorova Julia, obstetrician-gynecologist