Hydrothorax: causes, symptoms, principles of treatment
 Hydrotorax is the presence of fluid in one or both of the pleural cavities.Hydrotorax is often confused with exudative pleurisy - inflammation of the pleural sheets, which is accompanied by the formation of fluid.But with hydrothorax, if the infection has not joined, the formed effusion has a non-inflammatory character.In addition, with exudative pleurisy, the amount of fluid can be negligible and does not attract a full hydrothorax.
Hydrotorax is the presence of fluid in one or both of the pleural cavities.Hydrotorax is often confused with exudative pleurisy - inflammation of the pleural sheets, which is accompanied by the formation of fluid.But with hydrothorax, if the infection has not joined, the formed effusion has a non-inflammatory character.In addition, with exudative pleurisy, the amount of fluid can be negligible and does not attract a full hydrothorax.
Hydrothorax is also called chest water drop.
Contents:Hydrotarax of the lung: causes, mechanisms of development
Pleural cavity is a gap between the pleural sheets - one of them lining the thorax from the inside( parietal pleura), the other covers the lungs( visceral pleura).Normally, the pleural cavity is not absolutely dry - some amount of secretions is formed, so that during the respiratory movements between the pleural sheets of the chest and lung there is no friction.But this amount of pleural secretion is so small( in addition, the system of reverse absorption works) that physiological hydrothorax is not singled out as a separate concept.
The most common reasons why fluid can accumulate in the pleural cavities:
- heart failure at the stage when the compensatory mechanisms no longer work and stagnation occurs in the large circulation;
-
 various diseases of the kidneys - primarily those in which the kidney glomeruli are affected and the nephrotic syndrome develops - massive swelling, the presence of protein in the urine( proteinuria) and a decrease in the protein level in the blood( hypoproteinemia).Most often, hydrothorax is observed in a renal pathology such as glomerulonephritis, and in amyloidosis of the kidneys( accumulation of amyloid - a substance that is not normally observed in the body);
various diseases of the kidneys - primarily those in which the kidney glomeruli are affected and the nephrotic syndrome develops - massive swelling, the presence of protein in the urine( proteinuria) and a decrease in the protein level in the blood( hypoproteinemia).Most often, hydrothorax is observed in a renal pathology such as glomerulonephritis, and in amyloidosis of the kidneys( accumulation of amyloid - a substance that is not normally observed in the body); - cirrhosis of the liver - it also exhibits stagnation in the circulatory system;
- myxedema - a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones( extreme degree of hypothyroidism), because of which practically all the tissues accumulate fluid, as a consequence - develop massive swelling;
- large tumors that are localized in the mediastinum( an enclosed space bounded by the sternum, spine and both lungs) - they press on large veins( primarily hollow and brachiocephalic), thereby causing stagnant phenomena in them and provoking effusion of fluid inNearby structures( including, and pleural cavities);
- sometimes - alimentary( associated with malnutrition or malnutrition), dystrophy.In this case, the effusion to the pleural cavity is closely related to the lack of vitamins B and C, as well as a worsening of lymph drainage.
All the inconveniences and problems that provoke hydrothorax, are mechanical: accumulating in the pleural cavities, the liquid begins to press on the lung tissue, and then on the mediastinum organs .
Due to gravity, due to which the liquid rushes to the lower point of the pleural cavities, the fluid pressure initially extends to the lower parts of the lungs, which are less involved in the act of breathing( therefore the clinical symptoms are either not observed or not expressed).With a further increase in the amount of fluid in the pleural cavities, which are a closed space, the parenchyma of the remaining parts of the lungs is gradually squeezed, and then the mediastinum - down to its displacement to the healthy side( if hydrothorax is unilateral).
Signs of lung hydrotorax
Hydrotorax in most cases develops gradually - a few days, rarely several weeks. As the amount of fluid increases, the following clinical picture appears:
-
 has a feeling of heaviness in the chest.The feeling of discomfort in the chest decreases in the prone position on the diseased side.If the amount of liquid increases even more, the patient tries to be in a semi-sitting position( the liquid rushes to the lower parts of the pleural cavity and does not press on the parenchyma of the lungs or presses much less);
has a feeling of heaviness in the chest.The feeling of discomfort in the chest decreases in the prone position on the diseased side.If the amount of liquid increases even more, the patient tries to be in a semi-sitting position( the liquid rushes to the lower parts of the pleural cavity and does not press on the parenchyma of the lungs or presses much less); - there is a subjective feeling that less air enters the lungs;
- the patient begins to breathe more often and deeper - this does not always relieve him of the feeling of lack of air;
- cyanosis( cyanosis) of the skin and visible mucous membranes appear at later stages, therefore at the initial stages of the hydrothorax, the examination of the patient will not be informative.Cyanosis is due to deterioration in lung ventilation and an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood;
- due to the fact that this is a non-inflammatory process, the body temperature is not increased - in some cases even its decrease can be observed.
If the fluid has accumulated a lot, it interferes with the mobility of the chest, provokes the lagging of the affected half in the act of breathing and causes the intercostal spaces to become smoothed and then bulging - this is visible when the patient is examined.
Hydrotorax is often accompanied by:
- hydropericardium( presence of fluid in the pericardial cavity);
- ascites( accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity).
In these cases, in addition to the symptoms on the part of the respiratory system, the following symptoms will appear:
- from the heart; chest pain of pressing character; fast fatigue; increased dyspnea; cardiac dysfunction( determined by ECG);
- from the abdominal cavity - a feeling of raspryaniya in the stomach, pressing and aching not too intense pain, heartburn, growing nausea, often resulting in vomiting, bulging tissue in the navel, bloating and changing the shape of the abdomen,( in the lying position of the patient, he spread out,In the sessile - hangs downwards), a pronounced venous network on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall.
There have been cases when hydrothorax even developed first, but was less pronounced than the accompanying hydropericardium and ascites, and only a medical analysis allowed to establish the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity.
Possible complications
The main immediate complication of hydrothorax is acute respiratory failure. It arises from the compression of the pulmonary tissue by the fluid, more and more accumulating in the pleural cavity, which is too much for the pleural sheets to absorb.
In untreated hydrothorax, severe respiratory failure often develops during the first week after the fluid accumulates in the pleural cavities.With increased fluid production( due to severe diseases leading to hydrothorax, or congenital features of pleural sheets), respiratory failure may develop in the first days after the onset of hydrothorax.
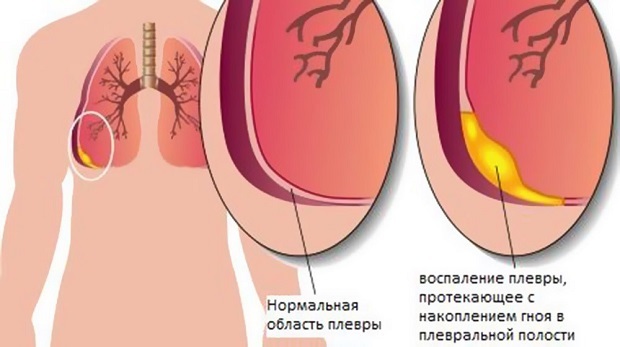
If an infection has joined, hydrothorax may be complicated by pleural empyema - a diffuse purulent lesion of pleural sheets.
Diagnostics
Complaints and changes in appearance of the patient are not specific for the pneumothorax, they can be observed in other types of respiratory pathology.Therefore, for the detection of fluid in the pleural cavity, a physical examination of the patient( palpation, tapping with fingers and listening to a phonendoscope), and additional instrumental diagnostic methods are necessary.
Because of the accumulation of fluid, the embossing of tissues in intercostal spaces is felt.When tapping on the chest, the sound becomes deaf( normally, when tapping objects with cavities it is characteristic, as if knocking on a box or a drum).When listening, the doctor will hear a weakening of the breath, as the liquid presses on the lungs and does not allow them to straighten out normally. In more severe cases( with a started hydrothorax or atypical rapid increase in the amount of fluid), the lung may not breathe at all because it does not spread in the place of fluid accumulation.
To confirm the diagnosis of hydrothorax, use such instrumental methods of examination of the chest as:
- fluoroscopy and igraphy;
- ultrasound examination;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Radiography is performed in a vertical and horizontal position - the diagnosis of the hydrothorax is confirmed by the fact that the uniform darkening in the image caused by the liquid is in the lowest parts of the pleural cavities, and when the position of the body changes, it moves to the lower point.
Computed tomography is a more accurate method that, in addition to detecting free fluid in the pleural cavities, will help to identify the reasons for which it was formed:
- tumor of the mediastinum;
- enlarged lymph nodes that press on the veins, worsening the outflow and promoting the accumulation of
fluid and so on.
Ultrasound examination is used for the purposeful examination of pleural cavities of . It not only reveals effusion in the pleural cavities - thanks to it, it is possible to more accurately determine the volume of fluid.
MRI of thoracic organs allows to reveal with high accuracy the changes in the thorax in case of confusion in the diagnosis of .
Classical laboratory methods for hydrothorax are not determinative - they play an auxiliary role to clarify the causes of hydrothorax:
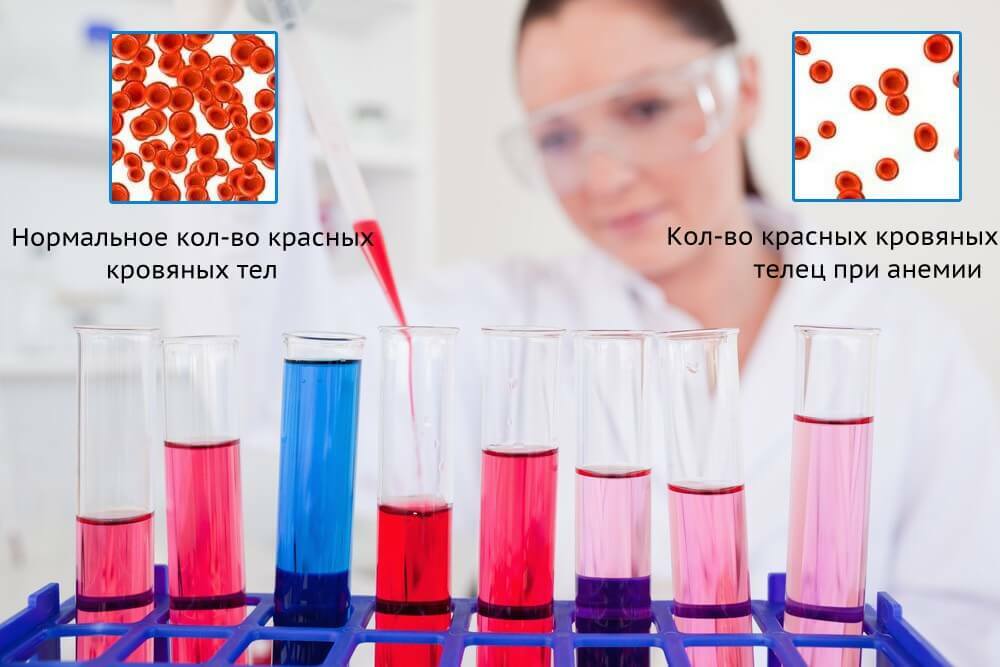
- , general blood test parameters may worsen in diseases of kidneys that provoked hydrothorax and mediastinal tumors - such diseases are confirmed by an increase in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentationESR, or ROE) and manifestations of anemia( decrease in the number of erythrocytes and hemoglobin);

- changes in general urine analysis with hydrothorax are observed if it is caused by kidney diseases that significantly impair their performance.This is manifested by the release of a large amount of protein in the urine, the detection of erythrocytes, leukocytes and specific formations-cylinders in the urine, as well as an increase in the relative density of urine;
- The expanded( biochemical) blood test worsens with pneumothorax, triggered by cirrhosis, kidney disease, or alimentary dystrophy.The main changes that can be detected are a decrease in the amount of protein in the blood, an increase in the level of nitrogenous slags, an increase in the amount of bilirubin and alanine aminotransferase.
Higher values for hydrothorax have:
- puncture of the pleural cavity and examination of the resulting fluid;
- Rivolt test, which helps to determine if fluid has formed in the pleural cavity due to inflammation or not;
- cytological examination( microscopic examination, performed to identify cells that are normal in the pleural cavity and on pleural sheets do not occur);
- bacteriological examination for the presence of microorganisms.
If suspicion of hydrothorax puncture of the pleural cavity is performed, not only to confirm the presence of effusion in the cavity, but also for laboratory testing of the fluid in order to clarify the diagnosis of . It should be clarified that this fluid is a transudate that is noninflammatory in nature, or exudate formed in inflammatory processes.This is important for further treatment tactics. The transudate extracted from the pleural cavity with the classical hydrothorax has the following characteristics:
- is a clear liquid;
- in color light yellow( in some cases slightly light greenish);
- has an alkaline reaction;
- without flakes, sediment and impurities.Sometimes the transudate has a bloody impurity, but this should not frighten the patient who undergoes puncture under local anesthesia, which means that he observes the process - the presence of blood is due to the wounding of small vessels when the puncture needle is punctured by the chest wall.
Rivolt test - determination of the presence of protein in the punctate( fluid obtained by puncture), which is carried out with the help of ordinary acetic acid.When it is added, the liquid formed by the classical hydrothorax does not grow turbid.If this is an inflammatory exudate, then when the liquid and acetic acid are mixed, turbidity is formed in the form of a cloud.
 Cytological examination of the effusion formed in the pleural cavity is necessary to distinguish hydrothorax from exudative pleurisy due to a tumor.In the tumor process, atypical cells are detected.
Cytological examination of the effusion formed in the pleural cavity is necessary to distinguish hydrothorax from exudative pleurisy due to a tumor.In the tumor process, atypical cells are detected.
Bacteriological examination of pleural effusion is primarily necessary to exclude pleural damage in tuberculosis.The liquid is plated on a nutrient medium and it is observed whether there is a characteristic growth of the colonies.
Treatment of lung hydrothorax
For the treatment of hydrothorax, the following methods are used:
- conservative( non-invasive - that is, without implantation into the pleural cavity);
- invasive is a pleural puncture.
The basis for the treatment of hydrothorax is conservative methods aimed at curing the diseases that provoked it . It is necessary to understand that should not simply rid the patient of hydrothorax, but also cure the cause of its appearance .If, with cirrhosis, glomerulonephritis or other diseases that provoke hydrothorax, the patient will extract the fluid with regular pleural punctures, thereby draining the pleural cavity, but doing nothing to cure provocative diseases - the effusion will still be produced, the effect of pleural punctureWill be short-lived. Often, with properly selected conservative therapy and a small amount of fluid in the pleural cavity, it disappears due to back absorption - a pleural puncture may not be needed.
For heart failure that provoked hydrothorax, adhere to the following tactics:
- the patient should optimize his work, physical activity and rest, avoid psycho-emotional factors leading to stress, normalize sleep;
- he should adhere to the diet number 10 or 10a - it implies a restriction of the intake of liquids and table salt, as well as fractional meals( it is necessary to take food in small portions up to 5-6 times a day);
- is prescribed medication.
At the heart of the medical treatment of heart failure, which led to the appearance of hydrothorax, is the unloading of the circulatory system , so that the blood does not stagnate, and effusion in the pleural cavity does not form . The following medicines are used:
-
 drugs that enhance the weakened contractility of the heart muscle( cardiac glycosides and β-adrenoreceptor stimulants);
drugs that enhance the weakened contractility of the heart muscle( cardiac glycosides and β-adrenoreceptor stimulants); - means that reduce the load on the muscle of the left ventricle( these include vasodilator drugs that can be venous, arterial or mixed, as well as ACE inhibitors( drugs with oppressive effect) that, in addition to cardiac, treat and kidney failure -Such a double effect can be actual with hydrothorax;)
- is a diuretic with the help of which excess fluid is excreted from the body( inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase, diuretics with potassium-sparing action and other timesOf diuretics).
Treatment regimen for hydrothorax caused by kidney disease( especially in the presence of nephrotic syndrome):
- bed rest( it promotes urine production);
- diet number 7, which foresees a strict restriction on the intake of table salt, and with edematic syndrome - its complete exclusion;
- control of the drunk liquid( its amount may exceed the amount of daily urine by no more than 200-300 ml);
- for hypoproteinemia - replenishment of depleted protein stores in the body.
Correction of violations of protein metabolism is carried out:
- sufficient intake of proteins with food( primarily meat, beans);
- by drug prescriptions.
Drug regulation is carried out with the help of medication such as:
- drugs that reduce the loss of proteins in the urine( ACE inhibitors);
- protein fractions, which are injected intravenously into the body( in particular, albumin is used);
- diuretics( potassium-sparing drugs).
At the base of the appointments for hydrothorax caused by cirrhosis of the liver, there are:
- diet number 7 with a restriction on the amount of drunk liquid( not more than 1.5 liters per day) and eaten table salt;
- control for the intake of a sufficient number of proteins( their daily dose should be at least 70-80 grams);
- if necessary - diuretics;
- hepatoprotectors( agents that protect liver tissue).
If conservative treatment is ineffective and takes time to correct or is delayed, a large amount of effusion accumulates in the pleural cavity.In this case it is necessary to resort to a pleural puncture.It plays both a diagnostic and therapeutic role.
Pleural puncture is an invasive but technically uncomplicated and not dangerous procedure in which the chest wall is pierced and inserted into the pleural cavity in order to draw a fluid and, if necessary( for example, for reinsurance against infection), enter the medication cavity.Despite the fact that the pleural cavity is a rather narrow space, the patient should not be afraid that with a pleural puncture the doctor traumatises the lungs - their parenchyma is resilient and can not easily puncture.
Pleural puncture is carried out with a special needle under local anesthesia so that the patient can be in a sitting position - thanks to this pose, the fluid drains into the lower parts of the pleural cavity.Thus the patient sits half-bent and leaning on hands.After processing the puncture site( this is the 8th intercostal space in the middle axillary line), layer-by-layer anesthesia of the tissues is performed, while the needle is advanced deeper and deeper.
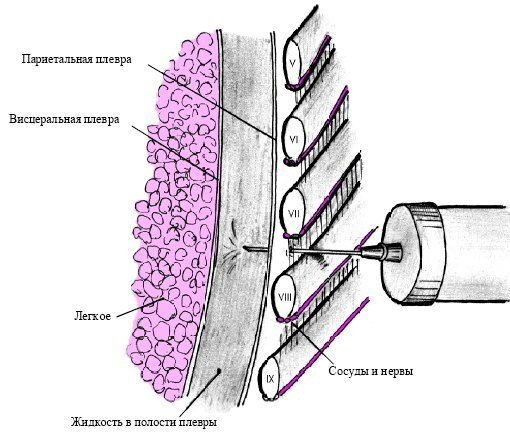
If you get into the pleural cavity, there is a feeling of "failure".After that, the liquid is aspirated. Suction is carried out slowly, no more than 1.5 liters of liquid is removed per puncture( even if it accumulates more).With rapid suction of large amounts of fluid, the negative consequences of pleural puncture are possible:
- displacement of the mediastinal organs;
- lowering of blood pressure.
After the procedure, the needle is slowly removed, keeping it perpendicular to the chest wall, a sterile bandage is applied to the puncture site.The next day, repeat radiography is done to check if the fluid in the pleural cavity accumulates repeatedly.
Puncture of the pleural cavity does not require special preparation of the patient.If necessary( if conservative therapy has not yet managed to stop the process of fluid formation in the pleural cavity) pleural puncture can be repeated many times.
Prevention
It is possible to warn hydrothorax if:
- prevent the occurrence of diseases that lead to its occurrence;
- if such a disease has evolved, it is timely to treat them.
Forecast
With timely detection of hydrothorax and adequate treatment, the prognosis for health and life is favorable. If the diagnosis and treatment of this condition have been carried out late, hydrothorax may aggravate the severity of the underlying disease - especially in cardiovascular failure.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician