Streptococcus and infectious diseases caused by it
 Streptococci are bacteria that live in the bodies of animals, on the skin, in the respiratory system and the intestines of a person.Many of these microorganisms are not dangerous for people, that is, they belong to the saprophyte microflora.However, there are pathogenic streptococci, which cause serious diseases, ranging from angina and streptoderma, ending with meningitis and sepsis.In addition, streptococci play an important aetiological role in the development of a number of systemic ailments - rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, endocarditis, etc.
Streptococci are bacteria that live in the bodies of animals, on the skin, in the respiratory system and the intestines of a person.Many of these microorganisms are not dangerous for people, that is, they belong to the saprophyte microflora.However, there are pathogenic streptococci, which cause serious diseases, ranging from angina and streptoderma, ending with meningitis and sepsis.In addition, streptococci play an important aetiological role in the development of a number of systemic ailments - rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, endocarditis, etc.
Diseases caused by streptococci
All streptococci are divided into four groups( depending on biochemical, biological and other properties):
- Alpha hemolytic.
- Beta-hemolytic( A, B, C).
- Gamma-hemolytic.
- Non-hemolytic.
Non-hemolytic streptococci for a person are not dangerous - they do not cause any illnesses, which can not be said about their hemolytic congeners.
So, alpha-hemolytic streptococci are the cause of infectious endocarditis( inflammation of the inner shell of the heart and damage to the heart valves), purulent periodontitis( inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding the root of the tooth), and when internal organs enter abscesses in internal organs.In addition, the microorganisms of this group play a leading role in the development of caries.
Beta-hemolitic streptococci - the most pathogenic among all streptococci. The development of the following diseases is associated with them:
-
 With group A streptococcus - scarlet fever, sore throat, erysipelas, streptoderma, purulent inflammatory processes in the internal organs, sepsis, rheumatism, glomerulonephritis.
With group A streptococcus - scarlet fever, sore throat, erysipelas, streptoderma, purulent inflammatory processes in the internal organs, sepsis, rheumatism, glomerulonephritis. - With streptococcus group B( they are especially dangerous for newborns) - skin pustular diseases, meningitis and sepsis in infants.These microorganisms live in the urogenital organs of 15-45% of women and, in the presence of conducive conditions, enter the baby's body in utero or during childbirth.In this case, the mother of any manifestations of streptococcal infection may not be, or signs of inflammation of the urinary tract develop.
- With streptococcus group C - erysipelas.
Finally, gamma-hemolytic streptococci is in most cases the saprophytic( normal) microflora of the intestine and upper respiratory tract, which, under certain conditions, can cause infections of the urinary system, wounds, and also septic endocarditis.
How does streptococcal infection occur?
Sources of pathogenic streptococci are sick people and healthy carriers. Infection occurs mainly airborne and contact-household( through a common dish, dirty hands, care for the sick, etc.) ways.This penetrates the pathogen into the body through the respiratory tract, less often through damage to the skin, as well as umbilical wound in newborn babies.
After colonization in the primary focus, streptococci begin to actively release enzyme substances, due to which microbial cells manage to penetrate into the blood and lymph.In addition, streptococci in the process of vital activity produce toxins, because of which patients develop a pronounced syndrome of intoxication and other signs of the disease.
In addition to the above described ways of infection with streptococcus, autoinfection is possible. For example, when streptococci enter the blood from the abscesses on the skin with unsuccessful squeezing out, from purulent foci in the oral cavity with dental manipulations, and also from the nasopharynx when removing the palatine tonsils or adenoids.In this way, microorganisms spread to internal organs and cause development of purulent processes there.
But systemic diseases, provoked by streptococci, arise not so much because of infection, but because of allergization of the body.Developed by the immune system antibodies to streptococci, are able to attack their own tissues in the joints, kidneys, heart.Therefore, when these microorganisms are long present in the human body or re-enter into it, due to the hyperimmune reaction, the tissues of these internal organs are damaged.
Symptoms of the most common streptococcal diseases
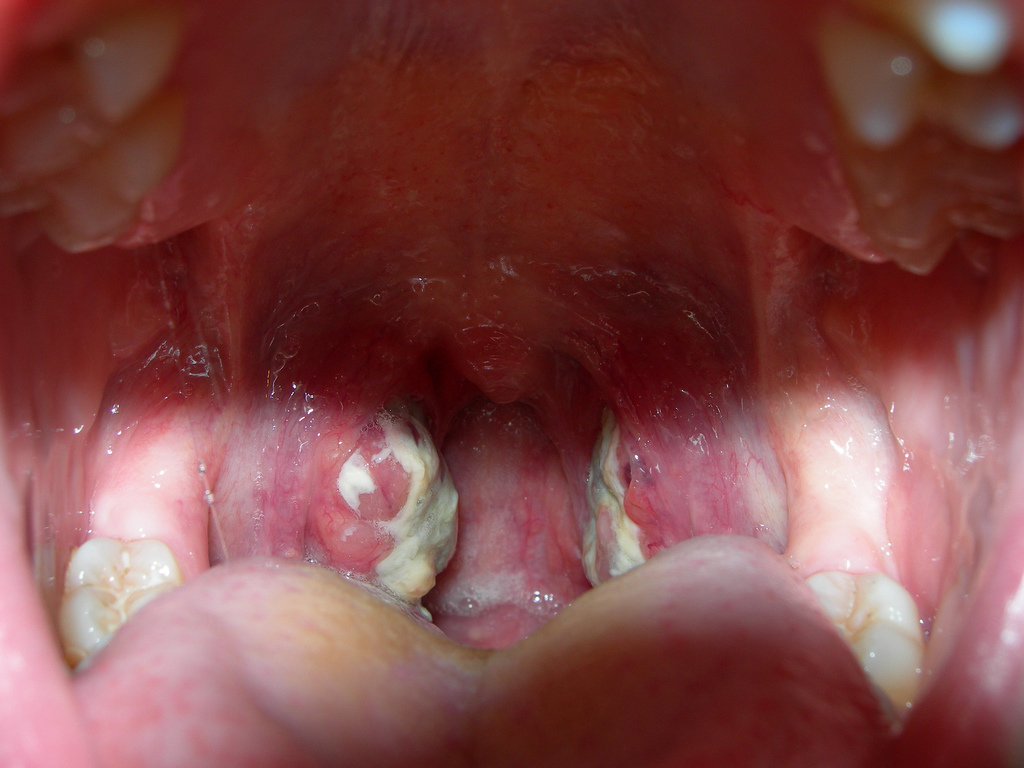
In childhood, streptococcal infection usually occurs in the form of scarlet fever, and in adults - angina.If you do not start taking antibiotics in time for these diseases and allow a prolonged persistence of streptococci in the body, rheumatism, endocarditis, arthritis and glomerulonephritis may develop.
Streptococcal angina appears with the following symptoms:
- A sudden jump in body temperature to high digits( 39 degrees and above).
- Pain in the throat.
- Weakness, headache, chills.
- Relief in the joints.
- Increased palatine tonsils( they seem to swell and are covered first with small pustules, and over time - yellowish purulent deposits).
- Increased cervical lymph nodes.
In addition to the involvement of tonsils and internal organs( purulent processes in them do not have symptoms specific for streptococcal infection), streptococci cause specific skin diseases:
-
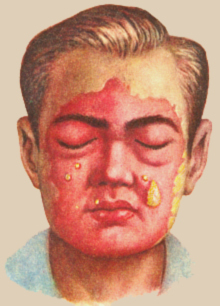 Roger( erysipelas) . This is an acute and often recurrent disease in which general symptoms( high fever, weakness, muscle pain) and local signs of infection appear - red spots with clear boundaries, rising above the skin and covering large areas of the body, can be blisters.For the first time erysipelas appears on the face, and recurs more often on the lower extremities.
Roger( erysipelas) . This is an acute and often recurrent disease in which general symptoms( high fever, weakness, muscle pain) and local signs of infection appear - red spots with clear boundaries, rising above the skin and covering large areas of the body, can be blisters.For the first time erysipelas appears on the face, and recurs more often on the lower extremities. - Streptoderma - streptococcal pyoderma.It provokes the development of this ailment skin pollution, exposure to high or low temperatures, varicose veins, micro-trauma and reduced immunity caused by stress, etc.The superficial form of streptoderma manifests itself as impetigo.It develops in the open parts of the body, in the corners of the mouth, on the wings of the nose, behind the auricles.First there are patchy-tubercular rashes, then in order bubbles, ulcers, honey crusts that last for several days and disappear completely.With deeper skin lesions, streptococcus develops vulgar ectima( deep ulcers are formed), leaving behind scars.
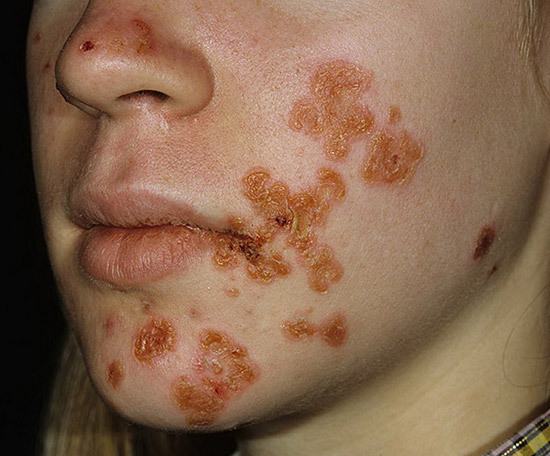
Streptococcus in children
For streptococcal and newborn infants, streptococcal infection presents a great danger.They are due to infection with streptococcus from the mother in utero or in childbirth develop skin diseases( impetigo, vulgar ectima), as well as very severe meningitis and sepsis.To prevent infection of newborns, all pregnant women are examined for streptococci in the last trimester, risk factors are assessed( sowing of pathogenic streptococci from urine during pregnancy, neonatal streptococcal infection in previously born children, etc.) and, if necessary, prophylactic antibiotic therapy.
In children after a year, streptococcal infection is most often manifested in the form of scarlet fever.
Symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- The rash, after its disappearance, the skin is strongly flaky.
- Angina.
- "Crimson" language.
- High temperature.
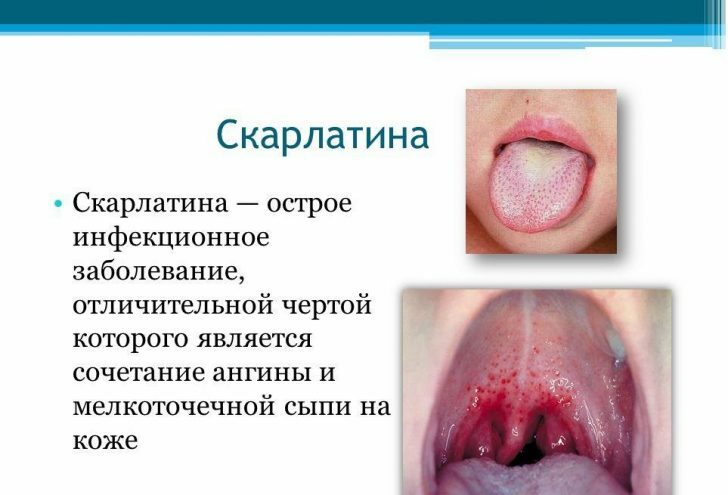
This disease against the background of antibiotic therapy almost always ends in complete recovery on the 7-10th day.In the subsequent entry into the body of pathogenic streptococci leads to the development of angina, repeated cases of scarlet fever - a rarity.
Diagnostics
 Most of the diseases caused by streptococci, doctors diagnosed by a specific clinical picture( this refers to scarlet fever, sore throat, erysipelas, streptoderma).To confirm the diagnosis, an analysis is made for streptococcus( take smears from the surface of the tonsils, inflamed foci on the skin, sow urine, pus, blood, etc.).For more rapid diagnostics of streptococcal infection, modern express tests are increasingly being used.
Most of the diseases caused by streptococci, doctors diagnosed by a specific clinical picture( this refers to scarlet fever, sore throat, erysipelas, streptoderma).To confirm the diagnosis, an analysis is made for streptococcus( take smears from the surface of the tonsils, inflamed foci on the skin, sow urine, pus, blood, etc.).For more rapid diagnostics of streptococcal infection, modern express tests are increasingly being used.
Treatment of streptococcal infection
 The main and mandatory component of anti-streptococcal therapy is antibiotic therapy . It allows much quicker elimination of the infection and prevent the development of complications from the heart, kidneys and other organs.In the case of angina and scarlet fever, no local antiseptic drugs can replace the use of antibiotics.The choice of a specific antibacterial agent for the treatment of these diseases is determined by the sensitivity of microorganisms.And since all streptococci are sensitive to penicillins, with streptococcal infection, first of all, drugs of this group are used, and as an alternative - cephalosporins, macrolides.
The main and mandatory component of anti-streptococcal therapy is antibiotic therapy . It allows much quicker elimination of the infection and prevent the development of complications from the heart, kidneys and other organs.In the case of angina and scarlet fever, no local antiseptic drugs can replace the use of antibiotics.The choice of a specific antibacterial agent for the treatment of these diseases is determined by the sensitivity of microorganisms.And since all streptococci are sensitive to penicillins, with streptococcal infection, first of all, drugs of this group are used, and as an alternative - cephalosporins, macrolides.
For skin diseases caused by streptococcus, the advisability of systemic antibiotic therapy is determined by the physician individually.However, erysipelas and protracted streptodermia with a widespread nature of the inflammatory process are always an indication for the prescription of antibiotics.
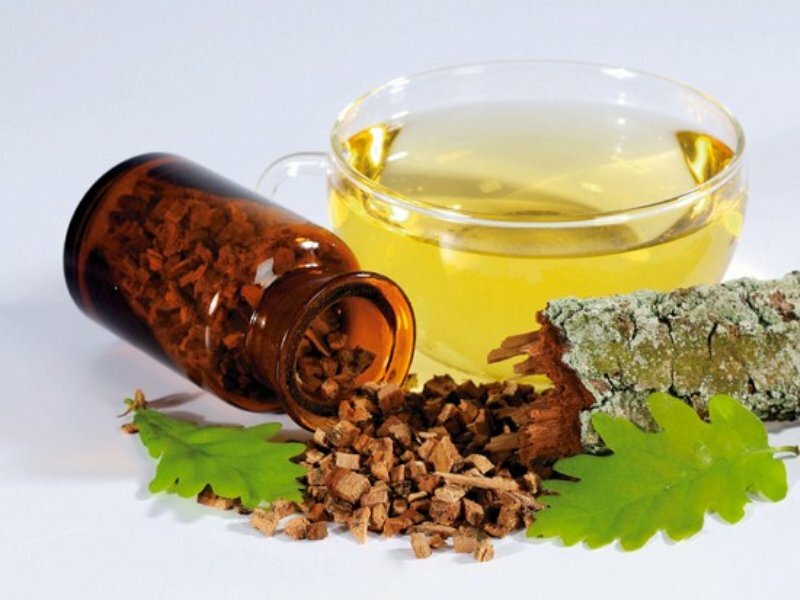 Treating folk remedies with streptococcal infection can also be used, but solely as ancillary.In particular, the medicinal herbs( oak bark, chamomile, string) are considered effective.They are recommended for use for gargling and treating the affected skin.In addition, you can prepare broths of dogrose, cranberry fruit and take them inside.These drinks contain a lot of vitamin C, which is necessary for fighting the infection.
Treating folk remedies with streptococcal infection can also be used, but solely as ancillary.In particular, the medicinal herbs( oak bark, chamomile, string) are considered effective.They are recommended for use for gargling and treating the affected skin.In addition, you can prepare broths of dogrose, cranberry fruit and take them inside.These drinks contain a lot of vitamin C, which is necessary for fighting the infection.
Prevention of streptococcal infection
There is no vaccine for streptococcal infection, therefore, strong immunity can only withstand pathogenic microorganisms trapped in the body.In addition, in a weakened organism, even "their own" streptococci can cause serious diseases. Therefore, the main thing in the prevention of streptococcal infection is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and the implementation of measures that promote the strengthening of general and local immunity.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist-doctor