Drunkenness and alcoholism: the causes and classification of these conditions

Questions about alcohol consumption sooner or later affect almost everyone.Almost everyone knows that drinking is harmful.Alcohol is a poison that affects primarily the brain, then the rest of the nervous system, heart, liver.Great damage suffers the psyche.
But some doctors and specialists of other professions say that alcohol is harmless in small doses, moreover, even useful.Shops abound in a variety of alcohol.In this case, the streets are full of alcoholics - people who have drunk, have lost everything: work, family, apartment, health. ...The most terrible thing is that among them there are women, teenagers and even children!
Let's try and find out where is the "good", where the "harm" of alcohol.Whether there is a culture of drinking or not, why do some drink without dependence, a little and rarely, while others, after trying, slide into the bottomless pit of loss of health in a few years, and can not rise from the social bottom.
For a start, let's define in terms of alcoholism and alcoholism.Are they synonyms or not?
Contents: What is drunkenness?Why do people start drinking? Classification of drunkenness What is behind the concept of "alcoholism"?Classification of alcoholism Forms of drunkenness Degrees of intoxicationWhat is drunkenness?Who is a man who can be called a drunkard?
In everyday life, a drunkard is considered to be someone who is constantly seen "drunk" and with the smell of alcohol.If not every day, then often.How does the narcology look at this problem?
Note: , despite the fact that the townsfolk consider alcohol consumption to be drunk in significant quantities, most specialists working in this area refer to alcohol drinking as drunkenness.And it does not matter - you drink at least once a day, at least once a year, at least for the first time in your life.That is, took a dose - then he was drinking.But is this a disease?Of course not.Not yet. ... .

Why people start drinking
We recommend reading:The first time the motive is the same for all - imitation.I really want to try what has been forbidden so far, to feel at the "level" of the rest.Especially, the surrounding friends instill the opinion: once you have not tried it means inferior.Under the weight of these desires and suggestions, a man takes his "starter" glass.Those who like the very first dose, units.Most often the beginner does not feel any taste, or pleasant sensations.But after a short time, there is lightness in the body, clarity in my head, it becomes easy and fun at ease.There is a condition called euphoria.And if after it there were no signs of poisoning, then it pulls to repeat. ..
Here it begins: the desire comes a habit, and the habit - the dependence: psychological, and then deeper - physical.
The active ingredient of any alcoholic beverage - ethanol - is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and then comes into contact with the nerve cells of the brain.Thus, alcoholic beverages affect the function of neurochemical brain systems.Thus, the creator of the scientific school of medical and biological problems of narcology, IP Anokhin argues that, as in the case of dependence on nicotine, the formation of alcohol dependence is facilitated by the effect of ethanol on catecholamine, in particular dopamine, mediation in the localization of brain reinforcement systems.In the brain, an "alcohol center" is formed, the impulses of which begin to possess human emotions, moods and desires.Cells of the nervous system do not stand up and die under the influence of alcohol poison, irreversible changes occur. ..
How does this process happen?Are all doomed to alcohol "slavery"?After all, you can also drink "culturally" - use small doses and rarely.
About the causes of alcoholism tells a psychologist, a cognitive psychotherapist, VA.Tsygankov:
Classification of drunkenness
Consider the accepted classification of this phenomenon:
- I group.It includes non-drinkers ( abstinent), or practically non-drinking .The latter include those who drink very little, not more than 2-3 times a year, and then, under the strong pressure of others, without experiencing any pleasant sensations from alcohol and not trying to "repeat".
Some of these people get sick even from a small dose of alcohol, they are categorically negative about alcohol.Individuals encounter complete alcohol intolerance caused by congenital insufficiency of the enzyme - alcohol dehydrogenase , which causes the breakdown of alcohol into the final metabolites - water and carbon dioxide.
- II group - episodic drunkenness of . This includes those who can afford to drink once in two or three months a small amount of alcohol, usually not strong( wine, champagne).Such a person will sit at the table sober and will rise because of him the same.
All that can be achieved with such consumption of alcohol - an easy degree of intoxication( euphoria).Deeper degrees of this group do not like.Once having experienced them, occasionally drinking in every possible way tries to avoid repetition.If there is a desire to experience a more "strong" euphoria, then you can safely refer yourself to the next group.
- III group - situational drunkenness.In this version, they drink more often.The amount of alcohol is growing.Drinks are also becoming stronger, more and more drinkers are beginning to give preference to vodka, cognac, tequila, other highly alcoholic spirits.
Middle degrees of intoxication appear, waiting for the forthcoming alcoholization causes an increased mood, "resistance" to the dose increases.If earlier it was quite enough 100 ml of vodka, now the "degree of comfort" is 300 ml.There is an illusion of health( can drink a lot and not get drunk).
Although in fact it is only a matter of getting used to poison.A person who often consumes alcohol generates an energy surplus, since alcohol is very energy-intensive, as a result of which the food is stored in the "depot" and the person recovers.Paralysis of the vessels of the face gives an external healthy "pink" look to the drinker.
But this is not a disease yet.It's not the norm, it's not alcoholism either.Just situational drunkenness.What happens next?If a person does not change his mind, and does not say to himself: "enough", he goes to the next group.
- IV group - malicious drunkenness.The dose for one alcoholization increases to 500 ml.Excesses with such an amount are already quite frequent, up to 2-3 times a week.Between them there may be "light" intervals of sobriety, or acceptance of small doses - 100-150 ml, as well as the use of lighter beer and wine.
It should be noted that those who drink vodka are more skeptical about wine.In the IV group, the phase of "euphoria" - an upbeat mood, talkability, a sense of complete comfort and carelessness( for the sake of which they try to reach intoxication) lasts no longer 2-3 hours, as in the first groups, but 6-8 hours.The gag reflex is extinguished.Looking at people who belong to a malicious group, no one is wrong anymore.It's about a drunkard.
There are family and work conflicts, a person becomes unnecessary, cheeky, in his behavior more often slip traits of rudeness, rudeness, flat humor.This is all a consequence of brain damage.
But this is not a disease.In this stage, the drinker can still stop himself and begin to lead a completely sober life or go back to the 3 or 2 group.But if it can not already, then, most likely, we are talking about the disease - alcoholism .
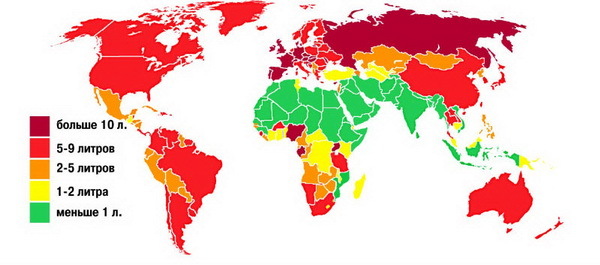
World's per capita alcohol consumption statistics in liters
Note: what is the difference between alcoholism and alcoholism?The main thing - a drunkard can stop and "roll back" to previous stages, but the alcoholic is no more.He has only two ways - to drink or not to drink at all, otherwise the development and progression of the disease - alcoholism is inevitable.
What lies behind the concept of "alcoholism"?
What is this pathology?Define it:
Alcoholism is a biosocial, mental illness that occurs with chronic alcohol poisoning, signs of addiction and a pathological addiction to alcohol.Over time, there is a degradation of the drinker and the development of severe concomitant diseases.
In medicine, the term "chronic alcoholism" is applied, which was introduced in practice in the XIX century by a doctor from Sweden, Magnus Guss.
In everyday life, the term "alcoholism" is used in a broader sense, combining it with drunkenness.
Classification of alcoholism
In its classical development, alcoholism goes through three stages:
- Initial - lasting from 1 to 6 years.It can be reduced to a year or to be a lifetime, with a slow-progressing current.
- Deployed clinical manifestations.At this stage, most alcoholics are located, one lasts the longest period, an average of 10-12 years.
- The ultimate - lasting about 5-7 years.
More detailed information on the stages of alcoholism you will get by viewing the video review of the psychologist, cognitive psychotherapist Vladimir Tsygankov:
Forms of drunkenness
Now our task is to get to know the forms of drunkenness for alcoholism.It's about ways of drinking alcohol, which can occur at all stages of the disease.
Specialists identify:
- One-day drunkenness with hangover syndrome.The patient drinks a large dose of alcohol for one day.In the morning, experiencing abstinence, he pohmelyaetsya, and then for some time he does not drink at all.This form is most common in the 1st stage of alcoholism.
- Non-regular drunkenness with hangover syndrome.Alcoholic drinks for several days in a row, with a severe degree of intoxication is not achieved.But in the morning it takes "to get drunk".The working capacity is maintained.This variant of alcoholization is also inherent in stage 1.
-
 Constant drunkenness.With this form, the addicted person drinks daily for a long time.Necessarily there is a hangover.Resistance to alcohol is growing steadily.This type of abuse can occur at all stages of alcoholism.
Constant drunkenness.With this form, the addicted person drinks daily for a long time.Necessarily there is a hangover.Resistance to alcohol is growing steadily.This type of abuse can occur at all stages of alcoholism. - Drunken drunkenness.One of the most severe forms of alcoholism.The binge begins with a period of sobriety.The patient is completely excluded from life and drinks around the clock.Drinks day and night, almost without eating.Usually he is at home and goes outside for just one more dose.The binge can last for several days and weeks, until a period of complete exhaustion occurs, a gag reflex to alcohol reappears.The way out of the binge is very difficult, at this very moment the most serious complications of alcoholism occur - psychoses.Then comes the period of sobriety, which can last several days, often weeks or even months.
Note: should not confuse the true binges and pseudo-snags , the easier cases when alcoholics drink while they have the funds, then live soberly.This option is often found in factory workers who were able to consume alcohol twice a month - during the pay and advance payments.
- Intermittent drunkenness is the heaviest type of alcohol use, characteristic of a malignant course of the disease.With this form of alcoholism, drunkards are drunk on constant drinking.
Degrees of intoxication
Both in drinking and alcoholism, three degrees of intoxication are distinguished:
- I degree( light).External signs of intoxication are hardly noticeable.There is an improved mood, loquacity, relaxedness, ease.But already with an easy degree, inhibited reactions are observed.Alcohol in the blood 0,5 - 1,5;
- II degree of intoxication( medium).Observed in a person with pronounced euphoria, or vice versa - malice, depression, inadequate behavior, attacks of aggression, complete disinhibition, excessive self-esteem, self-praise.Externally - a red face, speech and gait disturbance, uncoordinated movements.From drunk spreads a strong smell of alcohol.The concentration of alcohol is from 1.5 to 2.5.The content above these figures indicates a strong intoxication.
- III degree( heavy).With this degree of intoxication, the drunkard can not maintain equilibrium when walking, speech is difficult and indistinct, there is a violation of orientation, unrecognized people, stunned.Gradually, the patient develops a narcotic sleep, which can go into a coma and end with death.The blood alcohol content is 3-5.Above these values, poisoning is deadly.
A fact that indicates that 80% of young people up to 16-18 years of age have already been associated with alcohol is a sad fact.Consumption among young people of beer and low-alcohol drinks is growing.
Based on what data can you understand that the patient is no longer just a drunkard, but an alcoholic?The answer to this question will be found in the clinical manifestations of the stages of alcoholism, which we will discuss in the next article.
Important: can be diagnosed with alcoholism only by a psychiatrist-narcologist and no one else.
Alexander Lotin, narcologist physician