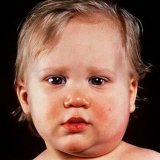
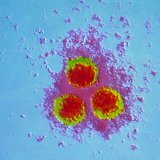
Staphylococcus in children: symptoms and treatment
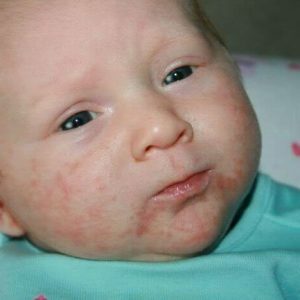
Staphylococcal infection leads TOP of childhood infectious diseases.Especially often it is diagnosed in infants and newborns.
Staphylococci are a group of bacteria belonging to the family Staphylococcaceae.They are facultative anaerobes, i. E.Organisms that develop in an environment where there is no oxygen.However, oxygen itself is not harmful to the life of bacteria.
Cells of these microorganisms are spherical;When dividing, bacteria form colonies resembling grapes.Microbes produce endo- and exotoxins, as well as enzymes that negatively affect the cells of human organs and systems in the course of their vital activity.It is the action of these toxins that determines the symptomatology observed in a sick child.
Contents: Understanding aureus classification of staphylococcal infections Types staphylococci detected in children Symptoms of staph in children Diagnosis Treatment of staphylococcal infections in children PreventionUnderstanding aureus
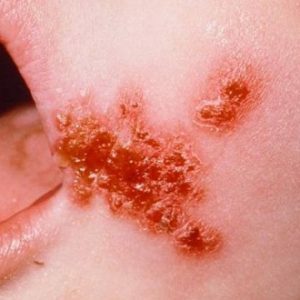
source of the spread of the infectious agent are patients and carriers of pathogenicStrains.Particular danger to others is represented by patients with pneumonia and open foci of purulent inflammation.The causative agent is transmitted by airborne, contact-household and alimetar.Pre-school children often become infected by eating contaminated food and in contact with sick peers.
The group of diseases, the combined term "staph infection" refer pustular inflammation of the skin, digestive disorders in the intestine, ENT pathology, bone inflammation, etc.An infectious agent can be detected in blood, feces and scrapes from the skin surface.
Not all varieties of staphylococci pose a serious threat to adults and children.Moreover, often pathogenic cocci of this family can not cause serious harm to the child.For example, the presence of bacteria on the mucous membranes of the throat does not lead to serious consequences if the baby has a sufficiently high level of immunity.
The greatest danger is Staphylococcus aureus, especially in the active phase of the disease in infants.Relatively high incidence among newborns is due to the fact that at the beginning of life the child does not synthesize IgA immunoglobulin, which largely determines the level of local immunity.
Note: Staphylococcus aureus got its name because of the ability of bacteria to synthesize the pigment that colors the colonies, settling on solid media in a characteristic golden or orange.
classification of staphylococcal infection
According to the accepted international classification, there are the following variants of the disease:
- staphylococcal food poisoning;
- septicemia with unspecified causative agent;
- septicemia caused by Staphylococcus aureus ;
- septicemia, due to other specified staphylococci.
Note: staphylococcal infections usually are sporadic( irregular) character, but in maternity hospitals and wards of hospitals there are epidemic.
Types staphylococci detected in children
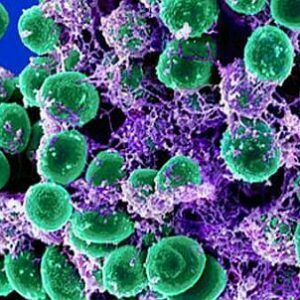 are several types of staphylococci:
are several types of staphylococci:
- saprophytic;
- epidermal;
- is a hemolytic;
- is golden.
Saprophytic is detected in children relatively rarely.It affects the skin and mucous membranes of the urogenital system, causing acute inflammation of the urethra and bladder.This infectious agent is considered to be the least dangerous for the child;With adequate therapy from him can get rid of just a few days.
Epidermal can reproduce in any areas of the skin and mucous membranes of the ENT organs and eyes.It provokes conjunctivitis, purulent urinary tract infections and postoperative complications.In severe cases, endocarditis and even sepsis are not excluded.In the risk group - weak and premature babies, as well as children who underwent various operations.For a child with high immunity, he is not dangerous;The very fact of the presence of epidermal staphylococcus on the mucous membranes of children is regarded as a norm, if the baby's well-being is good.Skin lesions are an indication for local therapy.
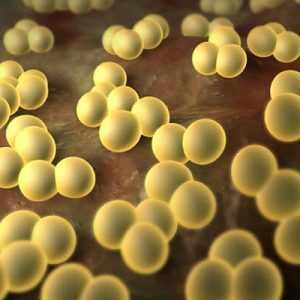 Hemolytic staphylococcus can cause purulent inflammation in many organs.It affects the skin, organs of the urinary system and endocardium.Against the background of this infection with reduced immunity and in the absence of treatment, the development of a septic state is possible.
Hemolytic staphylococcus can cause purulent inflammation in many organs.It affects the skin, organs of the urinary system and endocardium.Against the background of this infection with reduced immunity and in the absence of treatment, the development of a septic state is possible.
Staphylococcus aureus is the most pathogenic for humans, since it can cause severe purulent inflammation in virtually any tissue and organs.It is characterized by high virulence( disease) and resistance to drying, boiling, solar ultraviolet and the effects of antiseptics such as hydrogen peroxide and ethanol.
Specific feature of this pathogen is the ability to synthesize the enzyme coagulase.Infectious agent quickly adapts to antibiotics, acquiring resistance( immunity).Especially dangerous are methicillin-resistant strains resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics( preparations of cephalosporin and penicillin series). Detection of this infectious agent in feces analysis or swabs from mucous membranes is the basis for initiating complex therapy only when the child's deteriorates.
Symptoms of staphylococcus in children
Clinical manifestations of staphylococcal infection are very diverse.
They depend on the following factors:
- type of pathogen;
- the age of the child;
- immune status;
- previous sensitization;
- microorganism habitat;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- general condition of the baby.
Important: the most pronounced reaction from the immune system is observed when infected with Staphylococcus aureus.
The task of the doctor is the timely establishment of the correct diagnosis and the appointment of adequate therapy.Parents at the same time need to inform the specialist in detail about changes in the state of the child.Self-medication is unacceptable, since it can cause serious and even life-threatening complications of the baby.
It is accepted to consider 2 forms of staphylococcal infection in children - early and late.In the first case, the clinical symptomatology develops a few hours after the infectious agent enters the child's body.In the second - signs of the disease appear only after 2-5 days.
The main symptoms of staphylococcus in children:
- pyoderma( pustules on the skin);
- boils;
- skin rashes and the appearance of areas of pigmentation;
- stomatitis( inflammation of the oral mucosa);
- inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye;
- temperature increase( up to 38 ° C and above);
- moodiness;
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- restless sleep;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea.
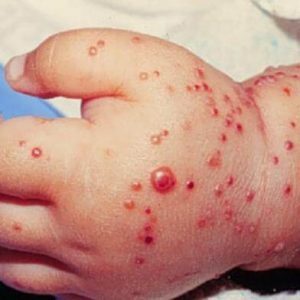
Important: if the timely treatment of staphylococcus is not initiated, children may develop generalized septic lesions.
Diagnosis
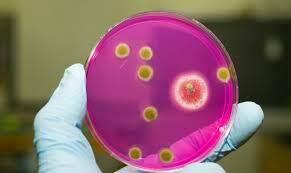 It is not possible to establish the nature of the infection( type of pathogen) at home, so when a child develops the first symptoms of staphylococcal infection, it is strongly recommended that you seek medical help immediately.
It is not possible to establish the nature of the infection( type of pathogen) at home, so when a child develops the first symptoms of staphylococcal infection, it is strongly recommended that you seek medical help immediately.
For the identification of an infectious agent, a doctor primarily assigns a series of tests.A laboratory study of blood, feces, purulent discharge and washings from the skin and mucous membranes is carried out.It is advisable to take a material intake in the acute phase of the disease, since microorganisms are most active during this period, and they are easier to detect.
Important: The presence of staphylococci in the blood does not yet indicate sepsis.If the reproduction of bacteria is not observed, then we are talking about so-called."Transient bacteremia".
The next step is to establish the sensitivity of the detected strain of staphylococcus aureus to antibacterial drugs.This is necessary for the appointment of adequate antibiotic therapy.
Important: in the course of a standard blood test, Staphylococcus aureus is not always immediately apparent.The most informative laboratory diagnostic method is bacteriological culture.
Serological blood test
The material for the study is the blood serum of a sick child.The diagnosis is confirmed if it contains specific antibodies to the infectious agent.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction is an additional analysis that allows to identify single molecules of staphylococcus DNA.
Analysis of expressed breast milk of the mother
This study is necessary if staphylococci are detected in the stool of a breastfeeder in an amount exceeding the permissible standards.Analysis allows you to identify a possible source of infection( microorganisms are easily transmitted to the baby from the mother).
Positive result is a good reason for the immediate interruption of breastfeeding with the transfer of the child to artificial milk formula.
Note: the insignificant presence of bacteria in the body of the baby still does not allow talking about staphylococcal infection, especially if the child's well-being does not suffer.Treatment in such situations is not required.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection in children

Treatment of staphylococcus in children is prescribed after assessing the overall clinical picture and the combination of symptoms and laboratory data.
Local treatment of staphylococcus in children
Local treatment involves the treatment of wounds( including postoperative) and skin rashes with antiseptic drugs for external use.One of the most effective antiseptics is the pharmacy solution of the brilliant green, i.e., the usual "zelenka".To her is very sensitive even the most dangerous of staphylococci - golden.For external treatment of the skin, hydrogen peroxide, 70% ethanol and Vishnevsky liniment are also used( this ointment is especially effective in pyoderma).
As an additional treatment method, washing and rinsing of the throat and mouth with weak antiseptic solutions are indicated.
General treatment
Antibiotic therapy plays the leading role in the therapy of infection.The drugs can be injected( intramuscularly, and in the hospital according to the indications - and intravenously) or prescribed for reception per os.The child with staphylococcal infection shows the intake of vitamin and mineral complexes, agents for improving the overall metabolism, as well as immunoglobulins to strengthen immunity.
With generalized infection( sepsis) in hospitals, staphylococcus is treated in children using blood transfusions - blood and plasma transfusions.
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be indicated, the purpose of which is to sanitize the focus of purulent inflammation.
Prevention
It is known that any infection, including staphylococcal infection, is much easier to prevent than cure.For healthy children with high immunity, staphylococcus is of no danger - protective mechanisms are able to cope with it independently.Thus, the main goal of prevention is to prevent the impact of negative factors on the child's body.
Among the factors that adversely affect immunity, include:
-
 low level of personal hygiene;
low level of personal hygiene; - inactivity( insufficient activity);
- improper power supply;
- lack of vitamins in the diet;
- stress;
- adverse environmental conditions.
A child from an early age should be taught to wash hands regularly with soap( young children should be assisted by parents), he should not be allowed to put toys and other objects on which bacteria can be present.
 Important: to strengthen immunity and reduce the likelihood of developing staphylococcus in children, kids need to often take out for a walk in the fresh air, with preference given to mobile games.In the diet it is undesirable to include smoked products, sausages and, especially, fast food.Consumption of flour and sweets should be limited.It is desirable to travel more often with the child to country walks, so that he has the opportunity to breathe uncontaminated air.
Important: to strengthen immunity and reduce the likelihood of developing staphylococcus in children, kids need to often take out for a walk in the fresh air, with preference given to mobile games.In the diet it is undesirable to include smoked products, sausages and, especially, fast food.Consumption of flour and sweets should be limited.It is desirable to travel more often with the child to country walks, so that he has the opportunity to breathe uncontaminated air.
Preschool and primary school children are shown to be hardened( regular rubbing and pouring) to strengthen the body's defenses, as well as physical education and sports.
Chumachenko Olga, pediatrician