Pulmonary fibrosis: symptoms and treatment
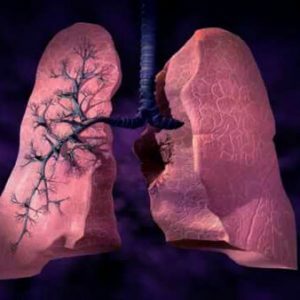
The process of formation in the lungs of cicatricial( fibrous) tissue in medicine is classified as pulmonary fibrosis.This pathology is characterized by impairment of respiratory function, decreased elasticity and extensibility of lung tissue, difficulty in passage of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the wall of the alveoli.
Table of contents: Types and forms of pulmonary fibrosis Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis How to diagnose lung fibrosis Treatment of pulmonary fibrosisTypes and forms of pulmonary fibrosis
This disease can be one-sided, two-sided.In addition, doctors distinguish focal pulmonary fibrosis( a condition where only a small fragment of the lung is affected) and total( pathology captures all of the lungs).
The proliferation of connective tissue can occur at different intensities, this fact makes it possible to distinguish between the following forms of pulmonary fibrosis:
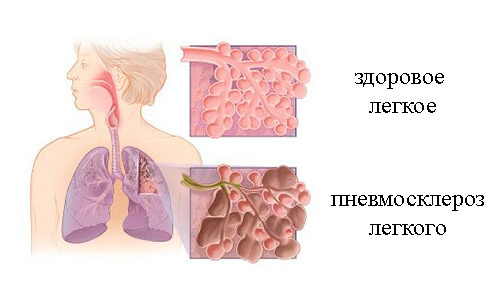
- pneumofibrosis( fibrosis) - the proliferation of connective tissue is mild, it always alternates with unchanged pulmonary tissue;
- pneumosclerosis( sclerosis) - replacement of pulmonary connective tissue sites is of a crude nature, there is a compaction of the lungs;
- Cirrhosis of the lungs - lung tissue was completely replaced by a connective tissue, the bronchi and lung vessels were damaged.
As the reasons for the development of the disease under consideration are many, physicians distinguish its forms according to this factor:
- is a drug fibrosis - it develops on the background of a forced long-term use of medications prescribed for the treatment of arrhythmia or oncological neoplasms;
- primary( idiopathic) fibrosis - pathology develops for no apparent reason;
- fibrosis is a consequence of pulmonary diseases of the lungs - we mean silicosis, asbestosis and others;
- fibrosis against the background of existing connective tissue diseases in the body - for example, systemic scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis and / or systemic lupus erythematosus;
- fibrosis of an infectious origin - may occur after pulmonary tuberculosis or pneumonia.
From the above data it can be concluded that the causes of lung fibrosis development are:
- long-term administration of specific medications;
- pneumonia;
- effect of harmful production factors;
- pathology of connective tissue;
- vasculitis( inflammation of the walls of blood vessels);
- pulmonary tuberculosis.
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis
There are several specific signs of the disease in question. The most important symptom is shortness of breath, which first appears only on the background of physical exertion, but as the disease progresses, this symptom worries the patient and at rest. Another specific symptom of lung fibrosis is a cough that can be dry or wet with the separation of a small amount of sputum, but is always characterized by a prolonged course and the uselessness of the treatment.
In addition to these specific features, for pulmonary fibrosis will be characteristic:
-
 pallor, and as progression of pathology and cyanosis / cyanosis, skin integument;
pallor, and as progression of pathology and cyanosis / cyanosis, skin integument; - change in the shape of the fingers - thickening of the fingers, bulge of the nail plate, which are noted only in the long course of the pathological process;
- heart failure( pulmonary heart) - characterized by increased heart rate, swelling on the legs, swelling and pulsation of the cervical veins, chest pains, it can only be with prolonged pulmonary fibrosis and with extensive damage to the respiratory system.
Literally from the first days of the considered disease a person begins to note weakness, increased fatigue.These symptoms are not specific, therefore, special attention does not deserve the opinion of the patient, although during the diagnostic activities the specialist will be able to identify pulmonary fibrosis.
How the diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis is carried out
First of all, the physician will collect the following information from the patient:
- complaints - weight loss, dyspnea, persistent cough, general weakness;
- history of the disease - when the first symptoms appeared, whether the intensity of its manifestations was noted;
- history of life - the patient should notify the doctor about cases of tuberculosis or pneumonia, rheumatoid arthritis or systemic scleroderma.Moreover, it does not matter when the patient has suffered these diseases, whether they are present at the moment.
For the accurate diagnosis, the doctor will perform a number of instrumental and laboratory studies of the patient:
-
 auscultation - listening to the lungs;
auscultation - listening to the lungs; - percussion - tapping of the lungs;
- spirography - elucidation of lung volume and degree of respiratory function;
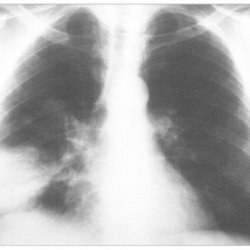
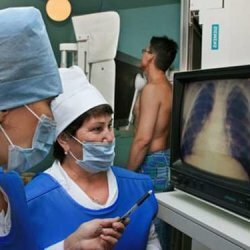
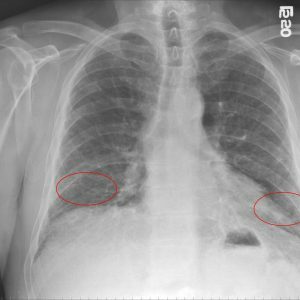
- chest X-ray - this study allows specialists to detect changes in lung tissue and continue diagnostic activities;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging - allows more detailed identification and study of the nature of pathological changes in the lung tissue;
- lung biopsy is a histological examination of a small piece of lung tissue that the doctor receives while endoscopically examining the bronchi.
Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis
There is no specific treatment for the disease under consideration, but the general recommendations are as follows:
- The effect of damaging factors should be avoided.It's about professional harm, and here the patient does not have any options - just a change of labor activity.
- Regularly conduct oxygen therapy.Such a procedure is carried out exclusively in policlinic conditions and according to the prescription of the attending physician, represents inhalation of oxygen by means of special apparatuses.
- If limited areas of pneumosclerosis have been diagnosed, but they do not appear clinically, the therapy is not performed at all, but the physician should conduct dynamic observation of the patient.
Note: if the patient has been diagnosed with total pulmonary fibrosis, then lung transplantation is indicated, and if there is a functionally inadequate limited area of fibrosis, then it is completely removed.
Despite the absence of any specific treatment, the patient should be supervised and follow all the recommendations of specialists. If diagnosed lung fibrosis is ignored, complications may develop:
- pulmonary hypertension;
- chronic respiratory failure;
- "pulmonary heart" of chronic course;
- attachment of secondary infection.
Pulmonary fibrosis is considered quite an insidious disease - it is difficult to diagnose and at the late stages of development, there is no medication for any medication, but there is always a risk of developing the above complications.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapist of the highest qualification category