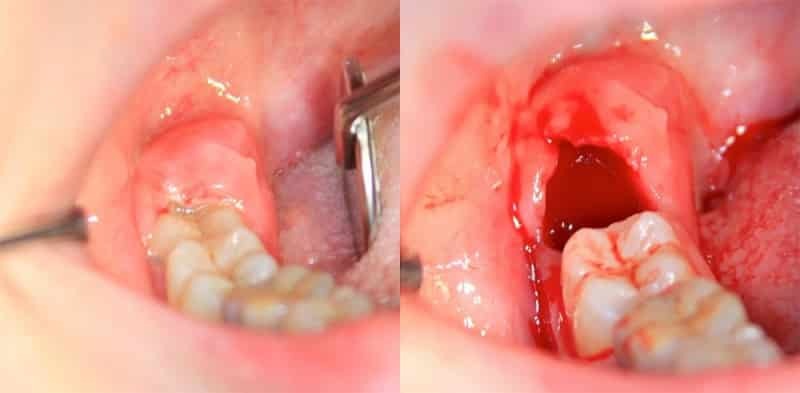
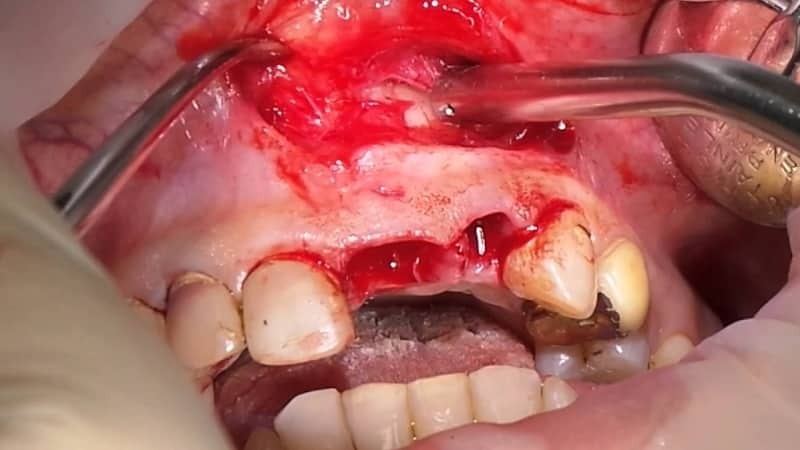
Acute arterial obstruction
Embolism more often leads to acute arterial occlusion. Under embolism is meant getting into the channel of the artery of an alien body, which causes its blockage. Most often emboli are pieces of an organized thrombus, gas or fat accumulation, other foreign bodies( metal objects, plastic tubes, bullets).Acute arterial obstruction in the form of embolism of peripheral arteries occurs more often in 2 times in women than in men, which can be explained by greater female susceptibility to rheumatism and the greatest duration of life. Embolisms can be observed at different ages, but most often at the age of 40-80 years.
The main sources of embolism of peripheral arteries are today considered to be heart diseases( in 95% of situations).In this case, more than half of them usually occur in atherosclerotic cardiopathies: myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, cardiac aneurysms, post-infarction period. The heart defect is about 40-43%, and congenital malformations - 1-2%.In the case of atherosclerotic cardiopathies, a thrombus is often located in the left ventricle area, and in the case of heart defects in the left atrium or its auricle.
Following arterial embolism, there is also an acute form of limb ischemia or organs that are supplied with the blood of this vessel basin.
Its severity depends on:
- How much the roundabout circulation is expressed;
- Arterial spasm;
- Continued thrombosis;
- The state in which central hemodynamics is located.
The pressure drop inside the vessels to the level of stagnation causes platelet aggregation and the formation of thrombi within the microcirculation system. There are, as consequences, irreversible changes in the tissue structure. Further development gets thrombosis and arteries that are larger in size. Different tissues differ in the degree of tolerance to ischemia. Thus, in the tissues of the limbs irretrievable changes in the case of complete ischemia are formed 6-8 hours later, in the intestinal region after 2 hours, in the kidney region - after 40-50 minutes, in the brain region after a few minutes.
Arterial obstruction in the case of embolism has a major symptom of pain in the site of the affected limb. It is formed quite suddenly and has the strongest influence. Occasionally, the sick fall, can not stand the strongest pain. Together with the pain, patients often notice a sensation of numbness in the limbs.
In case of viewing, the color change of the skin surfaces of the extremities is striking: from a pronounced pale color to a "marble" color. At a late stage of ischemia, when thrombosis of the venous bed is carried out, skin coloring acquires a cyanotic shade.
In the case of comparative palpation, a difference in skin temperature is also noticeable, especially in the distal limb compartments. There is also a disorder of each kind of sensitivity( tactile, painful and deep).The limits of the sensitivity disorder are not the same as the level of occlusion of the artery, but are located below, which is not obliged to cause confusion to the diagnostician.
Arterial obstruction .
Arterial acute obstruction, when it comes to embolism, no less obvious symptom is the worsening of active movements in the limb joint area, which may vary in degree from the restriction to the final plethysm. At a late stage of severe ischemia, there can be no passive movements, which are caused by the rehydration of the joints and muscles. Contracture of joints is an unfavorable sign that indicates the non-viability of the limbs.
In the case of pronounced edema of the limb, there are some difficulties in determining the pulse. Slow filling of the veins under the skin or, as it is called, the "groove" symptom, also indicates a worsening of circulation. It can be noted occasionally an increased pulsation on the arteries, which are located proximally from occlusion, which is determined in the case of comparative palpation.
In advanced situations, you can observe severe muscle soreness in palpation, subfascial edema and rigidity. To assess the severity of limb ischemia, a variety of classifications were suggested. The most complete practical goals are the classification, which was proposed by VS Saveliev in 1978 together with co-authors.
Embolism of the main arteries is usually diagnosed on the basis of information obtained by physical methods. As additional methods of investigation, one can note radiopaque and radioisotope antigraphy, as well as ultrasound techniques. At the same time, their main purpose is to establish arterial patency of the arteries, which are located more distally than the occlusion. It should be noted that in connection with the spasm of both collateral and main vessels, the information content of these methods drops sharply.
Pain removal can be achieved by the introduction of analgesics or drugs. An important step is the injection of anticoagulants to prevent continued thrombosis. If acute obstruction arises, cardiotonic agents are prescribed.
The main way to treat embolism of the aorta, as well as peripheral arteries, should be precisely the surgical one, which is aimed at restoring the blood flow in every patient who does not have absolute contraindications to the operation.
These include:
- gangrene of the limb;
- agonal state of the patient.
As relative contraindications, we can distinguish:
- in the case of embolism of the extremities of the lower or upper limb;
- ischemia of tension or first degree in an elderly patient;
- in the case of embolism of the upper extremities with relative compensation of blood circulation and severe condition.