Foodborne diseases: symptoms and treatment
 Foodborne toxicosis is an acute gastrointestinal disease that occurs after eating foods containing toxins from microorganisms.Infection by the bacteria themselves in this pathology may not occur, so it is not always possible for doctors to determine which infection caused vomiting and diarrhea.
Foodborne toxicosis is an acute gastrointestinal disease that occurs after eating foods containing toxins from microorganisms.Infection by the bacteria themselves in this pathology may not occur, so it is not always possible for doctors to determine which infection caused vomiting and diarrhea.
For foodborne toxic infections is very characteristic development of pathological manifestations at once in several people, for example, after a festive feast or a visit to their catering establishments.In this case, the intensity of symptoms may differ for persons who eat the same food.It all depends on how many toxins were "eaten", as well as on the state of the digestive tract of patients.
Table of contents: Causes of foodborne toxic infections What happens in the body?Symptoms of Foodborne Diseases Treatment of Foodborne DiseasesCauses of Foodborne Diseases
Recommended Reading:There are quite a few bacteria that are able to produce toxins outside the human body.These substances can withstand temperature changes and persist for a long time in a nutrient medium, which are usually
dairy, meat products, dishes with mayonnaise, as well as cream confectionery.To microorganisms whose toxins cause the development of foodborne diseases:
-
 Proteas.
Proteas. - Clostridia.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Klebsiella.
- Pseudomonas.
- Enterobacteria, etc.
Most of these microorganisms are widely distributed in nature and live in the intestines of humans and animals, therefore it is not difficult to get into food for potentially dangerous bacteria, for example if a person who cooks forgets about hygienic and sanitaryRules.In addition, improper storage of food plays a role in the contamination of food by microorganisms and their active development( when ready meals are stored with raw foods or the temperature regime is not respected).It should be noted that the taste of food containing toxins, as a rule, does not change, that is, the taste does not always manage to recognize the danger.
What happens in the body?
 After entering the gastrointestinal tract, the toxins of bacteria begin to act on the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the digestive system.And the features of this action are determined by the properties of toxins: they can be enterotoxic and cytotoxic( the latter cause more severe forms of the disease).So, due to the influence on the intestinal mucosa of enterotoxins, the secretion of salts and fluid in the intestinal lumen increases, which causes vomiting, profuse diarrhea and dehydration.After the cessation of the entry into the body of poisonous substances and exfoliation of the initially affected epithelium, the stool is normalized.
After entering the gastrointestinal tract, the toxins of bacteria begin to act on the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the digestive system.And the features of this action are determined by the properties of toxins: they can be enterotoxic and cytotoxic( the latter cause more severe forms of the disease).So, due to the influence on the intestinal mucosa of enterotoxins, the secretion of salts and fluid in the intestinal lumen increases, which causes vomiting, profuse diarrhea and dehydration.After the cessation of the entry into the body of poisonous substances and exfoliation of the initially affected epithelium, the stool is normalized.
But the mechanism of action of cytotoxins on the intestinal epithelium is somewhat different.These substances not only cause the secretion of water in the lumen of the intestine, but also increase the permeability of the intestinal wall, due to which they are actively absorbed into the blood, penetrate into other organs and provoke more intoxication.In addition, cytotoxins damage the microcirculatory bed of the intestinal wall and thus lead to inflammatory changes in the mucosa.Restoration of the digestive tract after such a lesion, as a rule, is more prolonged.
Symptoms of foodborne infections
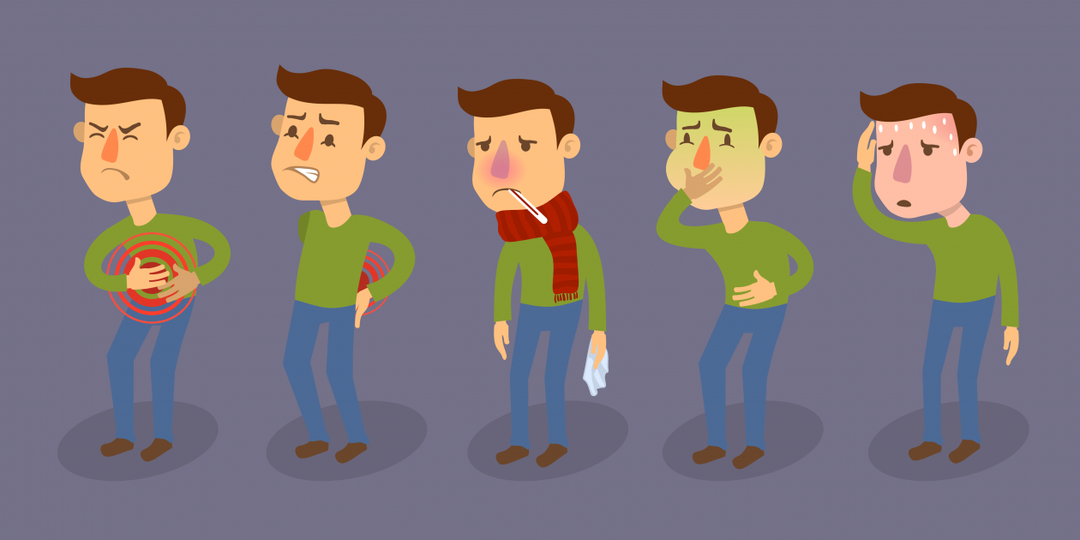
The first symptoms of foodborne toxic infections occur only a few hours after eating contaminated food( rarely the incubation period increases to a day). The patient appears:
- Hyperthermia( increased body temperature).
- Nausea, vomiting, which brings relief.
- Diarrhea( can be up to 10-15 times a day with cramping pains).
- Severe weakness and headache.

In addition, with profuse vomiting and diarrhea, signs of dehydration develop:
- Thirst.
- The slowness of the voice.
- Dryness of the skin.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Rare urination( with very concentrated urine).
- In young children, the fall of the temples.
- Convulsions.
Treatment of foodborne diseases
The main goals of treatment of foodborne disease are the rapid removal of toxins from the body and restoration of loss of fluid and salts. For this, the following activities are carried out:
- Rinsing the stomach with boiled water at room temperature or with a weak soda solution.
- Sorbents Sorbex, Smekta, Enterosgel and others are assigned.
- The means for rehydration are used - Regidron, Toastrol, Orsol and others.The rehydration solution can be prepared independently from 1 liter of boiled warm water, 3 grams of ordinary rock salt and 18 grams of granulated sugar.
Antibiotics and intestinal antiseptics for poisoning with microbial toxins, as a rule, do not apply.
It is also important to remember that the means that stop diarrhea( for example, Loperamide), with foodborne toxic infections are strictly contraindicated.Toxic substances are gradually eliminated from the body with feces, so the delay of defecation can provoke an even more intoxication of the body.
In severe cases, patients with foodborne toxicosis are hospitalized, and already in a medical facility, they undergo parenteral rehydration and detoxification, and other symptomatic treatment is performed depending on the clinical picture.
Diet
Compliance with diet for foodborne infections is no less important than drug treatment. With the help of proper nutrition, you can provide the best conditions for the recovery of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and normalization of digestion processes.
We recommend to read:In the first days of illness the food should be as gentle as possible mechanically, chemically and thermally.That is, ready dishes should be made as homogeneous as possible, not sharp, not acidic, medium temperature( warm).With regard to the composition of the diet, then it should predominate protein food, fats and carbohydrates - in the minimum amount.Thus, the best dishes for patients with food poisoning are low-fat soups with mashed meat and cereals, low-fat cottage cheese, mucous porridges, boiled fish of low-fat varieties in crushed form, steam omelettes.
Prevention of foodborne diseases

In order not to become a victim of foodborne infection, it is necessary:
- Always and everywhere wash hands( especially before meals).If this is not possible, be sure to have wet wipes.
- Do not eat past-due products, even if in appearance they are quite edible.
- Do not snack "stall" food.And in general, avoid various roadside catering establishments.
- Purchase dairy products and sausages in hermetically sealed, labeled packages.
- Do not buy ready-made salads in stores.
- Do not feast on cakes and pastries in unchecked cafes and confectioneries, especially not to buy such products from your hands.
- Store products at the correct temperature.
- Thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits before use.
In addition, it is worth remembering that even the freshest milk, cottage cheese or sour cream from the market is potentially dangerous products, which should be heat-treated before consumption.A sausage, cutlets, sandwiches, cooked at home with all the rules, on the beach or picnic during the hot season can very quickly become an excellent environment for the development of bacteria and the release of toxins, if not take care of the portable refrigerator.
When traveling to the regions with an unfavorable sanitary and hygienic situation, it is desirable and at all to eat only freshly prepared hot dishes and drink with their own hand boiled or disinfected water.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist