General blood test: norms, transcript of blood test and preparation for analysis
 Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma, as well as cells( shaped elements), whose concentration can vary significantly under different pathological conditions.Deciphering the clinical analysis of blood allows to judge the possible presence or absence of inflammation, intoxication of the body, dehydration( dehydration), bleeding, cancer, diseases of the hematopoietic system, etc.
Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma, as well as cells( shaped elements), whose concentration can vary significantly under different pathological conditions.Deciphering the clinical analysis of blood allows to judge the possible presence or absence of inflammation, intoxication of the body, dehydration( dehydration), bleeding, cancer, diseases of the hematopoietic system, etc.
What blood tests do they take?
Modern laboratory diagnostics is based mainly on blood research.The indicators of this basic binding substance of the body can tell a lot about the state of human health.The most informative - and therefore most often conducted - are a biochemical and general blood test.
What is a common blood test?
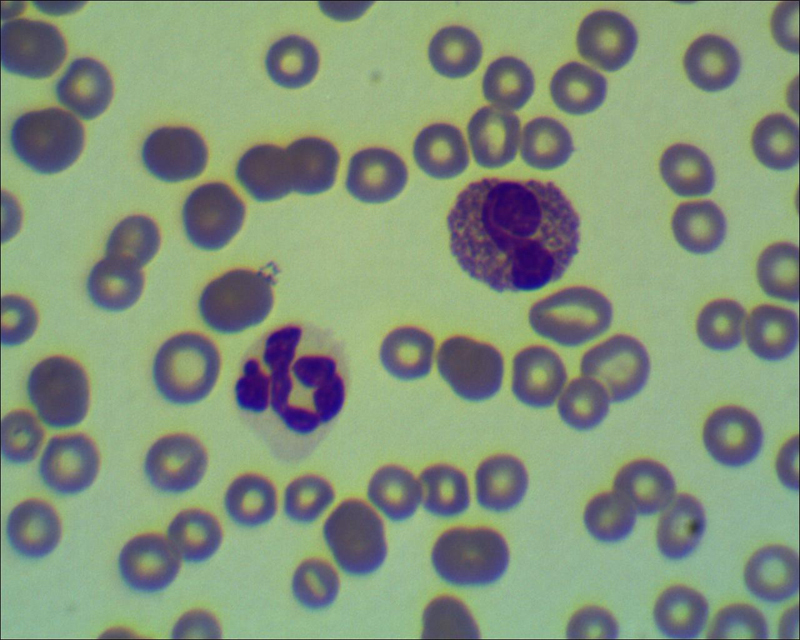 A general blood test is one of the most important clinical trials that is performed in most diseases, as well as in the preventive examination( clinical examination).When diagnosing blood diseases, this test is given a leading role.
A general blood test is one of the most important clinical trials that is performed in most diseases, as well as in the preventive examination( clinical examination).When diagnosing blood diseases, this test is given a leading role.
Important: a common finger blood test is taken on an empty stomach in the morning.To avoid distortion of results for 8 hours you can not eat, and you can drink only water.
Before taking a blood test, drinks containing alcohol, as well as tea, coffee and juices are not allowed.
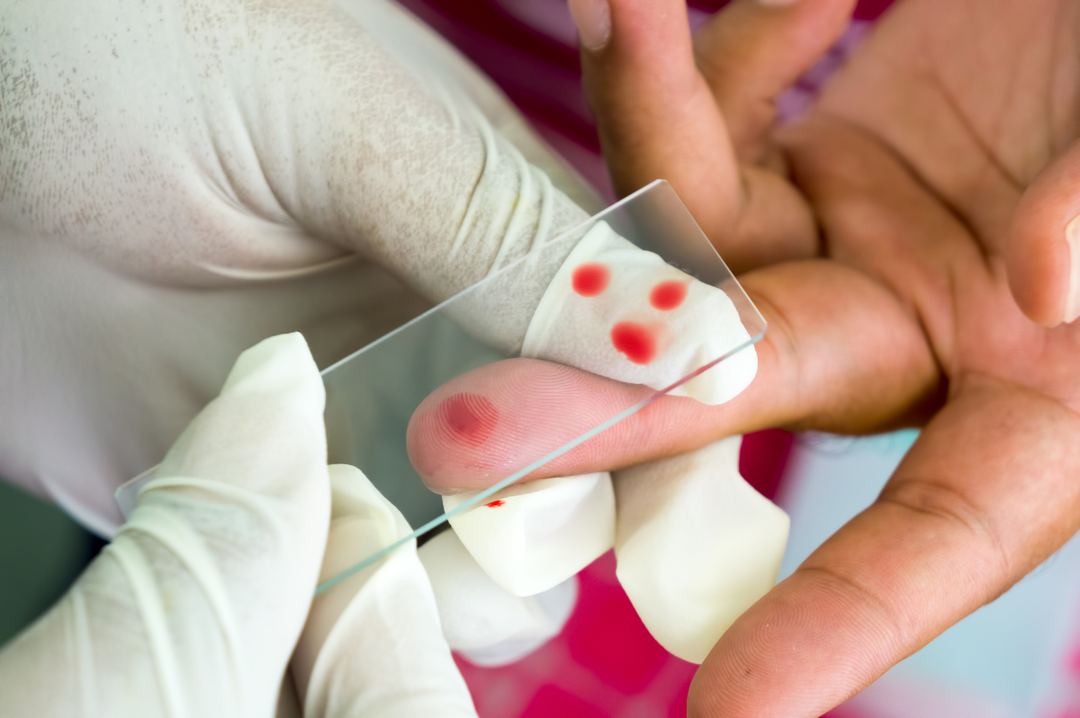
Traditionally, blood sampling is carried out from an anonymous finger, piercing the skin with a sterile scarifier to a depth of 2-3 mm.The first drop is usually removed with a cotton swab, then blood is taken to determine the hemoglobin level and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the next batch is to establish the amount of white and red blood cells.Smears for microscopy are done with the help of glasses.
 The laboratory study assumes:
The laboratory study assumes:
- determination of the number of different shaped elements( cells);
- establishing the main parameters of blood cells( size, appearance, etc.);
- measurement of the level( concentration) of hemoglobin;
- definition of the leukocyte formula;
- definition of hematocrit.
Key indicators UAC
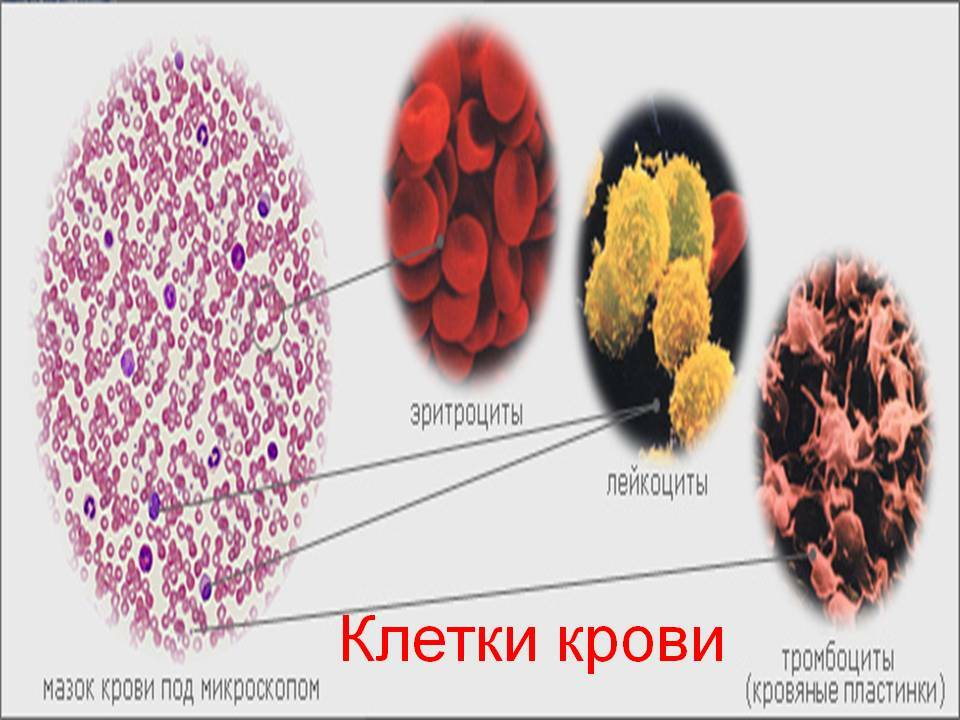
 Hematocrit is the percentage that determines the volume ratio of cell mass to plasma.Erythrocyte indices reflect the main characteristics of red blood cells.
Hematocrit is the percentage that determines the volume ratio of cell mass to plasma.Erythrocyte indices reflect the main characteristics of red blood cells.
Hemoglobin( HGB) is a "respiratory pigment" - an iron and protein compound that is responsible for transporting oxygen to organs and tissues.
Note : Physiological reduction in hemoglobin is possible in infants of the first year of life.
A low level of hemoglobin indicates the development of anemia( anemia).
Important: anemia often develops on the background of blood loss, disturbance of red body formation or during their accelerated destruction.It can be a clinical manifestation of a number of pathologies or be an independent disease.
Erythrocytes( RBC) are highly differentiated cellular elements.They have no nuclei, and the intracellular space is filled with hemoglobin.
The color value of red blood cells reflects the level of respiratory pigment in these red blood cells.
The average volume of red blood cells( MCV) is an indicator that is used to diagnose various types of anemia.Also, in the differential diagnosis of anemia types, an index reflecting the average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes is necessarily taken into account.
The distribution of red blood cells by size( RDW) allows to establish the degree of anisocytosis, that is, the presence of red cells of different volume.
Reticulocytes are called young forms of red cells.
Platelets( PLT) are the cells that form in the red bone marrow, which are responsible for the process of blood coagulation.The granules of these non-nuclear shaped elements contain clotting factors and biologically active substances that are released upon activation of platelets.These cells can attach to the walls of blood vessels and to each other, forming a clot that "clogs" the damage to the vascular walls.The life span of a platelet in the blood is not more than 1-1.5 weeks.Increased bleeding develops if the concentration of these cells is less than 50x103.Such conditions can pose a serious threat to the life of the patient.
Note : in the blood test of a pregnant patient, the number of platelets is reduced, which is the norm.Physiological thrombocytopenia is also recorded in women with menstruation.The number of these cells increases against the background of physical activity.
ESR is the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes.In women, this indicator is normally higher than that of men, which is explained by regular physiological blood loss.An increase in ESR may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process, the presence of infectious agents in the body or into intoxication.
White blood cells( WBCs) are white blood cells formed in the lymphatic system and bone marrow.They provide protection of the body due to the recognition and neutralization of foreign agents, as well as own cells that have undergone pathological changes.Leukocytosis( increase in the number of leukocytes), as a rule, speaks about the development of the inflammatory process.Leukocytes in particular include neutrophils( rod-shaped and segment-nucleated), basophils, eosinophils, monocytes( large white cells) and lymphocytes( elements responsible for acquired immunity).
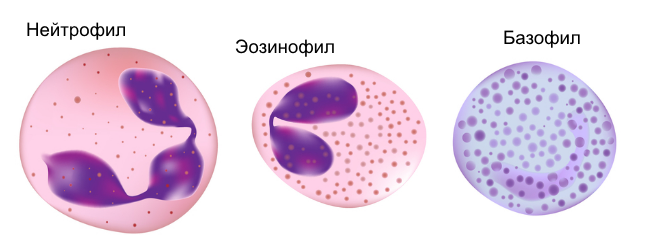
Increasing the number of eosinophils often speaks of helminthic invasions or the presence of diseases of allergic genesis.
Blood test results are prepared in the laboratory for one day.
Normal values
To interpret the results, ie to make any conclusions on the basis of the data obtained in the laboratory blood test, only a doctor can.Nevertheless, some conclusions can be drawn by comparing their common blood test from the finger to the reference( normal) values in the tables given.
Important: the adult blood test values differ from the results of this study in the child.
Table blood test standards in adults:
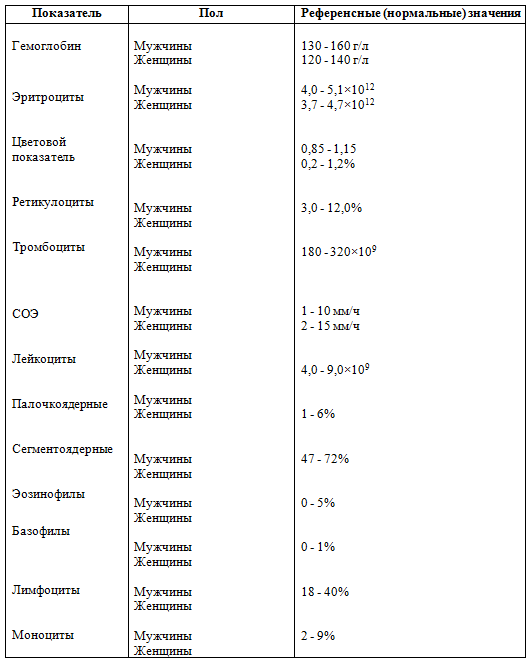
table for decoding of blood tests in children( normal):
| Age | Erythrocytes h1012 | Hemoglobin | Platelets h109 | Leukocytes h109 | erythrocyte sedimentation rate( ESR), mm / h |
| Newborns | 5,0-5,8-6,0 | 215-180 | 273-309 | 30-12 | 2,5-2,8 |
| 1-12 months | 4,6-4,7 | 178-119 | 280-290 | 10-10,5 | 4-7 |
| 2-3 years | 4,6-4,7 | 117-126 | 280-290 | 10,5-11 | 7-8 |
| 4-5 years | 4,6-4,7 | 126-130 | 280-290 | 10-11 | 7-8 |
| 6-8 years | 4,7-4,8 | 127-130 | 280-290 | 8,2-9,7 | 7-8 |
As evidenced by the deviation?
The cause for concern may be leukocytosis, that is, an increase in the number of white blood cells.
The reason for the increase in the number of leukocytes are pathologies such as:
- bacterial infections accompanied by purulent inflammation;
- any malignant neoplasm;
- blood diseases( leukemia).
If there is leukocytosis, then this is the reason for an in-depth and comprehensive medical examination.If there is a suspicion of infectious diseases, an additional blood test for antibodies can be performed.
Important : It should be noted that the number of white blood cells can temporarily increase in the postoperative period, after vaccination, as well as after ingestion or considerable physical exertion.
Leukopenia( a decrease in the number of leukocytes) is often due to a lack of vitamins, adverse environmental conditions or viral infections.As a rule, it is not a reason for serious fears.
ESR depends on the positive charge of the red blood cells, due to which they repel each other.At some pathologies erythrocytes lose a charge, owing to what begin to settle more quickly.
It should be examined if the indicator is 3-5 times higher than the normal values.
The cause of the increase in ESR can be:
- kidney disease - inflammation of the renal pelvis( pyelonephritis) or glomeruli( glomerulonephritis);
- bacterial pneumonia( pneumonia);
- viral hepatitis;
- foci of purulent inflammation( abscesses and phlegmon);
- sepsis( generalized process);
- tuberculosis;
- inflammatory diseases of the pancreas, gallbladder and other organs of the digestive system;
- diseases of rheumatic( autoimmune) origin - rheumatoid arthritis and SLE( systemic lupus erythematosus);
- malignant neoplasm.
Important : To exclude cancer, a special clinical blood test for oncomarkers is performed.
Women should not worry if the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation increases before the onset of menstruation is a physiological norm.The indicator is also increased during pregnancy( from 5 weeks) and comes back to normal only by the fourth week after the baby's birth.
Thrombocytopenia refers to a decrease in the number of platelets below 100 × 109 / L.
Possible causes of thrombocytopenia may include:
- Acute infectious diseases;
- aplastic form of anemia;
- Malignant blood diseases( leukemia).
Please note : special caution should be exercised in detecting a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood test of pregnant women.One of the causes of the pathology is antiphospholipid syndrome, which often leads to miscarriage.
Thrombocytosis( an increase in the number of these cells) indicates the possible presence of the following pathologies:
- acute inflammation;
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process;
- amyloidosis( impaired protein metabolism);
- malignant tumor.
Note : there is no reason to worry if the thrombocytosis is fixed in the postoperative period or after significant physical exertion.
A decrease in the level of hemoglobin with a high probability indicates iron deficiency anemia.
The reasons for the low level of hemoglobin can be:
- Vitamin B12 vitamin deficiency due to impaired digestion( typical for patients suffering from atrophic gastritis and for elderly and senile patients);
- absence in the diet of products of animal origin( vegetarian diet);
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- regular blood loss( including physiological with menstruation).
An increase in this indicator is also a cause for concern.High hemoglobin is noted in malignant smokers, as well as with a large amount of meat in the diet and non-compliance with the drinking regime( insufficient fluid intake).
About the clinical analysis of blood( norms, preparation for analysis and the need for its delivery) tells the pediatrician:
Plisov Vladimir, dentist