Meningococcemia in children
 Meningococcal infection is an acute infectious disease caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and characterized by the polymorphism of clinical phenomena.There are localized forms of infection( meningococcal nasopharyngitis, bacteriocarrier), as well as generalized( meningococcemia, meningitis, meningococcemia in combination with meningitis).The greatest danger is meningococcemia, for which a high percentage of deaths are characteristic.Meningococcemia is mainly found among children.
Meningococcal infection is an acute infectious disease caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and characterized by the polymorphism of clinical phenomena.There are localized forms of infection( meningococcal nasopharyngitis, bacteriocarrier), as well as generalized( meningococcemia, meningitis, meningococcemia in combination with meningitis).The greatest danger is meningococcemia, for which a high percentage of deaths are characteristic.Meningococcemia is mainly found among children.
Causes of
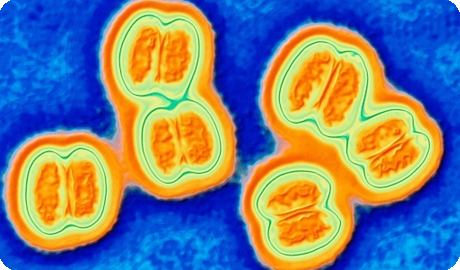
The causative agent of meningococcal disease is diplococcus Neisseria meningitidis.Under the microscope, the bacteria look like beans or coffee beans, located in pairs.Meningococcus is ubiquitous.However, the bacterium is not very stable in the external environment.So, at a temperature of 50 degrees perished in five minutes, and at -10 degrees - after two hours.Direct sunlight kills the bacterium in 2-8 hours.That is why cases of meningococcal infection are rare.The infection is characterized by a seasonal rise in morbidity during the winter and spring periods.Periodically, at an interval of ten to fifteen years, the incidence rate increases.
The source of meningococcal infection is a person:
- Bacteric carrier;
- A patient with meningococcal nasopharyngitis;
- Patient with a generalized form of meningococcal infection.
 The main source of infection is the bacterium carrier.The transmission mechanism is airborne, when a sick person( bacterial carrier) secretes bacteria with saliva into the external environment.Neisseria meningitidis fall on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx.In the place of introduction of bacteria an inflammatory process occurs.If the microorganisms remain in the mucous layer and do not penetrate further, the carriage develops, if they already penetrate into the submucosa, meningococcal nasopharyngitis develops.
The main source of infection is the bacterium carrier.The transmission mechanism is airborne, when a sick person( bacterial carrier) secretes bacteria with saliva into the external environment.Neisseria meningitidis fall on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx.In the place of introduction of bacteria an inflammatory process occurs.If the microorganisms remain in the mucous layer and do not penetrate further, the carriage develops, if they already penetrate into the submucosa, meningococcal nasopharyngitis develops.
If the bacteria overcome the protective barriers of the mucosa and the submucosa and penetrate the bloodstream, meningococcemia develops.In the blood as a result of the action of protective mechanisms, bacteria are destroyed, endotoxin is released - a factor of pathogenicity.Clinically, this is manifested by severe intoxication, as well as the appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhage( endotoxin increases the permeability of the vascular wall).With the blood flow, meningococci spread throughout the body and are able to settle in different organs.In particular, when a bacterium enters the brain, meningitis develops.
About 80% of cases of meningococcal infection occur in children, half of them between the ages of one to five, and the remaining 20% occur in young people between the ages of eighteen and thirty.Among adults, bacteriocarrierism is more prevalent.
Symptoms of meningococcemia
Meningococcemia is a meningococcal sepsis that occurs with marked symptoms of toxicosis.The course of meningococcemia can be mild, moderate, severe, and also very severe( lightning-fast form).The duration of the incubation period is 1-10 days, but more often 5-7.
The disease occurs sharply, the temperature at the time rises to 39-41 degrees.
Often the parents of a sick child can even name the exact time when the child is sick, so it happens suddenly and with vivid clinical manifestations.
Simultaneously with fever, there are other signs of intoxication: severe weakness, muscle pain, loss of appetite, thirst, pale skin. In addition, there are signs such as:
- Heart rate increase;
- Lowering blood pressure;
- Increased respiratory movements;
- Shortness of breath;
- Decreased urination;
- Stool retention / diarrhea;
- Skin rash.
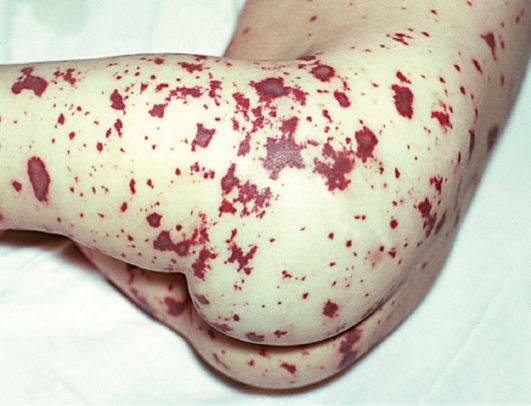
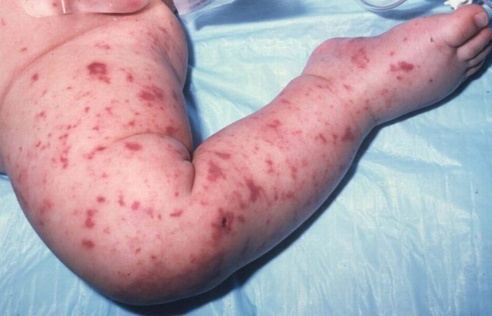 Skin rash is the most characteristic and very significant sign.And the rash can appear already in the first hours after the onset of the disease.Most often, the elements of the rash appear on the legs, feet, buttocks, hands, hands.Rashes have a stellate irregular shape from a few millimeters to centimeters.To the touch, the elements are dense, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin.
Skin rash is the most characteristic and very significant sign.And the rash can appear already in the first hours after the onset of the disease.Most often, the elements of the rash appear on the legs, feet, buttocks, hands, hands.Rashes have a stellate irregular shape from a few millimeters to centimeters.To the touch, the elements are dense, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin.
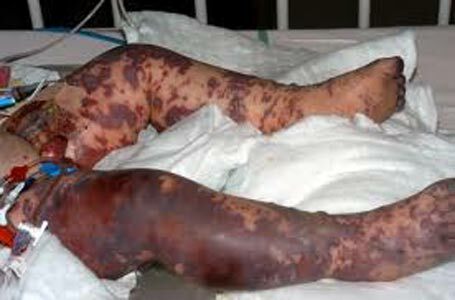
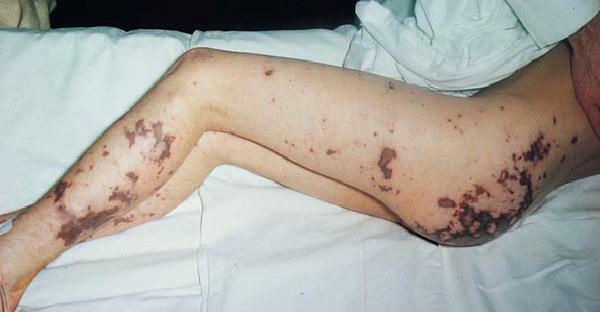
In severe forms of the disease, the rash can spread all over the body, and on the limbs look like extensive hemorrhages with clear edges, resembling cadaveric blemishes.The face usually remains free from rashes, except that the elements can appear on the ears, the tip of the nose.In particularly severe cases, the hemorrhage areas merge and form a zone of continuous lesion in the form of high boots and gloves.Such changes are usually incompatible with life.
In the initial period of the disease, in parallel with the hemorrhagic rash, rose-osseous-papular elements may appear on the body, but after a couple of days they disappear.
Hemorrhages also occur on the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctiva, sclera.
Abundance of skin rash, its nature, rapidity of spread are an important criterion of the severity of the patient's condition.
In the future, rashes of small size are pigmented, and then disappear.Large hemorrhages are covered with crusts, and after their rejection, scars are determined.In addition, necrosis and gangrene of the fingers, hands, feet, ears, nose are possible.
Lightning-fast meningococcemia
This is a very severe, extremely unfavorable form of meningococcal infection from a prognostic point of view.Sometimes death develops a few hours after the onset of the first symptoms.In fact, lightning-fast meningococcemia is an infectious-toxic shock.
Suddenly, the body temperature rises above 40 degrees, chills appear, muscle aches, heart palpitations, increased blood pressure.
From the very first hours of the disease, a profuse, rapidly spreading hemorrhagic rash arises on the skin.In addition, there are vast reddish-cyanotic spots that shift when the position of the body changes.
Against this background, the body temperature drops to 36.6 degrees and even less. The following symptoms occur:
- Drop in blood pressure;
- Increased heart rate;
- Increased respiration rate;
- Severe headache;Pale skin, cyanosis;
- Consciousness disorder;
- Convulsions;
- Anuria;
- Possible vomiting, diarrhea, nosebleeds.
Death occurs as a result of cardiac or respiratory activity.
Meningococcemia with meningitis
Meningococcemia rarely occurs in isolation, in 2/3 of cases in combination with meningitis.
We recommend to read:Against the backdrop of fever, weakness, hemorrhagic eruptions, a burning painful headache arises, vomiting that does not bring relief.The intensification of pain causes a bright light, sounds, a change in position.The doctor detects meningeal signs, as well as the revitalization or suppression of tendon reflexes, the appearance of pathological reflexes.There are signs of lesion of the cranial nerves, more often III, IV, VI, VII.
Young children take a specific pose of a "pedigree dog" when the child is on his side with his head thrown back and brought to his stomach knees.
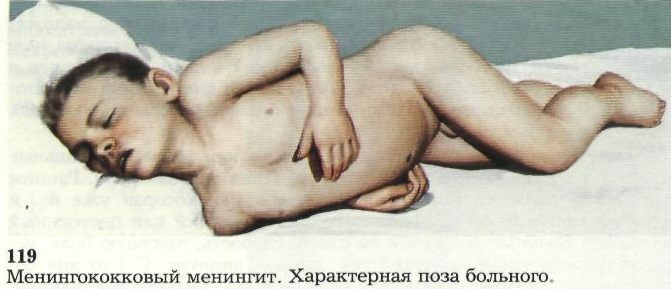
At the onset of the disease, a psychomotor agitation develops, soon followed by a disorder of consciousness.Sometimes from the onset of the disease to the development of a coma, several hours pass, so the infectious process can be so aggressive.The patient may experience seizures, complicated apnea.
Complications
In the background of meningococcemia, the following complications can occur in the acute period of the disease:
- Infectious-toxic shock;
- Acute renal failure( ARF);
- DIC-Syndrome;
- Acute adrenal insufficiency( synonymous with Waterhouse-Frideriksen syndrome);
- Edema and wedging of the brain;
- Syndrome of cerebral hypotension;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Panophthalmit.
Important! In the absence of treatment for meningococcemia, lethal outcome is observed in almost a hundred percent of cases.Even with the timely start of therapy, from a hundred patients, ten to twenty people die.Often after the infection, serious irreversible complications develop: deafness, blindness, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, dementia.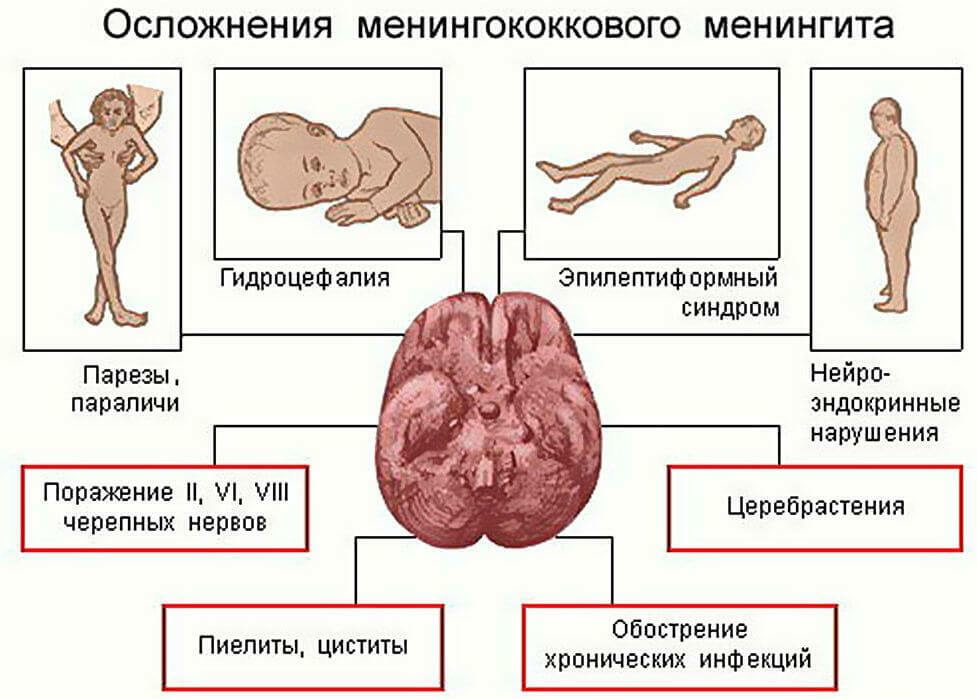
Diagnostics
Meningococcemia has its own characteristic signature, therefore it is not difficult for a doctor to suspect an infection in the presence of symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Clinical blood test - increase of leukocytes, acceleration of ESR, decrease of platelets, erythrocytes, hemoglobin;
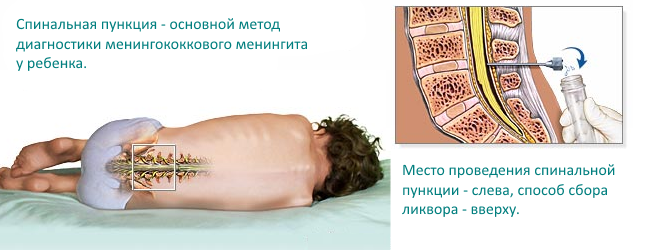
- Spinal fluid examination - characterized by neutrophilic pleocytosis, detection of diplococci;
- Bacteriological method - allocation of meningococcus as a result of seeding of biomaterial on nutrient media;
- Serological tests - detection of antibodies to meningococcus and the growth of their titer;
- PCR is the detection of meningococcal DNA.
Treatment
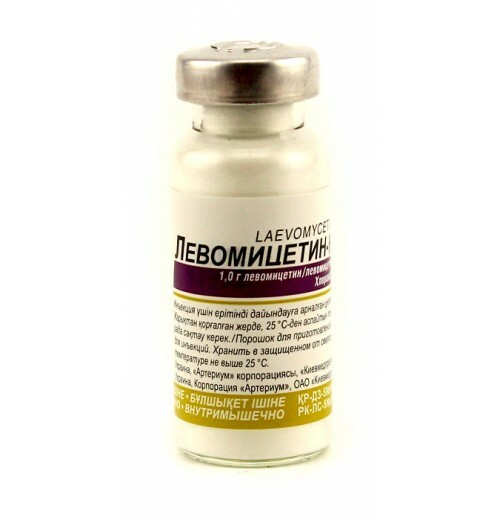 The central link in the treatment of meningococcemia is the administration of antibiotics.With meningococcal infection, levomycetin succinate is effective.When treating this drug, endotoxic reactions develop much less frequently than when treated with penicillins.Levomycetin succinate is administered intramuscularly at 50-100 ml per day in three to four doses.With a lightning-fast form of the disease, the drug is administered intravenously every four hours until the blood pressure stabilizes, after which they switch to intramuscular injection of levomycetin.The duration of the drug is at least ten days.A few rarely use drugs from the group of cephalosporins: ceftriaxone, cefotaxime.
The central link in the treatment of meningococcemia is the administration of antibiotics.With meningococcal infection, levomycetin succinate is effective.When treating this drug, endotoxic reactions develop much less frequently than when treated with penicillins.Levomycetin succinate is administered intramuscularly at 50-100 ml per day in three to four doses.With a lightning-fast form of the disease, the drug is administered intravenously every four hours until the blood pressure stabilizes, after which they switch to intramuscular injection of levomycetin.The duration of the drug is at least ten days.A few rarely use drugs from the group of cephalosporins: ceftriaxone, cefotaxime.
Pathogenetic therapy aims to combat toxemia. Use preparations:
- Detoxification agents: Ringer's solution, 5% glucose solution, plasma and its substitutes, albumin;
- Furosemide - for prevention of cerebral edema;
- Anticonvulsants( sibazone);
- Vitamins C, group B;
- Glutamic acid;
- Glucocorticosteroids( hydrocortisone, prednisolone) - with severe infection.
Important! Meningococcemia is a very dangerous infectious disease.Only timely treatment can save the life of the patient.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer