Ventriculomegaly in the child: causes and effects
Contents:
- What is ventriculomegaly
- Causes of
- What is moderate ventriculomegaly?
- Diagnosis
- How the treatment is performed
- Consequences and complications of the disease
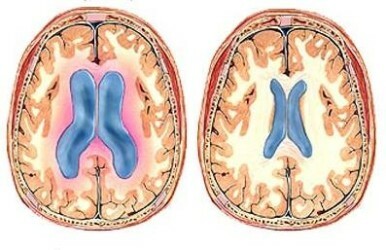
 Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is a pathological condition in which the ventricles of the brain expand due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them. In this case, the ventricles can increase to 20 mm, with an appropriate rate of 1-4 mm.
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is a pathological condition in which the ventricles of the brain expand due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them. In this case, the ventricles can increase to 20 mm, with an appropriate rate of 1-4 mm.
What is ventriculomegaly
First you need to understand two related concepts and determine what hydrocephalus is, and what is ventriculomegaly, and what is the difference between them in principle. So, hydrocephalus is an expansion of the ventricles, as a consequence, an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and a violation of its circulation into the subarachnoid space.
Hydrocephalus is accompanied by a certain symptomatology( see Symptoms of hydrocephalus).In contrast, from hydrocephalus, ventriculomegaly in a child is only an increase in ventricular size greater than 10 mm, without accompanying symptoms. That is, hydrocephalus is a consequence of ventriculomegaly, but an increase in the ventricles of the brain does not always cause neurologic symptoms.
 What is the asymmetry of the lateral ventricles? Find out the causes of the pathology.
What is the asymmetry of the lateral ventricles? Find out the causes of the pathology.
Read how dangerous the ventriculomegaly of the fetus is and how to identify the pathology in the early stages of pregnancy.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the development of ventriculomegaly in newborns are divided into 2 classes:
- Idiopathic - the cause remains unknown, and the disease develops in completely healthy parents, against the background of a good course of pregnancy.
- Symptomatic - previously transmitted infectious diseases during pregnancy, fetal hypoxia, congenital pathology of brain structures, genetic or chromosomal diseases.
Types of ventriculomegaly:
- lateral type - an increase in the left and posterior ventricle;
- enlargement of the third ventricle - fluid accumulates between the visual hillocks and anterior frontal part;
- increase in the fourth ventricle - the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Symptom complex can be different depending, on the degree of severity. In newborns, this is manifested by increased excitability, crying, anxiety, or vice versa, lack of interest. If ventriculomegaly is strongly pronounced, it manifests itself in an increase in the volume of the head, the protrusion of veins on the head.
What is moderate ventriculomegaly?
This increase in the ventricular cavity from 12 to 15 mm. Moderate ventriculomegaly in the baby requires regular examination by a doctor and an appropriate examination. If neurologic symptoms are absent or not expressed, then no treatment approach is required.
Ventriculomegaly in adults can be inadvertently detected with a planned MRI of the brain. An incidentally detected mild or moderate increase in the ventricular cavity does not require further examination or treatment. Because, this is considered as a variant of the norm or anatomical features. If the increase in cavities in the brain is a consequence of a craniocerebral trauma or brain infection, then treatment should begin immediately.
Diagnosis
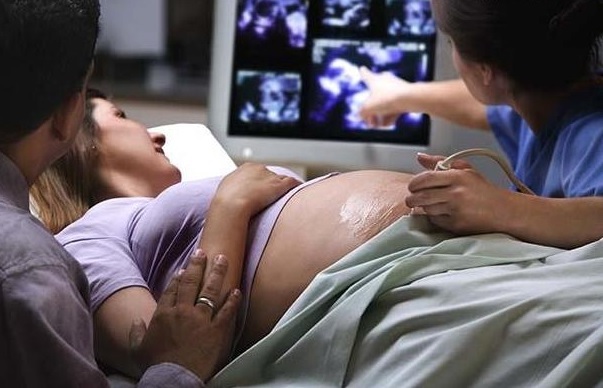
It is possible to suggest an increase in the ventricles of the brain with ultrasound diagnosis( UZD) still in utero. The study is conducted from the 17th week of pregnancy, although the greatest performance after 25 weeks. After birth, the ultrasound of the head of the newborn. In adulthood, an MRI is performed.
How to treat
Treatment of verteculomegaly in the fetus is prescribed in no more than 20% of cases. The rest of the children are under observation. If pathological changes do not progress, then further treatment is not required. Drug therapy is prescribed, only to compensate for neurologic symptoms.
 Drugs used for treatment:
Drugs used for treatment:
- Nootropics are a group of drugs that enhance cerebral circulation and improve metabolism in the brain tissues. With long-term medication intake, cognitive( cognitive) brain functions improve, concentration of attention increases.
- Antihypoxants - increase the resistance of brain tissue to ischemia( oxygen deficiency).A group of antihypoxants improves the metabolism of oxygen, and thereby increases the endurance of brain tissue in conditions of its lack. In this group, you can also include antioxidants.
- Diuretics - reduce the amount of intracranial fluid, by increasing diuresis and reducing the volume of circulating blood.
- Metabolic drugs and vitamins - help to restore neural connections and improve metabolic processes in the brain tissue.
- Massage and therapeutic gymnastics.
Please note! A group of drugs, dosage, and duration of treatment are prescribed only by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism, and the severity of the disease.
Consequences and complications of
The effects of ventriculomegaly in the fetus may have different outcomes. From favorable to violations in the central nervous system( CNS) and the development of cerebral palsy.
Ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles in a child is called isolated ventriculomegaly and is considered the most favorable by projections. This type of disease does not break the structure of the brain and, as a rule, does not require treatment.
If a violation of the outflow of intracranial fluid occurs against the background of genetic diseases, then this may have an unfavorable prognosis, since the underlying genetic disease causes viability disruption.
 Read how subarachnoid hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain appears.
Read how subarachnoid hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain appears.
Learn everything about increased intracranial pressure in newborns: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment.
What are the consequences of birth injuries parents may encounter? Learn about the causes of the pathology.
If the cause of enlarged cavities of the ventricles was intrauterine infection, which for a long time caused hypoxia of the brain, this eventually leads to psychoneurological disorders of varying severity or to cerebral palsy. This form is difficult to treat.
In conclusion, it should be noted that any changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain require an additional examination to prevent complications. The tactics of treatment are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease, and can be from simple observation of the child to prescribing medication.
write the question in the form below: