AIDS: symptoms, treatment, prognosis
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome( AIDS) is a serious illness that develops against the background of HIV infection and, in fact, is its terminal stage.People infected with HIV do not die from the pathological effects of the immunodeficiency virus on the body, but from the consequences of AIDS - opportunistic infections and oncological diseases.
Table of contents: Who is diagnosed with AIDS?First signs of AIDS Tuberculosis and AIDS Treatment of AIDS ForecastWho is diagnosed with AIDS?
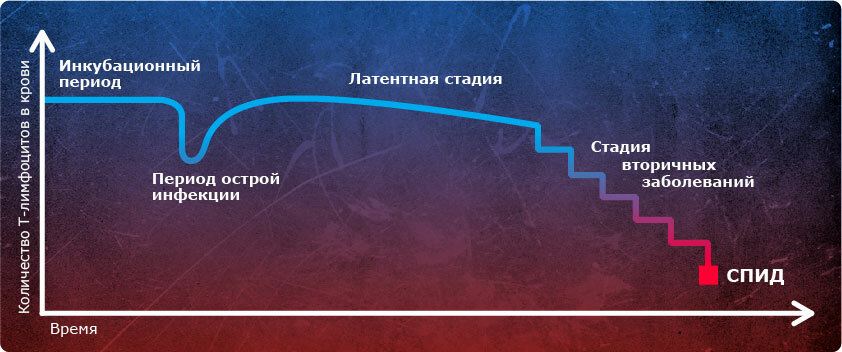
The transition of HIV infection to AIDS is established when a patient has a number of criteria:
-
 Positive HIV test.
Positive HIV test. - Reduces the number of CD4 + lymphocytes to less than 200 cells per μL of blood.These cells are most affected by the immunodeficiency virus, so it is for them to assess the state of the immune system of the patient with HIV infection.
- The emergence of AIDS-indicator diseases - pathological conditions, which in most cases develop in people with HIV due to a critical decrease in immunity.
AIDS-indicator diseases include:
- Bacterial infections( tuberculosis, severe recurrent pneumonia, diseases caused by atypical mycobacteria, widespread salmonellosis).
- Fungal infections( severe candidiasis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia).
- Viral infections( chronic lesions of the skin, mucous membranes, bronchi, lungs, esophagus, caused by the herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus and papillomavirus infections, specific CNS damage by polyomavirus - multifocal leukoencephalopathy).
- Protozoal infections( toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidosis, microsporidosis).
- Other diseases( Kaposi's sarcoma, invasive cervical cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, HIV-encephalopathy, debilitating syndrome, etc.).
Infectious diseases that affect people with AIDS are called opportunistic. Their peculiarity is that the causative agents of these infections often live in the human body, but the immunity does not allow them to become more active.Activation is indicative of severe immunodeficiency.Therefore, the emergence of opportunistic infections is always a direct indication of being tested for HIV.
First signs of AIDS
The manifestations of AIDS are very diverse.Their nature largely depends on the age, conditions and lifestyle, the quality of medical care provided and even the geographical location of the patient.For example, in developing countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis, this infection is the most dangerous for AIDS patients, in Europe, viral and fungal infections come to the fore.
Dermatological signs of AIDS:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which is manifested by a rash, fatty scales on the skin of the face, head, chest, back, severe itching, dandruff.
- Kaposi's sarcoma is a malignant disease in which reddish-brown or bluish spots and nodules appear on the body( more often on the legs).In addition, there is swelling of the extremity and ulcers at the site of the rashes.Similar manifestations can be on the oral mucosa, in the gastrointestinal tract and lungs.The development of Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS is associated with the activation of special herpesvirus.
- Simple and herpes zoster, prone to severe and protracted flow with extensive damage to the skin and visible mucous membranes.
- Multiple warts, molluscum contagiosum, genital warts in the genital area, on the face, in the mouth.
- "Hairy" leukoplakia of the oral cavity - white lines and spots in the tongue, which are of a viral nature.
- Persistent candidiasis of the oral cavity and perianal zone.
- Fungal infection of the skin and nails.
Gastrointestinal manifestations:
- Diarrhea, which lasts more than a month and leads to a violation of absorption of nutrients in the intestines, so patients are very weak.
- Inflammation of the esophagus, which is characterized by heartburn, difficult and painful swallowing of food, nausea, a feeling of something stuck in the throat.The occurrence of such inflammation can be associated with the activation of candida fungi or herpetic infection.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Inflammation of the rectum( proctitis), which is accompanied by itching, burning, sensation of heaviness in the anus.In homosexuals most often develops herpetic proctitis.
Respiratory manifestations:
- Frequent and severe pneumonia that does not respond well to treatment.The most characteristic of AIDS is pneumonia, caused by pneumocysts.
- Tuberculosis of the lungs.
Neurological manifestations of ( may be the result of defeat of the immunodeficiency virus of nerve structures or consequence of opportunistic infections):
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Pathological conditions in which the myelin sheath of nerve fibers in the brain or spinal cord is damaged, which results in impaired conduction of nerve impulses and the appearance of various neurological symptoms( paresis, speech and vision disorders), as well as mental problems.
- Encephalopathy with the development of dementia.
Manifestations from the side of the eye:
- Retinitis( inflammation of the retina) caused by the activation of cytomegaloviruses and herpesviruses.It is accompanied by a persistent drop in vision.
- Choroiditis( inflammation of the choroid of the eye), characteristic of pneumocystis infection.
- Kaposi's sarcoma, localized on the eyelids and conjunctiva.
Tuberculosis and AIDS
Many people become infected with mycobacterium tuberculosis as a child, but the development of the infectious process is blocked by the immune system.Therefore, it is quite natural that the activation of tuberculosis in HIV-positive individuals occurs very often.And with the transition of HIV infection to the stage of AIDS, the tuberculosis process spreads throughout the body.It affects not only the lungs, but also the bone marrow, urogenital system, bones, digestive tract, liver, lymph nodes, CNS and other organs.In addition, patients have severe intoxication, exhaustion.People simply "burn out" if they are not provided with medical assistance on time. In developing countries, tuberculosis is the leading cause of death in AIDS.
Treatment of AIDS
Treatment of AIDS patients includes several areas:
- Mandatory hospitalization of patients in specialized departments of clinics dealing with HIV-infected patients.
- Skilled care.
- Complete nutrition.
- Active antiretroviral therapy, which even at the stage of AIDS makes it possible to increase the number of CD4 + lymphocytes so that the patient's body at least somehow began to resist infections.
- Specific treatment aimed at combating evolved secondary diseases.
- Chemoprophylaxis of opportunistic infections
Forecast
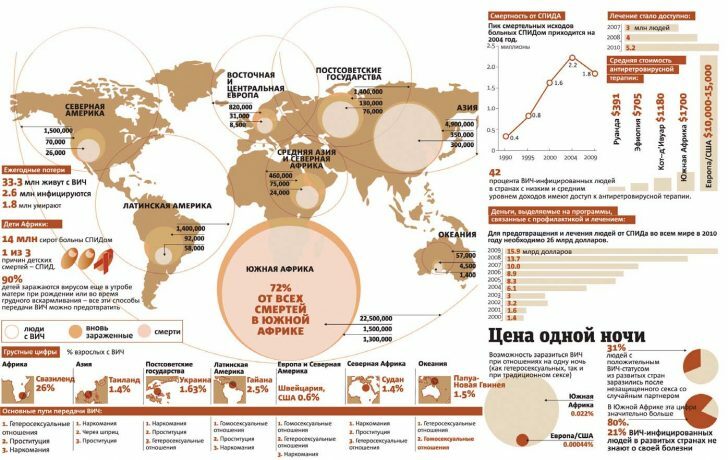
The lifespan of patients after diagnosing AIDS without proper treatment is only one to two years.Qualified medical care can extend this period.
In addition,
- has a significant impact on the survival of patients with AIDS: The tolerability of medications taken( many patients have serious side effects during antiretroviral treatment).
- Relation of patient to prescribing physicians.
- Living Conditions.
- Presence of concomitant diseases( eg, viral hepatitis).
- Drug taking.
That is, we can conclude that the life expectancy for AIDS patients is very disappointing. Therefore, do not be afraid of HIV testing, especially if there are any risk factors.This terrible infection must be identified and treated in a timely manner, rather than waiting for the development of AIDS!
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist-doctor