Lymphoma of Hodgkin: symptoms, treatment

Lymphomas are malignant neoplastic lesions, affecting mainly the lymph nodes and vessels.As the process develops, it affects all organs and systems, and causes anemia( anemia).More than three dozen diseases of this group are divided into 2 main types - Hodgkin's lymphoma( lymphogranulomatosis) and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
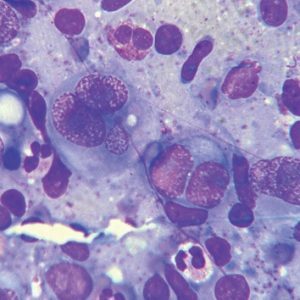
Note: type of lymphoma is determined during microscopy of tissue samples of lymph nodes.A characteristic feature of lymphogranulomatosis is the presence of abnormal Reed-Sternberg cells.
Table of contents: Causes of development of Hodgkin's lymphoma Classification of Hodgkin's lymphoma Symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma Diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma Treatment options for Hodgkin's lymphomaHodgkin's lymphoma( lymphogranulomatosis) is a well-studied pathology.More recently, this systemic disease was regarded as incurable, but nowadays with timely diagnosis and adequate complex therapy one can achieve complete recovery of the patient or persistent long-term remission.
Hodgkin's lymphoma is detected in people of any age;Sometimes it is diagnosed even in children under 10 years old.Earlier it was believed that there are 2 age peaks of incidence - from 15 to 40 years and after 50 years.However, in a retrospective study of histological samples using the immunophenotyping procedure, it was found that in many cases the diagnosis previously exposed to people of age was erroneous, and the second peak was virtually absent.Older patients have a higher probability of recurrence.
Note: for Hodgkin's lymphoma accounts for 1% of the total number of malignant tumors. In our country, the incidence rate is 2-3 cases per 100 thousand people.In men, this tumor is diagnosed more often.
Causes of development of Hodgkin's lymphoma

To date, the exact reasons for the development of Hodgkin's lymphoma are not completely clear.In the second half of the last century, a correlation was established between the incidence of lymphogranulomatosis and the infection with the Epstein-Barr virus.It is believed that in a number of cases there is a genetically conditioned predisposition.
Note: lymphogranulomatosis more often develops in people belonging to the Caucasoid race.
The most likely causes of Hodgkin's lymphoma are:
- the effect of substances with a carcinogenic effect( including agricultural pesticides and herbicides);
- diseases of infectious genesis( in 40% of cases - mononucleosis);
- hereditary predisposition;
- decreased immunity( mainly - with HIV infection).
Classification of Hodgkin's lymphoma
According to morphological characteristics, it is common to distinguish 4 types of Hodgkin's lymphoma:
- variant with nodular sclerosis( up to 45% of cases);
- mixed-cell type( 35%);
- lymphogistiocytic( approximately 15%);
- lymphoid depletion( about 5%);
There is also a nodular( nodular) form with a lymphoid predominance.This type of disease is characterized by the most favorable course and leaves a high chance for complete recovery.
Symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma
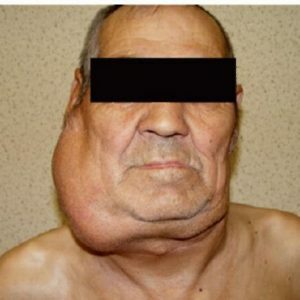
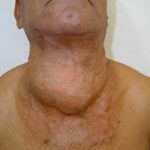
The most common symptom of the initial stage( in 60-75% of cases) is an increase in lymph nodes without the development of pain syndrome and deterioration in overall well-being.Usually, lymph nodes of the cervico-supraclavicular region suffer primarily.More specific signs of pathology in the early stages are not detected.
At each of the four stages of development of lymphogranulomatosis, asymptomatic flow is possible.
The most typical symptoms of the acute stage of Hodgkin's lymphoma are:
- febrile reaction( a sign of intoxication);
- profuse sweating at night;
- intense itching;
- weight loss of 10% or more.
Important: fever, significant weight loss and intense sweating at night in 10% of cases may be the first symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma, and a small increase in lymph nodes is noted later.With this variant of the development of the disease, anemia and a decrease in the number of leukocytes are detected in the laboratory blood test.
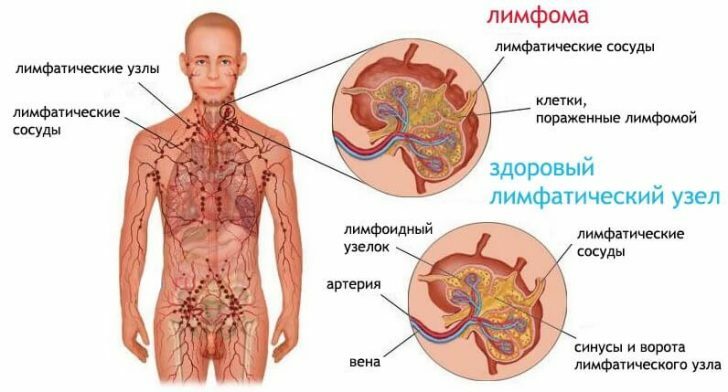
As the progression of lymphogranulomatosis increases, the mobile nodes coalesce into fairly large conglomerates.
Note: sometimes patients note the appearance of pain syndrome in the lymph nodes after taking drinks containing ethyl alcohol.
At every fifth patient, the mediastinal lymph nodes are fixed at the initial stages.Often this is detected by chance on fluorography.
Symptoms of the appearance of a large conglomerate in the mediastinum are:
- dyspnea;
- cough;
- swelling of the face;
- cyanosis of the skin of the facial region;
- pains in the chest area( infrequently).
Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by various pathological changes from the skin.Specific tumor lesions of the skin are rare, but often allergic manifestations and dermatitis are noted.An excruciating itch of the skin( such complaints are made by every third patient) is the cause of numerous scratching, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, and in some cases - neuropsychiatric disorders.
Febrile reaction is characterized by a variety of options.Usually in the early stages of development, short-term daily increases in body temperature.First there is a chill and then follows a profuse sweating and a drop in temperature to normal numbers.The fever is easily removed by ordinary antipyretic agents - Butadion, Paracetamol, Indometacin, etc.
Sometimes in the early stages of development of Hodgkin's lymphoma paraaortic nodes are affected.The leading symptom in such situations is pain in the lumbar region, appearing or worse at night.
Very often, the pathological process extends to the lung tissue.In the lungs, the development of isolated foci or the infiltrative growth of a malignant neoplasm from the mediastinum is revealed.Clinical symptoms are usually erased, but in the course of instrumental diagnosis( radiography) in the pleural cavities, the presence of fluid is determined.
In the later stages, the spleen suffers 30% of the cases, which, as a rule, requires the removal of the spleen.
Any of the histological variants of lymphogranulomatosis can be complicated by the defeat of bone tissue( for every fifth patient).The vertebrae, most often the tubular bones, suffer most often.The main manifestation of the spread of the tumor on the bone becomes pain syndrome.
If bone marrow is affected, thrombocytopenia, anemia and a decrease in the number of leukocytes are possible.
Occasionally, Hodgkin's lymphoma affects the membranes of the spinal cord, which can cause neurologic symptoms and even lead to paralysis of the patient.
Pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract arise when malignant neoplasm develops or is compressed by an organ.Sometimes the submucosal layer of the small intestine and stomach suffers.
With Hodgkin's lymphoma, tumor neoplasms from the mediastinum have the property to germinate also into the esophagus, trachea and heart muscle.
The defeat of the liver is detected only when the disease is neglected, since this body has great opportunities for compensation and regeneration.In the advanced stages the liver is enlarged;When palpation is determined by its significant protrusion from under the costal arch.Biochemical blood analysis reveals a decrease in the level of the albumin fraction of plasma proteins and an increase in the activity of alkaline phosphatase.
Relapses can be early( develop within the first year after chemotherapy and radiotherapy) and later( after a year or more).Differentiation of relapses is important when choosing a medical tactic and making a prediction.
Diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma
This diagnosis can be confirmed or disproved only in the course of a histological examination of a sample of tissue taken from a biopsy.The criterion of Hodgkin's lymphoma is the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and their precursors( Hodgkin cells) in the biopsy.A normal cytological examination may not be sufficient for differential diagnosis with other lymphomas;In doubtful cases, the use of the immunophenotyping method is required.
Methods used in the diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma:
-
 complete physical examination;
complete physical examination; - blood test( general and biochemical);
- microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen from the lymph node;
- X-ray examination of the lungs( always in two projections!);
- Ultrasound of all groups of lymph nodes;
- bone marrow biopsy and myelogram;
- radiographic examination of bones.
Important: changes in the blood picture of Hodgkin's lymphoma are not particularly specific.Usually, lymphocytopenia, mild leukocytosis and minor neutrophilia are detected.
Additional indications are as follows:
- CT of mediastinum;
- laparotomy;
- scintigraphy with gallium;
- thoracotomy and biopsy of lymph nodes of the mediastinum.
Options for treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma
Important: in the mid-20th century 5-year survival of patients with this diagnosis did not exceed 5%.Innovative treatment programs have achieved 20-year survival without relapse in 60% of patients.With the "captured" in the early stages of development of Hodgkin's lymphoma, this indicator is close to 90%.
 Local lesions of groups of lymph nodes are successfully treated by radiotherapy, i.e. exposure to ionizing radiation.This technique has been used since the beginning of the last century.To treat Hodgkin's lymphoma, a multi-field or mantle-shaped irradiation is shown.The duration of therapy is 3-4 weeks, and the total dose reaches 40 Gy.
Local lesions of groups of lymph nodes are successfully treated by radiotherapy, i.e. exposure to ionizing radiation.This technique has been used since the beginning of the last century.To treat Hodgkin's lymphoma, a multi-field or mantle-shaped irradiation is shown.The duration of therapy is 3-4 weeks, and the total dose reaches 40 Gy.
Note: radical radiotherapy allows achieving remission in 95% of patients with I - II stage.
Polychemotherapy is also widely practiced, which, in combination with irradiation, makes it possible to achieve complete cure of patients even in stages III-IV with the generalization of the tumor process.Cyclic chemotherapy is performed until complete remission.Then 2 fixing courses are conducted.After 3 cycles, it is possible to achieve remission in every second patient with a more or less favorable prognosis.Generalized forms require 6 or even 12 courses.The recurrence-free survival rate reaches 60% within 20 years.
Important: The combination of polychemotherapy and radiotherapy reduces the number of relapses fourfold.
Possible side effects of polychemotherapy:
- deterioration in blood count;
- general lethargy and muscle weakness;
- reduced performance;
- headaches;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- intestinal disorders( not always);
- hair loss;
- frequent infection.
In severe cases, patients are shown chemotherapy with high doses of pharmacological agents( Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, Bleomycin, etc.) followed by bone marrow transplantation.
Treatment is initially performed in a hospital setting, and then the patient can receive the necessary preparations on an outpatient basis.
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer