Hepatitis B: symptoms, ways of infection, treatment
Hepatitis B is a fairly common form of inflammatory liver disease, which is characterized by severe course and complex treatment, in medicine the disease in question is also called serum hepatitis, because infection occurs through the blood.
Table of contents: Transmission routes of hepatitis B virus Risk factors for infection Hepatitis B development stages Hepatitis B symptoms Hepatitis B during pregnancy Hepatitis B treatment guidelinesTransmission routes of hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus sources are people who are sick with this disease,Or the carriers of the virus - the person is absolutely healthy, but in his blood the presence of the virus of the disease in question is detected.Transmission of the virus takes place through the blood, moreover, it has a property for a long time to be preserved in the smallest particles of blood.It is not surprising that infection can occur with the use of syringes many times( this applies to people with drug dependence), through medical instruments that have not undergone the necessary sterilization.The virus of hepatitis B is secreted and with sperm, therefore it is impossible to exclude the sexual way of infection.
 Please note: can be infected with the disease under consideration quite realistically and with blood transfusion.But in the conditions of the modern donor service, each donor undergoes a thorough examination, and all, without exception, portions of blood are full-fledged studies.
Please note: can be infected with the disease under consideration quite realistically and with blood transfusion.But in the conditions of the modern donor service, each donor undergoes a thorough examination, and all, without exception, portions of blood are full-fledged studies.
In addition, the hepatitis B virus can enter the body of a healthy person with ear piercing, tattooing, or during a visit to the dentist, but only if these procedures are performed with a non-sterile instrument.
Risk factors for infection
Most often, hepatitis B is diagnosed in young people aged 15-30 years, much less often in older and younger children. There are clearly identified categories of people who have an increased risk of infection:
- "lovers" of frequent visits to the dentist;
- those who regularly visit the salons of tattoos and piercings;
- dependent on drugs( refers to injecting drug users);
- people with promiscuity and homosexuality;
- patients of the nephrological departments of medical institutions who are constantly undergoing dialysis procedures;
- those who live with a hepatitis B.
Stages of hepatitis B development
The period from the moment of infection until the appearance of the first symptoms( incubation) of the considered disease is on the average 12 weeks, but this is a fairly conventional term - some people mark the firstSymptoms already after 2 months after infection, and some only after 6 months.
After the hepatitis B virus enters the blood, it quickly penetrates into the liver cells( hepatocytes), is introduced into them and begins to multiply actively.DNA virus is introduced into the DNA of healthy hepatic cells, which causes an inadequate response of the body's immune system - it starts healthy liver cells perceiving as alien and destroying them.It is this response of the immune system to the introduction of the hepatitis B virus and leads to an inflammatory process in the liver and the appearance of severe symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of hepatitis B
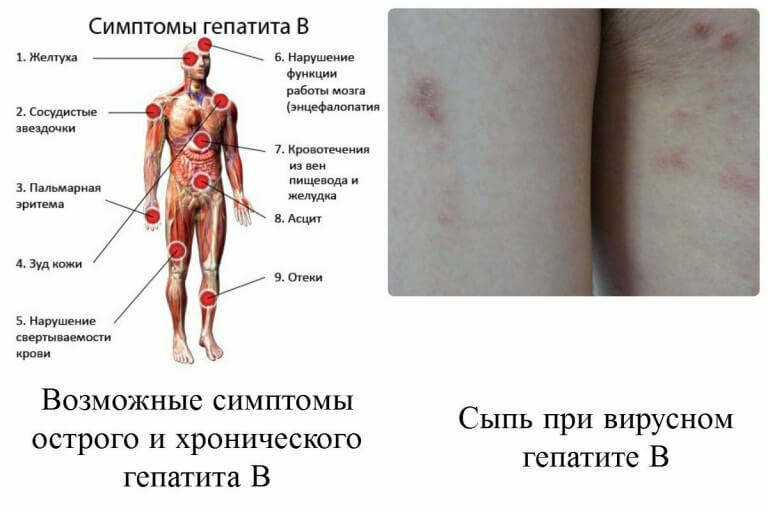
After a certain period of time after getting the hepatitis B virus into the blood of a healthy person, the symptoms of the disease begin to appear.It is worth noting that these symptoms are quite pronounced, and they are unlikely to be ignored - they bring some discomfort. The clinical picture for hepatitis B will be as follows:
- The patient complains of increased fatigue and weakness.Moreover, this state can not be compared with the absence of normal sleep or days off - both weakness and fatigue will be present in any case.
- Periodically in a person infected with the hepatitis B virus, the body temperature rises to 39 degrees, which is accompanied by chills and pains in the joints.
- The patient will notice a significant decrease in appetite, the appearance of almost constant nausea and vomiting, regardless of food intake.
- Urine and feces also change: urine becomes dark, its exit from the bladder is always accompanied by the formation of foam, and the feces, on the contrary, becomes pronouncedly light.
- Since the liver is affected by the virus, the patient will necessarily have discomfort, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium( the area of the anatomical location of the affected organ).
- With progressive hepatitis, the skin and mucous membranes become yellow.
Note: all of the listed symptoms can not be the cause of the diagnosis of hepatitis B!The fact is that such a clinical picture is observed with any inflammatory diseases of the liver, so the appeal to a specialist is inevitable.
Hepatitis B can occur in acute and chronic form.In the first case, the development of the disease will be rapid, all symptoms - pronounced.But at the same time acute hepatitis B is completely cured in 90% of cases, only in 10% of cases acute hepatitis B passes into a chronic form.
The chronic form of the considered disease proceeds cyclically: the phases of virus activation are replaced by remissions, the symptoms can be lubricated, or altogether absent.Even if in chronic hepatitis B, there are no symptoms of pathology, the person remains sick and is able to infect others.
Note: is the chronic form of hepatitis B that represents a danger to the patient.If he does not follow the prescribing and recommendations of the attending physician, then a rapid progression of the disease, which results in hepatic insufficiency, cirrhosis of the liver or liver cancer, is possible.
Hepatitis B during pregnancy
The virus of the disease under consideration is large enough and therefore can not penetrate the placenta by infecting the fetus - the hepatitis B virus is not transmitted from the pregnant woman to the fetus.But the risk of infection of the baby is, and it is high enough - during childbirth or when a placental puncture( for example, when carrying out a combined screening test for the definition of Down's syndrome in a fetus), the probability of the virus getting to the body is maximum.
If a woman with a diagnosed hepatitis B is taking birth, immediately after the birth of the child, he is injected with an immunoglobulin - antibodies, which immediately destroy the virus, preventing the spread of the disease.Then, in the first 12 hours after birth, the child is vaccinated against hepatitis B, and at six months of age the procedure is repeated.If such measures were taken, then the child should undergo only a one-year-old prophylactic examination - most likely, the hepatitis B virus will not be detected.
Principles of treatment of hepatitis B
Treatment of the two forms of the disease under consideration has a difference.
Acute hepatitis B
This form of the disease does not require the use of specific antiviral drugs, as the disease itself passes within 4-8 weeks.As a rule, a doctor prescribes maintenance therapy to such patients, which helps to alleviate the patient's condition and reduce the intensity of symptoms.
Mandatory for acute hepatitis The patient is prescribed a diet:
- completely excluded from the diet of alcoholic beverages, fatty fish and meat, spicy dishes, chocolate, carbonated drinks, any fried foods;
- is allowed to consume milk and dairy products, lean meats, fruit juices, soups and cereals on vegetable broths;
- food intake should be at least 5 times a day;
- portions of food should be small.
Within the framework of maintenance therapy for acute hepatitis B, special solutions are prescribed that can rid the body of the patient of toxins( doctors prefer to prescribe droppers with haemodesis).Necessary to the patient must be administered vitamins and appointed hepatoprotectors - specific drugs that are able to protect hepatocytes( liver cells).
Chronic hepatitis B
The chronic form of the disease in question implies the appointment of specific antiviral drugs - it is advisable to do this during periods of exacerbation of the pathology.These drugs include lamivudine and interferon alfa - they are often combined in various proportions.
Please note: reception of antiviral drugs for exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B should only be performed under the supervision of a specialist - the medicines provided can give powerful side effects.
In addition to antiviral drugs, chronic hepatitis B also supports maintenance therapy on the same principle as in the acute course of the disease in question.Treatment of chronic form of hepatitis B is different in duration - in some cases, the course of therapy can last 12 months or more.But not always experts appoint the patient antiviral therapy - the decision on the appropriateness of such treatment is made by the attending physician, having familiarized himself with the results of the patient's examination.
In case of exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B, the patient should observe a strict enough diet. Contraindicated in the diet:
- any fried foods and meals;
- beans, beans, peas, mushrooms;
- sorrel, spinach, radish, radish, pepper;
- any spices and spices;
- cocoa, chocolate;
- canned and marinated products;
- raw onion, garlic and vinegar.
In the menu of the patient with chronic hepatitis B in the acute phase should be present:
- whole milk and dairy products;
- soups, dairy and vegetable, but without preliminary passage of vegetables;
- white wheat bread, or rye, but in stale form;
- mild hard cheese and cottage cheese with a minimum level of fat content;
- meat of low-fat varieties and exclusively in boiled or stewed;
- fish of low-fat varieties in boiled or in jellied form;
- various baked vegetables;
- fruits and berries of non-acid varieties;
- various compotes and preserves;
- sugar and honey;
- eggs in the form of omelettes from protein;
- vegetable oils( refined sunflower, olive or soybean);
- butter.
Many people are worried about the possibility of a complete recovery in the chronic form of hepatitis B. Doctors say that this is realistic, but only in the case of clear fulfillment of all prescriptions and recommendations of the treating doctor, constant compliance with the diet.Often the following happens: according to blood tests - the norm, all the symptoms disappear, but the antigen of the hepatitis B virus( it is also called the Australian antigen) continues to circulate in the blood for another dozen years.In this case, we will talk about the carrier of the virus.
Preventive measures

The most reliable way to protect a person against infection with the hepatitis B virus is vaccination.Conducted to her newborn within 12 hours after birth, then the procedure is repeated in 1 month and half a year of life of the baby.As a rule, persistent immunity to the disease in question persists in this method of prevention until age 19, and for older people, vaccination should be carried out only if it is at risk.
There is also such a thing as emergency prevention of hepatitis B. It is carried out only if a person has contact with the patient's blood.The patient is injected with an immunoglobulin preparation and hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccination is repeated according to special schemes that are selected by the attending physician on an individual basis.
Hepatitis B is quite an insidious disease, which, however, modern medicine has learned to treat.It is enough only to pay attention to the first symptoms, provide timely diagnosis and undergo a full course of treatment.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapist of the highest qualification category