Tumor of the brain: symptoms and treatment
Tumors are understood as pathological tissue proliferation.If they slowly increase in size, do not give secondary foci( metastasis), and cells are similar to the elements of surrounding tissues, then it is a question of benign brain tumor .Such neoplasms usually do not pose a serious threat to the life of the patient, but must be surgically removed.Even benign tumors can squeeze the surrounding tissue, which leads to violations of the central nervous system.In a number of cases, they are subjected to malignancy, i.e., degeneration into malignant ones.
Cancerous tumors are characterized by rapid growth and metastasis in nearby tissues or distant organs with blood and lymph flow.The cells of such neoplasms differ from healthy cells, which is revealed by histological examination of a sample taken from a biopsy.
Brain cancer is a rare, little-studied and very dangerous disease that poses a clear threat to the life of the patient.Unfortunately, it is often diagnosed at later stages, and doctors have to deal with neglected and often inoperable tumors.In connection with these forecasts, in many cases, quite unfavorable.
Types of tumors Symptoms of brain tumor Brain cancer stages Treatment of brain tumorsTypes of tumors
All tumors are divided into primary and secondary( metastatic) by origin.Neoplasms are also classified according to the type of tissues from which they are formed, by localization and degree of malignancy.
Benign tumors include:
- meningiomas;
- hemangioblastoma.
The most commonly diagnosed are meningiomas, which account for more than 25% of detected primary neoplasms.They appear during the growth of the arachnoid epithelium( normal cells of the arachnoid membrane).Hemangioblastomas, developing from primitive cells of the walls of blood vessels or from stem cells, are detected less frequently.
Types of cancerous tumors:
- gliomas;
- Estesioneuroblastoma;
- sarcomas.
The most common type of malignant brain tumors( up to 60% of cases) is gliomas.They are formed during the degeneration and uncontrolled growth of the auxiliary nerve cells.
Especially aggressive are esthesioneuroblastomas from the overgrown and degenerated epithelium of the nasopharynx and nasal passages.Sarcomas are very rare;They consist of altered connective tissue cells.
Primary malignant neoplasms originate from cells of the brain tissue or its membranes, as well as nerves and vessels.If there are no metastases, and the tumor is small and has a clear localization, i.e., did not grow into surrounding tissues, then the prognosis is favorable.
In the event that cancer cells have got into the brain with a blood flow( with metastasis of distant tumors), we are talking about secondary tumors.They are treated much heavier( as in cases of germination in the brain tissue).
Symptoms of a brain tumor
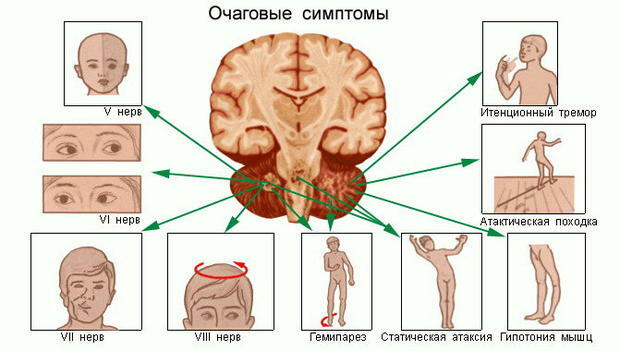
All need to be well aware of the symptoms accompanied by the development of brain tumors.When the first signs appear, you should immediately consult an oncologist and undergo a complete examination.Early detection of pathology significantly increases the chances of recovery.
 Important: refers to the number of symptoms that may indicate the likely development of malignancy in a young child, include frequent regurgitation, nervousness and moodiness.
Important: refers to the number of symptoms that may indicate the likely development of malignancy in a young child, include frequent regurgitation, nervousness and moodiness.
There are local and general cerebral manifestations.Local signs are characteristic, in particular, for damage to the cerebellum or pituitary gland.A number of common symptoms are similar to clinical manifestations of fatigue, concussion, poisoning or strokes.Pain syndrome is often "cheated" for migraines.
Common symptoms suggesting the appearance of a tumor:
- is an intense headache that worsens during physical exertion, sneezing and coughing( at stages 1 and 2 only in every second patient with a tumor);
- long without dizziness;
- sharp decrease in visual acuity, flashing of "flies" before the eyes and nystagmus;
- one-sided hearing loss or "ringing in the ears";
- seizures similar to epileptic( in the later stages in 5-10% of cases);
- marked weakness in the arms and legs( in later stages, paresis and paralysis are possible);
- nausea and vomiting( in the late stages there is vomiting with blood).
The appearance of neoplasms may be accompanied by nonspecific vegetative symptoms, including:
- pallor of the skin;
- sharp pressure jumps( at rest);
- change in heart rate for no apparent reason;
- hyperhidrosis( increased sweating).
Important: caution should also be indicated if there is a sharp weight loss in normal diet and exercise.
Nervous disorders can be indicative of impairment of the pituitary gland or individual parts of the brain.
Neurological symptoms developing with tumors include:
- increased irritability;
- causeless aggression;
- memory impairment( dips);
- personality changes;
- cognitive impairment;
- apathy;
- depression;Visual or auditory hallucinations
- .
If the tumor develops in the brainstem or pituitary gland, the coordination of movements and the ability to concentrate attention firstly disrupt.Patients may have diplopia( double vision).It is difficult for many patients to estimate the distance to a particular object.
 The defeat of the cerebellum is accompanied by spastic pain in the occipital region, nystagmus and frequent vomiting.In addition, symptoms that are characteristic of a pituitary tumor( these areas are in the neighborhood) may be noted.
The defeat of the cerebellum is accompanied by spastic pain in the occipital region, nystagmus and frequent vomiting.In addition, symptoms that are characteristic of a pituitary tumor( these areas are in the neighborhood) may be noted.
When the frontal lobe suffers, the intellect and the ability to distinguish smells suffer.Neoplasm in the frontal region often causes changes in the personality.
For lesions localized in the temporal lobe, retrograde( or short-term) amnesia, cognitive disorders, depression, an unmotivated sense of fear and unilateral limb sensitivity are characteristic.In addition, speech is disrupted, and intense headaches of a cutting nature develop.Often, there are syncope.
A tumor in the parietal lobe adversely affects the ability to perceive speech and construct sentences.In this area of the brain there are motor centers, therefore, oncology paralysis of the patient is not excluded.
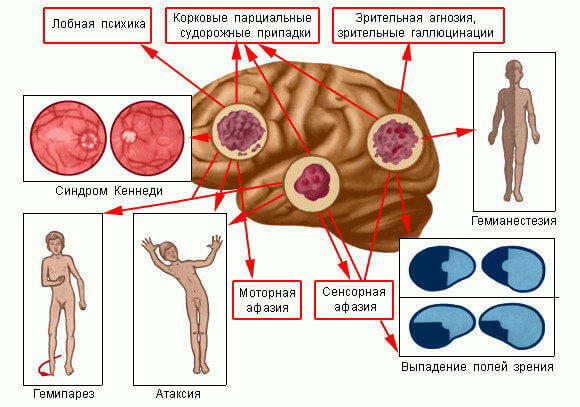 The defeat of the occipital lobe is manifested by a sharp decrease in visual acuity( one eye).
The defeat of the occipital lobe is manifested by a sharp decrease in visual acuity( one eye).
Important: with the concurrent appearance of several symptoms, you need to urgently undergo a test to confirm or exclude a diagnosis.The oncologist doctor directs the patient to the electroencephalogram, as well as computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Brain cancer stages
There are 4 stages of development of oncological diseases of the brain .
- The first stage is characterized by mildly expressed clinical manifestations.
Symptoms that may indicate the development of a pathology include:
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- headaches of varying intensity.
With timely surgical treatment and adequate complex therapy in the pre- and postoperative period, the prognosis is quite favorable.
- In the second stage, the growth increases in size and affects adjacent tissues.
Symptoms that are characteristic of the early stage are added:
- nausea and vomiting( they are associated with increased intracranial pressure);
- convulsions;
- epileptiform seizures.
Tumors at this stage are considered to be operable.The patient has a chance of a complete cure.
- In the third stage there is a rapid growth of the neoplasm and its active germination in surrounding tissues.
The patient additionally identifies:
- memory impairment;
- inability to concentrate;
- speech disorders;
- vision and hearing impairment;
- movement coordination disorder;
- imbalance in the vertical position;
- nystagmus( running pupil);
- paresthesia and numbness of hands and feet;
- muscle group twitching;
- convulsions.
The third stage, as a rule, is recognized as inoperable.Surgical intervention is extremely dangerous, in connection with which, usually only medical and radiotherapy is conducted.
Important: , in some cases, removes part of the tumor, after which a course of radiation and chemotherapy is prescribed.
- The fourth stage is characterized by a severe general condition of the patient, which is rapidly deteriorating.Often, consciousness is completely lost and a person falls into a coma, from which it no longer comes out.Such a cancer in the vast majority of cases is inoperable.Intervention is possible if the overgrown tumor has not affected vital centers.Successful can be an operation with an advanced brain tumor localized in the temporal lobe.
Note : Unfortunately, in most cases only palliative therapy is possible, the task of which is to alleviate the suffering of a patient with impaired vital functions.For such patients, oncology doctors prescribe potent drugs, including narcotic analgesics.
Factors influencing the prognosis of survival in patients with brain cancer:
- size of the lesion;
- tumor localization;
- stage of cancer;
- type and subtype of tumor;
- sex and age of the patient;
- the state of the immune system;
- medical tactics;
- presence of concomitant pathologies;
- character of the patient's nutrition;
- presence of bad habits;The emotional state of the
- .
Important : it is proven that cancer patients with a positive emotional state and a desire to recover live much longer and even sometimes defeat cancer.
Treatment of brain tumors
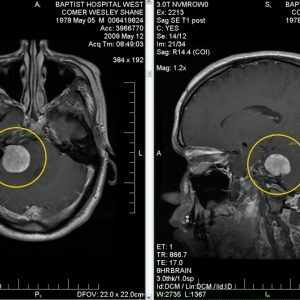 Chemotherapy is one of the main methods of cancer treatment, but it can be ineffective in oncological diseases of the brain.The fact is that the brain is "separated" from the main blood flow of the so-called.A hemato-encephalic barrier through which many foreign substances can not penetrate.
Chemotherapy is one of the main methods of cancer treatment, but it can be ineffective in oncological diseases of the brain.The fact is that the brain is "separated" from the main blood flow of the so-called.A hemato-encephalic barrier through which many foreign substances can not penetrate.
Operation with a brain tumor is also not always possible, since the tumor can be localized in an area that is difficult to access.In addition, surgical intervention is associated with a risk of damage to the brain tissue, and, as a consequence, a violation of the vital functions of the central nervous system.
Radiotherapy is one of the most effective treatments.Radiation therapy involves exposure to a tumor with dosed radioactive radiation.The technique in many cases allows to slow down or stop the uncontrolled division of cancer cells.
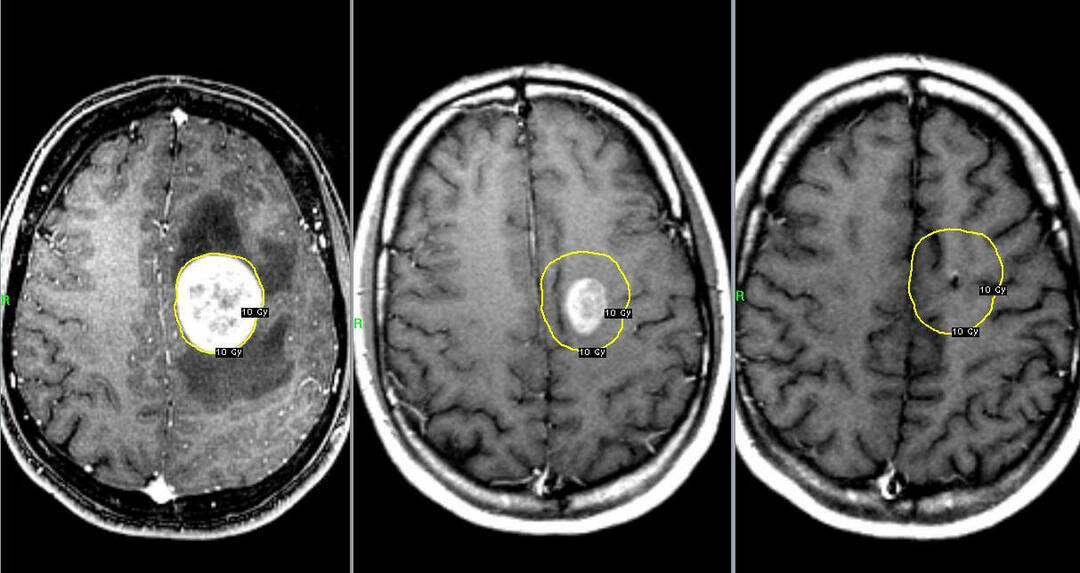
Important: the most effective method of treating malignant brain tumors is the so-called."Three-stage therapy," which involves the surgical removal of pathological proliferation of tissues followed by drug therapy and irradiation.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer