Tumors of the scrotum - classification, causes, diagnosis and symptoms
The scrotum is a skinny sac in which the appendages, testicles and the initial section of the seed canal are located.Sometimes it can swell, causing painful sensations.In most cases, they appear in the form of knots of different size, consistency and color.Some benign formations can be quite large.In addition to a cosmetic defect, they can create discomfort during walking.
Table of contents: Classification of tumors of the scrotum How to conduct a monthly examination?Common causes of swelling of the scrotum Symptoms of possible diseases Benign tumors of the scrotum Malignant tumors of the scrotum What should I do if a tumor is detected?Classification of scrotal tumors
Benign and malignant tumors of the scrotum are treated separately.This category includes only lesions of integumentary soft tissues.
Scrotal neoplasms are distinguished by histological structure and origin on:
-
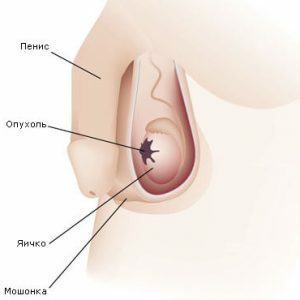 epithelial;
epithelial; - pigmented;
- soft tissue tumors;
- tumor-like lesions of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue;
- secondary foci formed as a result of the spread of malignant cells from other organs;
- is a non-classified tumor.
How to conduct a monthly survey?
It is best to conduct it while taking a bath, or after a hot shower.Under the influence of heat, the scrotum relaxes, and the testicles descend.In this state it is easier to detect anomalies.
First of all, examine the scrotum.Raise your penis with one hand and feel the scrotum.Note whether the shape and size have changed, and whether there are any red or dilated veins.The left part of the scrotum should hang slightly below the right side.Feel every egg.
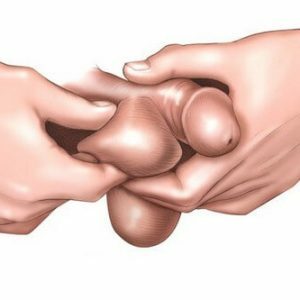 .Arrange the front of the left testicle with the thumb of the hand, the rest of the fingers behind.Carefully, but tightly squeezing the testicle, roll it between the fingers.In this way, touch the second testicle.Healthy testicles should be smooth, elastic, slightly sensitive and free to move.
.Arrange the front of the left testicle with the thumb of the hand, the rest of the fingers behind.Carefully, but tightly squeezing the testicle, roll it between the fingers.In this way, touch the second testicle.Healthy testicles should be smooth, elastic, slightly sensitive and free to move.
Check the spermatic cord.At the back of the testicle, find the appendage and the seminal cord that goes up from it.Pass it gently over the left testicle between the fingers.Check for tumors or hardens.Also, examine the second funicular.
Attention! If you find a dubious seal during the examination, consult a doctor.
Common causes of scrotal tumors
- scrotal injury;
- inflammation of the epididymis of a bacterial nature;
- hernia;
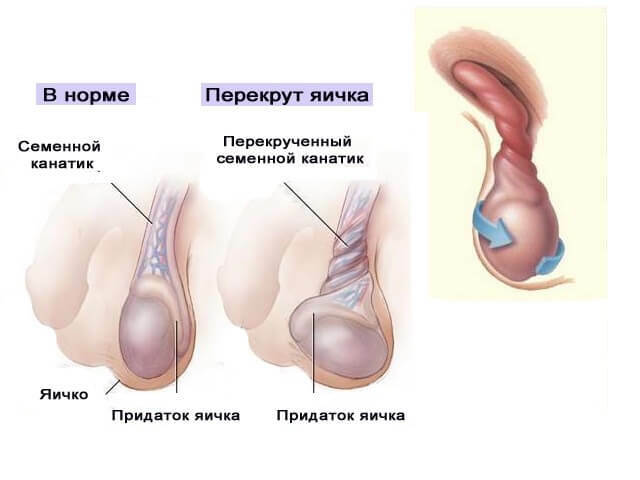
- formation in the scrotum of mass from sperm, blood and fluid;Torsion of the testis
- .
Symptoms of possible diseases
In addition to a tumor, other symptoms may appear, depending on the cause of the onset.
Inflammation of the epididymis.
This disease is characterized by an oblong, sensitive, hot to the touch tumor behind the testicle. There may be such symptoms:
- gradually increasing severe pain;
- skin on the scrotum thin, dry, flake off;
- gait waddling;
- pain in the lower abdomen from the side of the tumor;
- high temperature;
- discharge from the penis;
- cloudy urine;
- general malaise.Torsion of the testis.
.
In this acute case, the following symptoms occur:
- sudden severe pain in the testicle and in the area around it, which can give to the lower abdomen and strengthens during standing;
- dizziness and fainting;
- upset and swelling of the affected testicle;
- heat;
- nausea and vomiting.
Important! Never ignore the hardness in the scrotum.Immediately contact your doctor.
Benign tumors of the scrotum
Papillomas and epidermal cysts are the most common benign tumors. Less common are leiomyomas, fibromas, basiomas, lipomas and epitheliomas.
Very rarely diagnosed dermoid cysts, lymphangiomas, teratomas, hemangiomas.
In adolescents and young men, epidermal cysts usually develop, which are usually multiple and represent strained scrotal tumors with a diameter of 1 to 2 mm of yellowish color. Often the disease is asymptomatic.Sometimes it can be accompanied by itching.In some cases, small holes are formed on the surface of the cyst, from which a yellowish-white liquid flows out under pressure.Perhaps the development of the inflammatory process.Over time, cysts can be calcified.Apply a surgical method of treatment - removal of the scrotum by the atheroma.
Tumors of the scrotum of epithelial origin are called papillomas.There are single and multiple .Sometimes develop in combination with the papillomas of the penis, inguinal areas and perineum.They represent small knots of corporal, pink or brown color.As a treatment, electrocoagulation or electroexcision is used.
Other tumors are usually single, flow without symptoms and do not reach large sizes.Benign tumors of the scrotum are treated with a surgical technique.
Malignant tumors of the scrotum
The tumors of the epidermal origin are more often diagnosed.Liposarcomas, rhabdomyosarcomas and neurofibrosarcomas of the scrotum are less common.Cancer of the scrotum is squamous and basal cell.
More common squamous cell scrotal tumors develop with advanced ulcers and fistulas.On unchanged skin may occur with prolonged contact with fuel oil, soot, tar, or other carcinogens.
Important! Most often, tumors are diagnosed in men who for 10 years have been exposed to carcinogenic.The average age of patients is from 40 to 60 years.
It is extremely rare to diagnose a basal cell tumor of the scrotum.Risk factors and causes of development are not established.The tumor grows slowly and exhibits a low tendency to metastasize.
The diagnosis of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma of the scrotum is established on the basis of:
- of anamnesis and external examination data;
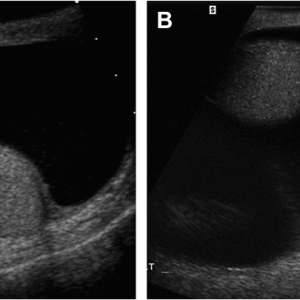
- MRI of the prostate;
- ultrasound of the scrotum;
- UZDG prostate;
- ultrasound of the penis and other studies.
The results of the above studies determine the prevalence of scrotal tumor and its size, assess the involvement of regional lymph nodes and nearby organs, as well as differential diagnosis of primary and secondary malignant scrotal disease.
 Important! The final diagnosis is made only after an aspiration biopsy, or after surgical removal of the tumor with subsequent histological examination.
Important! The final diagnosis is made only after an aspiration biopsy, or after surgical removal of the tumor with subsequent histological examination.
Treatment is prescribed taking into account the spread of the cancer process.
With local nodes, the tumor is excised from 2-3 cm of healthy tissues along the periphery and subject to a fleshy layer.
In large formations, plastic operations are performed.
Lymphadenectomy is performed in the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes.
What should I do if a tumor is detected?
After finding a tumor or hardening in the scrotum, urgently consult a urologist or andrologist, even if the formation is small and does not cause discomfort.
To alleviate symptoms, a specialist can prescribe a bed rest for the patient.Reducing severe swelling will help put under the scrotum of a twisted towel.To remove the pain and inflammation will help ibuprofen and aspirin.
Before appointing treatment, the doctor must find out the cause of the testicular tumor and exclude the formation of malignant formation.
Tumor in the scrotum can be caused and quite harmless reasons.But still, to postpone visiting a doctor is not necessary.Only during the examination can determine the causes of tumor development and exclude testicular cancer.
Radevich Igor Tadeushevich, doctor of sexopathologist-andrologist of the 1st category