DTP vaccine: from what protects and why it is so important
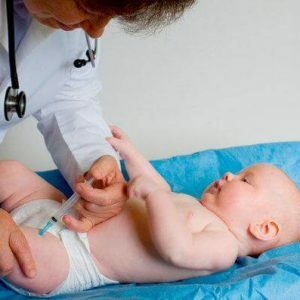 DTP vaccination protects children from three infections - pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus. Each of these diseases pose a great threat to the life of the child, therefore, refusing to vaccinate, parents consciously put their baby at risk.
DTP vaccination protects children from three infections - pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus. Each of these diseases pose a great threat to the life of the child, therefore, refusing to vaccinate, parents consciously put their baby at risk.
What are the risks of diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough?
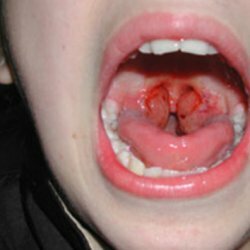
Diphtheria is a serious infectious disease transmitted by airborne and contact routes.In places of introduction of pathogens of this infection, fibrinous films are formed, which, if localized in the larynx, can completely block the airways.In addition, with diphtheria develops severe intoxication, the pathological process involves kidneys, heart, nerves.
Pertussis is another serious disease affecting the respiratory tract.The leading symptom of the disease is the strongest spasmodic cough, against which in young children breathing and convulsions may occur.Suffer from whooping cough mainly kids from year to 5 years, although the disease is found among adults, but they rarely occur in severe form.
 Tetanus among the listed diseases can be called the most dangerous, because patients who do not have tetanus immunity, without the introduction of tetanus toxoid can die from generalized seizures, cardiac arrest and breathing, even if the hospital has the latest equipment and the most modern medications.Such a severe course of the disease is explained by the detrimental effect on the nervous system of the toxin released by the pathogen.Infection with tetanus occurs when a contagion of the microorganism Clostridium tetani enters the wound.Especially dangerous in terms of infection with tetanus are contaminated deep wounds on the legs and hands.
Tetanus among the listed diseases can be called the most dangerous, because patients who do not have tetanus immunity, without the introduction of tetanus toxoid can die from generalized seizures, cardiac arrest and breathing, even if the hospital has the latest equipment and the most modern medications.Such a severe course of the disease is explained by the detrimental effect on the nervous system of the toxin released by the pathogen.Infection with tetanus occurs when a contagion of the microorganism Clostridium tetani enters the wound.Especially dangerous in terms of infection with tetanus are contaminated deep wounds on the legs and hands.
Important: vaccination in most cases prevents the development of these infections, but if the disease does occur, the patient tolerates it much easier than unvaccinated people.
Types of vaccines
There are several varieties of vaccines for the prevention of diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus:
- DTP;
- AACDS;
- ADS;
- ADS-m;
- AS and AD.
In childhood and adolescence, only the first four types of vaccines are used for routine immunization.In turn, antitetanus and antidiphtheria toxoins( AS and AD) are intended for emergency immunization of tetanus and vaccination against diphtheria in foci of infection.
Now more about these vaccines.
DTP is a three-component preparation containing the following:
- killed pertussis cell cells.
- diphtheria toxoid.
- tetanus toxoid.
Diphtheria and tetanus toxoid for humans are not dangerous - they can not cause the development of an infectious process, an abnormal immune response or poisoning of the body.But the pertussis component, represented by microbial cells, is just the cause of the appearance of various post-vaccination complications of .Reduce the risk of their occurrence can be, if you use acellular vaccine - AaDS.Its main difference from traditional DTP is the absence of whole bacterial cells( it contains only parts of microbes).The cell-free vaccine AACDS is better tolerated by children, it gives much less complications, , however, because of its higher cost, it is not always available in public medical institutions.
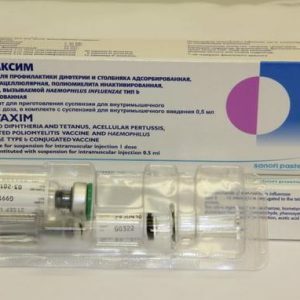 Both DTP and AaDCA can also be parts of complex vaccine preparations.For example, AaDS is included in the Pentaxim , which protects against five infections( pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, polio and Hib infection), and DTPA to Bubo-Kok for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and hepatitis B.Such multicomponent drugs minimizes the need for visiting the clinic and discomfort during the vaccination( the baby is only one shot, and not a few).
Both DTP and AaDCA can also be parts of complex vaccine preparations.For example, AaDS is included in the Pentaxim , which protects against five infections( pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, polio and Hib infection), and DTPA to Bubo-Kok for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and hepatitis B.Such multicomponent drugs minimizes the need for visiting the clinic and discomfort during the vaccination( the baby is only one shot, and not a few).
In children after three years, the DTP vaccine is not used.Vaccination and revaccination to older children are carried out with drugs ADS and ADS-m( weakened). They do not have a pertussis component, but there are only tetanus and diphtheria toxoids.This feature of the vaccination of schoolchildren is explained by the fact that they rarely suffer from whooping cough, so administering a drug that causes side reactions due to the pertussis component is inappropriate.
DTP: contraindications
Contraindications for the use of the DTP vaccine are the following conditions:
- progressive neurological disorders, encephalopathy;
- epilepsy;
- convulsions in the anamnesis;
- oncological diseases;
- severe postvaccinal reactions in the past.
Acute respiratory diseases, exacerbation of chronic pathologies, dysbiosis, allergic diseases are also contraindications for DTP vaccination, but after improving the child's condition, it is possible and even necessary to inoculate.
The small weight of a body( less than 2 kg) at a birth of the child can not be an occasion to postpone the inoculation of DTP.But there is a condition - the physical and psychomotor development of the baby should meet the age norms.
In order to identify contraindications and thereby to protect the vaccinee from undesirable consequences of vaccination, a physician or paramedic should examine the child before vaccination.
When contraindications are detected, doctors take a small patient under control and make up for him an individual immunization schedule.
DTP vaccination schedule
In accordance with the Russian immunization schedule, vaccination against diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus is carried out at the following times:
- at 3 months;
- in 4,5 months;
- in 6 months.
After these three vaccinations, the DTP revaccination is carried out in 18 months to fix the result of the prophylaxis.All subsequent revaccinations( at 6-7 years, at 14 years and then every 10 years) are made with a drug without a pertussis component - ADS.
Complications after DTP
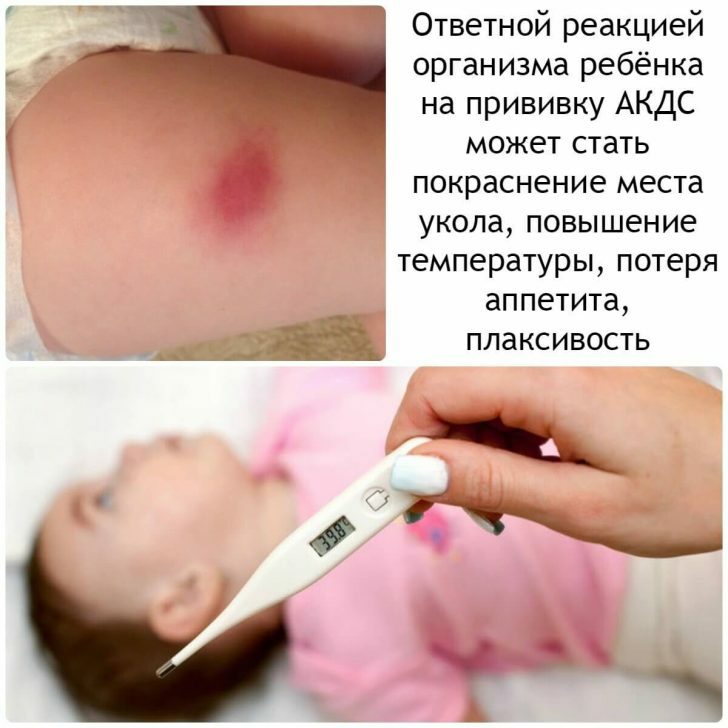
After every DTP vaccination, every fourth child develops light reversible post-vaccination reactions:
- increases body temperature;
- appears sluggish;
- appetite worsens;
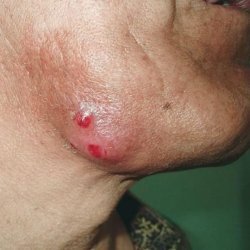
- , there are local skin changes at the injection site-compaction, redness, soreness( some babies begin to instinctively spare the leg they injected into, and the parents mistakenly perceive it as a disorder of the nervous system).
These reactions most often appear after 2, 3, 4 of the introduction of DTP. This is due to the peculiarities of the formation of immunity: when the vaccine enters the body for the first time, the development of an immune response takes time, and the repeated introduction of an immunobiological drug causes a more rapid and violent reaction.
In rare cases, DTP vaccination leads to the development of serious complications:
- convulsions;
- poorly stopping fever( the temperature rises to 40 degrees or more);
- severe allergic reactions;
- lesions of the brain( extremely rare - less than 1 case per 1 million vaccinated children).
Thus, the risk that the DTP vaccine will lead to undesirable consequences always exists.But parents should understand that in case of refusal from vaccination and the absence of immunity in the child, the probability of catching serious infections will be much higher.
Preparing for vaccination
No special preparation for DPT vaccination is required. If the doctor deems it necessary to prescribe an antihistamine before and after the vaccination, parents should listen to his recommendations.Independently, however, to give the child medicines for allergies is in no way impossible.
As for the other preparatory activities, they can be attributed to:
-
 Inspect the pediatric neurologist and give the general blood test , this item is especially relevant for the first DTP vaccination.Visit the polyclinic preferably a few days before the planned vaccination, so that in case of infection with ARI, which often occurs in medical institutions, the symptoms of the disease appeared even before the day of vaccination.
Inspect the pediatric neurologist and give the general blood test , this item is especially relevant for the first DTP vaccination.Visit the polyclinic preferably a few days before the planned vaccination, so that in case of infection with ARI, which often occurs in medical institutions, the symptoms of the disease appeared even before the day of vaccination. - Rational nutrition. You can not overfeed, wean out of the breast, or introduce a new lactation into your diet before the planned vaccination.
- Emptying the intestines. If there is a problem with the stool, it is advisable to start giving the baby lactulose syrup a week before the vaccination.
- Limitation of contacts. Visits to guests and receptions of guests must be rescheduled for another time.
- Acquisition of antipyretics. After vaccination, the baby may get fever, so mom should have paracetamol or ibuprofen in syrup and candles at hand.
A doctor( pediatrician, family doctor or paramedic) must necessarily examine the baby on the day of vaccination - the baby should be healthy. If the night before or the night of the baby was concerned, the mother should inform the doctor about it.In addition, if there is an infectious patient at home, this also needs to be told.After evaluating all the data obtained, the doctor will decide whether it is possible to do a small patient with an inoculation.
After vaccination, the mother must also adhere to certain rules:
- Do not bathe the baby for 1 day.
- Do not rub the injection site.
- Keep track of the temperature of the baby's body.If it goes up, give a febrifuge( which, it is advisable to discuss with your doctor in advance).
- Do not overfeed the baby( after vaccination it is recommended to pause for several hours), do not change the mixture and the lure.
- Give the baby more fluid.
- Longer and more often walk in the street( if there is no high temperature).
Fulfillment of all these recommendations will help the baby to transfer the vaccination more easily and will significantly reduce the risk of unwanted complications.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist