ALL THAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE FATHERLAND

Parents of the newborn usually know that on the head of the baby there is a fontanel or, as it is often called, a soft theme.Many of them are convinced that the fontanel in infants is a weak and vulnerable place, which once again should not be touched.Is this true?Is there a fontanel in newborns?What is it for?Let's figure it out.
Contents: Features of the skull structure of the fetus and the newborn. Functions and dimensions of the fontanel When the fontanum grows. Spring rod - signaling beacon. How the fontanel helps diagnose. FEATURES OF THE STRUCTURE OF A FRONT AND A NEWBORN
. Rodnichki in a newborn, and several of them,Given by nature "adaptations" to facilitate the process of the appearance of the baby to the light.During the passage of the fetus along the mother's birth canals, the head may deform( in a good sense of the word) and take the forms corresponding to the generic canal.This facilitates childbirth for both the baby and the mother.
Such anatomical "mutual understanding" is possible due to the peculiarities of the skull structure of the fetus.It consists of the same bones as the adult's skull.But the bones of the cranium of the skull of the baby are highly elastic and connected by a kind of shock absorbers - neocostenegivshimi connective tissue sites.
This is the seams and fontanels:
- frontal or metopic suture - between the frontal bones;
- coronary or coronary suture - between the parietal and frontal bones;
- sagittal or sagittal seam - between the parietal bones;
- occipital or lambdoid suture - between occipital and parietal bones;
- left and right scaly seams - between parietal and temporal bones;

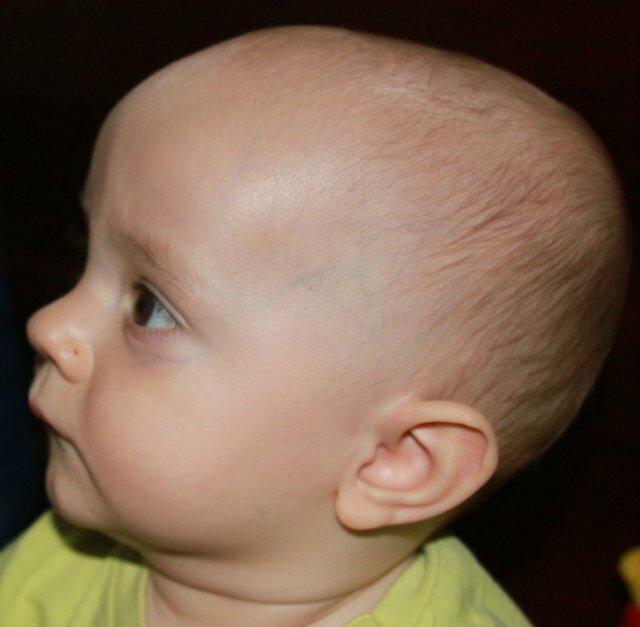
- front or large fontanel is a diamond-shaped membranous plate, from the corners of which the frontal and sagittal seams extend, the left and right parts of the coronal suture;
- posterior or small fontanel in children - a triangular depression at the intersection of the occipital and arrow-like sutures;
- left and right wedge fontanelles - at the junction of coronary and scaly joints;
- left and right mastoid fontanels - in the junction of lambdoid and scaly joints.
In a healthy full-term newborn of all listed membranous structures, the skulls remain open and only the large fontanel( anterior) and in rare cases the posterior small fontanel are determined.And all the seams and other fontanelles are closed.In preterm infants, some seams between the bones of the skull and the lateral fontanelles may remain partially open.
The connective tissue membrane, which forms the fontanel in children, resembles a canvas in its density.Therefore, to break the integrity of it is extremely difficult.Calmly bathe the baby, if necessary, use the comb, play with the baby, massage him and do not be afraid to damage the fontanel.
FUNCTIONS AND DIMENSIONS OF FITNESSES
The front children's fontanelle resembles a rhombus in shape.The dimensions of the fontanel are measured not by the diamonds of the rhombus, but by the lines connecting the middle of its opposite sides.
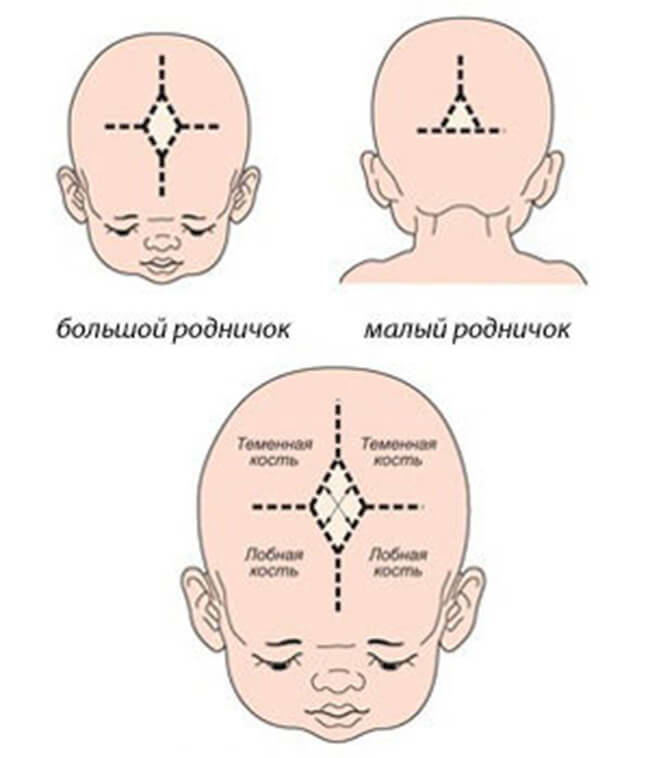
The sizes of the large fontanel in infants born on term vary from 2х2 cm to 3х3 cm. In preterm babies, not only the fontanelle is large, but the areas of the seam of the skull that remain adjacent to it remain open.
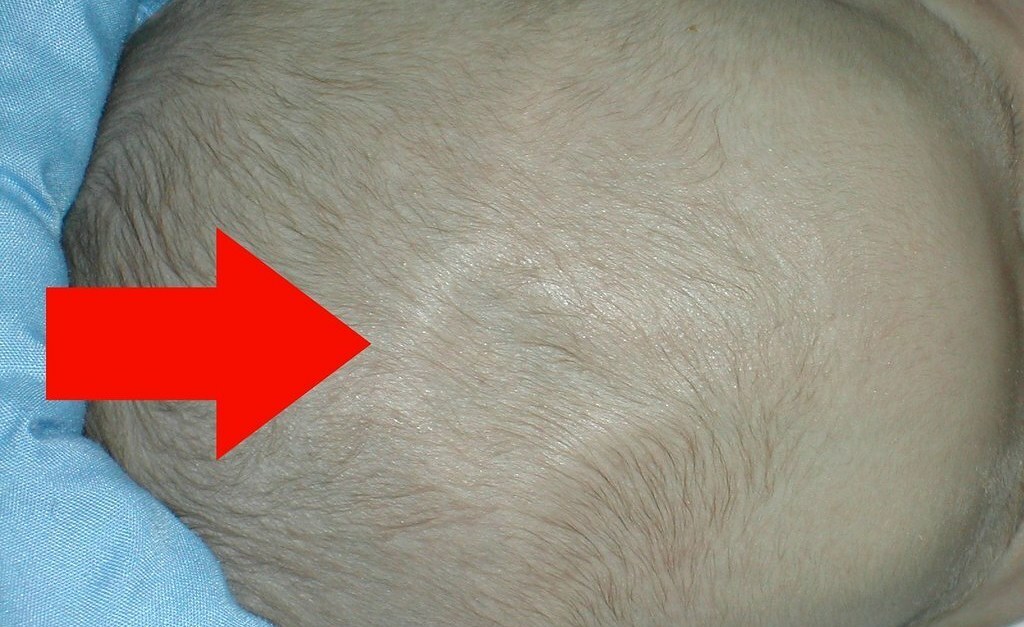 Normally, the anterior children's fontanel is at the same level as the surrounding frontal and parietal bones, or it sinks a little.If you look closely, you can see how the fontanel pulses.With strong crying and restlessness of the baby, it can slightly bulge.
Normally, the anterior children's fontanel is at the same level as the surrounding frontal and parietal bones, or it sinks a little.If you look closely, you can see how the fontanel pulses.With strong crying and restlessness of the baby, it can slightly bulge.
In the first year of the baby's life, the brain quickly grows in size.Due to the elasticity and suppleness of the fontanel, the cranium does not prevent the growth of the brain.
In addition, the fontanel at the infants performs the function of thermoregulation.When the body temperature of the child rises through the large fontanel, the excess heat is released by the shells of the brain, that is, they are naturally cooled.Therefore, febrile baby never swaddle with his head and do not wrap his head in caps and scarves.
In a full-grown baby, the size of the fontanel located behind, provided that it is not completely closed, is so small that the tip of the finger can hardly be placed in the triangular recess.
WHEN THE FASHION IS GROWING
In a healthy baby born on time, only the front large fontanel remains unclosed.But as the bones of the skull grow, its dimensions gradually decrease, and it closes.
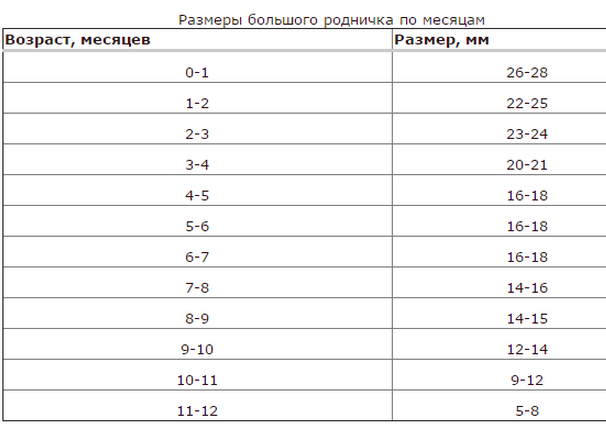
For the age at which the front children's fontanelle is completely closed, the norms are not strictly defined.In most newborns this occurs to 12, and sometimes to 18 months.But even if the fontanel is overgrown, and the child has not turned a year old, one should not worry.In a healthy baby this can be a variant of the norm, which the pediatrician will certainly tell you.
The back fontanelle is not even determined by the time of delivery.If you managed to find it, do not worry.Usually it happens like this: by the time the fontanelle overgrows the forehead, there is no trace left from the back.It closes to 1.5-2 months.
FASHION-SIGNAL BALL
Being the parents of a newborn baby, you should observe the state of the children's fontanel and tell all the changes to the district pediatrician.If you notice that your little one is strongly pulsating with the fontanel, or you think that he has a very small fontanel( you know the norms of his size, say), do not be silent, but share your observations with the doctor.
For neonatologists and pediatricians, the fontanel at the infants is a kind of signal beacon.He is the first to react to any trouble in the head of a newborn.By too early or very late overgrowing of the fontanel, a pediatrician may suspect a serious illness.
 If the front fontanelle is very small or absent at birth, first of all doctors exclude microcephaly and craniostenosis.In the first case, the child has all parts of the body normal size, and the head( brain skull and brain) are significantly lagging behind in development.Microcephaly is often a manifestation of severe chromosomal diseases, such as Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
If the front fontanelle is very small or absent at birth, first of all doctors exclude microcephaly and craniostenosis.In the first case, the child has all parts of the body normal size, and the head( brain skull and brain) are significantly lagging behind in development.Microcephaly is often a manifestation of severe chromosomal diseases, such as Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
With craniostenosis, the seams between the skull bones begin to heal, and the fontanels are closed.Because of this, the head deforms, the brain can not grow normally, intracranial pressure rises with all the resulting symptoms.
The pressure inside the skull can be so high that the fused bones again begin to diverge.
If a woman, being pregnant, consumed a lot of foods containing calcium( cheese, milk, cottage cheese, etc.) and was fond of multivitamin preparations, her child's fontanel can close early.A lack of calcium in the body can cause a late overgrowing of the fontanel.
If the full-term baby has a very large anterior fontanel and a back fontanel is open, it is examined for hydrocephalus( hydrocephalus) and congenital hypothyroidism( thyroid insufficiency).Doctors exclude or confirm intrauterine hypoxia, birth trauma and intrauterine infections, in which the fontanel sizes can also be above average.
A rodnichok in children reacts to an increase in intracranial pressure( ICP) by stress and swelling.
ICP in infants increases with the following diseases and conditions:
- congenital diseases( hydrocephalus, etc.);
- infection of the brain( purulent meningitis, etc.);
- voluminous formations in the cranial cavity( hematomas, tumors, etc.);
- perinatal encephalopathy;
- thrombosis of the sinuses and veins of the brain in severe infections, blood diseases, etc.
Important: if bulging of the fontanel has appeared immediately after the child has received an injury( head and not only), immediately contact the medical institution or call an ambulanceon house.
Be sure to pay attention not only to the bulging, but also to the fading fontanelle, which serves as an indicator of the degree of dehydration of the body.With intestinal infections due to vomiting and diarrhea, with neuroinfections due to repeated vomiting, dehydration develops very quickly.The child in this situation requires urgent medical attention.
Note: for meningitis, the fontanel first swells out due to an increase in ICP, and then, due to loss of body fluid, the baby sinks.
If a pediatrician or neurologist directs your baby to measure intracranial pressure, do not discard this study.The procedure is absolutely safe and painless, but its results are quite informative.They will help the doctor to diagnose correctly and prescribe a treatment in a timely manner, if necessary.
HOW FATHERAPY HELPS DIAGNOSTIC
The babies in babies are a kind of "window" through which one can "look" inside the skull and brain of the baby.
Therefore, infants with access through the fontanal perform some diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations, such as:
- subdural puncture under local anesthesia;
- puncture of the ventricles of the brain to measure the pressure of the CSF, to study its composition and subsequent ventriculography;
- non-puncture ICP measurement with special tonometers;
- two-dimensional echoencephalography and sonography - ultrasound;
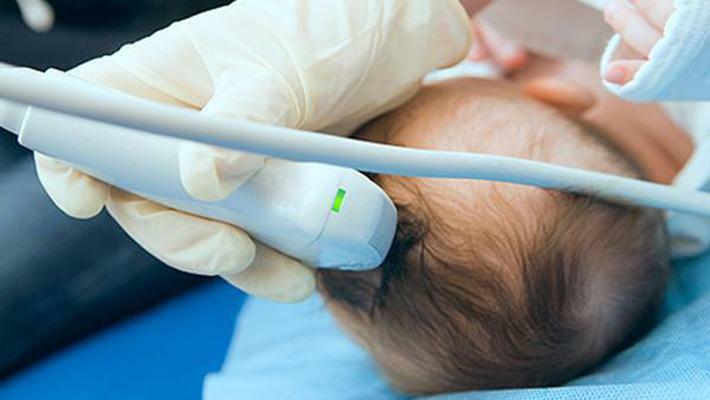
- radioisotope scintigraphy.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena, pediatrician