Enterovirus infection: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Enterovirus infection is a group of acute diseases of the digestive tract that are caused by RNA-containing pathogens of the genus Enterovirus.
Nowadays, outbreaks of enterovirus infection are increasing in many countries of the world.The danger of diseases of this group is that the clinical symptoms can be the most diverse.In most cases, there is a mild course characterized by mild discomfort, but serious complications can occur, including severe respiratory and central nervous system damage, as well as kidney and digestive tract.
Contents: Pathogens and their transmission routes Symptoms of enterovirus infection Signs of enterovirus infection in children Diagnosis Treatment of enterovirus infectionPathogens and their transmission
The vast majority of RNA-containing enteroviruses are pathogenic to humans.
To date, more than 100 types of pathogens have been identified, including:
- EDC viruses;
- Coxsackie viruses( types A and B);
- agents of poliomyelitis( poliovirus);
- unclassified enterovirus.
Pathogens are ubiquitous.They are characterized by a high degree of stability in the external environment, carry freezing, as well as treatment with antiseptics such as 70% ethanol, lysol and ether.Enteroviruses die quickly during heat treatment( do not tolerate heating to 50 ° C), drying and exposure to formaldehyde or chlorine-containing disinfectants.
Natural reservoirs for causative agents are water bodies, soil, some food products, as well as the human body.
Note : in faeces, enteroviruses retain their viability for up to six months.
In most cases, the source of the pathogen is a sick person or a virus carrier, which may have absolutely no clinical signs of enterovirus infection.According to medical statistics, up to 46% of people in some countries may be carriers of pathogens.

Main transmission routes of infection:
- fecal-oral( with a low level of hygiene);
- contact-household( through seeded items);
- airborne( if the virus is present in the organs of the respiratory system);
- vertical transmission pathway( from an infected pregnant woman to a child);
- water( when bathing in contaminated reservoirs and watering plants with wastewater).
Note : cases of infection with enteroviruses have been documented, even through water in coolers.
For this group of acute diseases seasonal outbreaks are characteristic during the warm season( summer-autumn period).Susceptibility to enterovirus in humans is very high, but after a long-term infection( up to several years) type-specific immunity persists.
Symptoms of enterovirus infection
Enterovirus infection in adults and children can cause a number of pathologies characterized by different degrees of inflammation.
The most severe pathologies include:
- myocardial inflammation( cardiac muscle);
- pericarditis( inflammation of the pericardial sac);
- hepatitis( anicteric);
- Serous meningitis( damage to the soft membranes of the brain);
- Acute paralysis;
- kidney damage;
- neonatal sepsis.

Less dangerous manifestations:
- three-day fever( incl. With skin rashes);
- gastroenteritis( inflammation of the digestive tract);
- herpetic sore throat;
- lymphadenopathy;
- polyradiculoneuropathy;
- conjunctival inflammation;
- inflammation of the choroid of the eye;
- lesion of the optic nerve;
- Vesicular pharyngitis.
Note : when entering the enterovirus D68, bronchopulmonary obstruction often develops.A characteristic symptom is a severe cough.
Severe complications rarely develop in adult patients with good immunity.They are typical for people with reduced resistance of the body - children( especially - early age) and those suffering from serious diseases( tuberculosis, HIV, malignant tumors).
Note : the variety of clinical manifestations is due to the specific affinity of enteroviruses for many tissues of the human body.
The most typical clinical signs of enterovirus infection in children and adults:
-
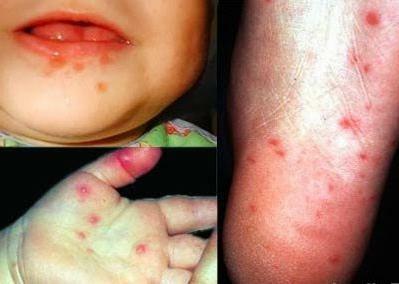 symptoms of general intoxication of the body;
symptoms of general intoxication of the body; - hyperthermia( increase in body temperature);
- catarrhal symptoms( inflammation of the mucous larynx and pharynx);
- abdominal symptoms( abdominal pain, digestive disorders);
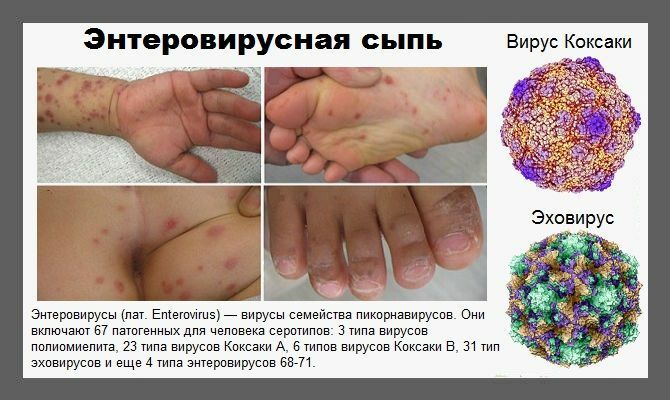
- skin rash( polymorphic exanthema).
The duration of the incubation period for enterovirus infections in most cases is from 2 days to 1 week.
Most often when the infectious agents enter the organism of a given variety, a person develops ARVI.
Symptoms of the catarrhal form of enterovirus infection:
- runny nose;
- cough( dry and rare);
- fever( usually within subfebrile values);
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the throat;
- digestive disorders( usually not very significant).
As a rule, a person recovers within a week from the onset of the disease.
Symptoms of enterovirus fever:
- febrile reaction within 3 days of onset of the disease;
- moderate signs of general intoxication;
- skin rashes( not always);
- worsening of general health( mild or moderate).
Note : enteroviral fever is also called a "small disease", as the symptoms persist for a short while and their severity is low.This form of pathology is relatively rarely diagnosed, since most patients do not even seek medical help.
Symptoms of the gastroenteric form:
-
 pain in the abdominal region( more often - on the right);
pain in the abdominal region( more often - on the right); - temperature increase;
- general weakness and increased fatigue;
- deterioration or lack of appetite;
- increased gassing in the intestine;
- watery diarrhea( up to 10 times a day);
- nausea;
- vomiting.
In this form of enterovirus infection, children may have symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection( catarrhal manifestations).In young children, the disease can last up to 2 weeks or more.
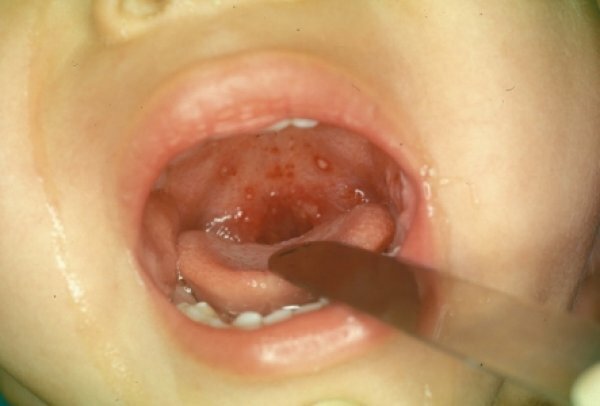 An indication of herpengina against the background of enterovirus infection is the formation of red papules on the mucous membranes.They are localized in the area of hard palate, tongue and arch.These small rashes quickly transformed into vesicles, which after 2-3 open with the formation of erosion or gradually resolve.Gerpangina is also characterized by an increase and soreness of the submaxillary and cervical lymph nodes, as well as hypersalivation( drooling).
An indication of herpengina against the background of enterovirus infection is the formation of red papules on the mucous membranes.They are localized in the area of hard palate, tongue and arch.These small rashes quickly transformed into vesicles, which after 2-3 open with the formation of erosion or gradually resolve.Gerpangina is also characterized by an increase and soreness of the submaxillary and cervical lymph nodes, as well as hypersalivation( drooling).
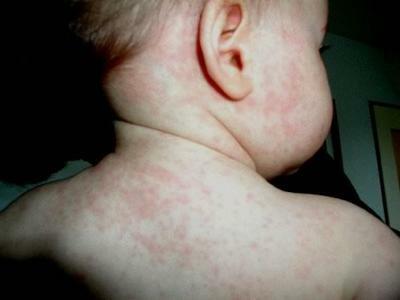 The main clinical manifestation of enterovirus exanthema is the appearance on the skin of patients of rashes in the form of spots and( or) small bubbles of pink color.In most cases, skin cells disappear after 2-3 days;On the place of their resolution there is peeling of the skin, and the upper layers come off in large fragments.
The main clinical manifestation of enterovirus exanthema is the appearance on the skin of patients of rashes in the form of spots and( or) small bubbles of pink color.In most cases, skin cells disappear after 2-3 days;On the place of their resolution there is peeling of the skin, and the upper layers come off in large fragments.
Important : Exanthema can be diagnosed in parallel with meningeal symptoms.
Symptoms of serous meningitis in the presence of enterovirus infection:
- photophobia( photophobia);
- increased sensitivity to sounds;
- severe headache when bringing the chin to the chest;
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- psychoemotional arousal( not always);
- high body temperature;
- convulsions.
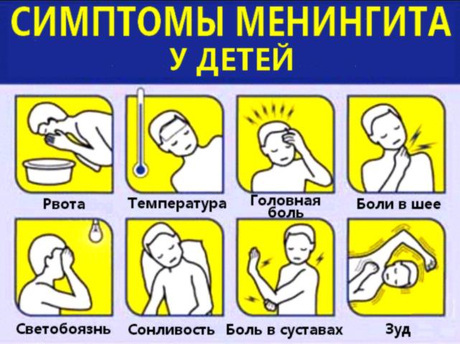
Oculomotor disorders, impaired consciousness, muscle pain and increased tendon reflexes are also possible.
Meningeal symptoms persist from 2 days to one and a half weeks.In cerebrospinal fluid, the virus can be detected within 2-3 weeks.
Symptoms of enterovirus conjunctivitis:
- pain in the eyes;
- tear;
- photophobia;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- puffiness of the eyelids;
- copious discharge( serous or purulent).
Note : Enterovirus conjunctivitis first affects one eye, but soon the inflammatory process spreads to the second.
Signs of enterovirus infection in children
For children( especially for children under the age of 3 years), the acute onset of the disease is characteristic.
The most frequent clinical manifestations of enterovirus infection are:
- sleep disorders;
- fever;
- chills;
- diarrhea;
- catarrhal symptoms;
- myalgia;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- exanthema and( or) angina( not always).
Diagnosis
Currently, the causative agent of enterovirus infection can be detected in one of four ways:
-
 The immunochemical method is based on the determination of characteristic antigens in the patient's blood.
The immunochemical method is based on the determination of characteristic antigens in the patient's blood. - Serological diagnostic method allows to determine the infection by the presence of immunoglobulin markers.
- Molecular biological methods are based on the detection of fragments of characteristic viral RNA.
- The virological method involves the detection of enterovirus in the patient's biological fluids, faeces or washings from the mucous membranes.
Changes in the general blood test:
- minor leukocytosis;
- hyperleukocytosis( rarely);
- neutrophilia( at an early stage);
- eosinophilia and lymphocytosis( as the disease progresses).
Important: establishing the presence of the virus in the body is not an indisputable proof that this particular pathogen provoked the disease.There is often asymptomatic carriage.The diagnostic criterion is an increase in the number of antibodies( in particular - immunoglobulins A and M) by 4 or more times!
Differential diagnosis
Herpes sore throat, which is caused by the Coxsackie virus, should be differentiated from herpes simplex and oral candidiasis( fungal stomatitis).Serous meningitis caused by infection with enteroviruses should be distinguished from the meningococcal etiology of the meningococcal etiology.
For gastroenteric symptoms, other intestinal infections should be excluded.Exanthemum is important to differentiate from rashes on the background of rubella, scarlet fever and hypersensitivity reactions( allergic urticaria).
Treatment of enterovirus infection
 No etiotropic( ie, specific) treatment methods have been developed to date.
No etiotropic( ie, specific) treatment methods have been developed to date.
Treatment of enterovirus infection in adults involves the conduct of detoxification and symptomatic therapy.Therapeutic tactics are determined individually for each patient, depending on the nature, localization and severity of the pathological process.Patients on indications are given antihistamines, antiemetics, analgesics and antispasmodics.
In the treatment of enterovirus infection in children, rehydration therapy, that is, the elimination of dehydration of the body and the restoration of electrolyte balance, is often on the foreground.To this end, saline solutions and 5% glucose are either given orally or administered by intravenous infusions.Children are also given detoxification therapy and, if necessary, are given antipyretics( antipyretic drugs).
To combat viruses, intranasal administration of a solution of leukocyte interferon is indicated.
If complications occur due to the attachment of a secondary bacterial infection, the patient is given course antibiotic therapy.Lesions of the nervous system often require hormonal therapy with corticosteroids.

You can see the symptoms of enterovirus infection, its manifestations, methods of treatment of diseases and their prevention by watching this video review:
Konev Alexander, the therapist