Uphulular abscess: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
 There is a mass of purulent diseases.The principles of development are similar, the methods of treatment are the same.In other words, purulent diseases are like a family of relatives who differ only in details.The pharyngeal abscess stands alone in this family - because of the dangerous localization( proximity of the upper respiratory tract) surgeons pay special attention to its treatment.
There is a mass of purulent diseases.The principles of development are similar, the methods of treatment are the same.In other words, purulent diseases are like a family of relatives who differ only in details.The pharyngeal abscess stands alone in this family - because of the dangerous localization( proximity of the upper respiratory tract) surgeons pay special attention to its treatment.
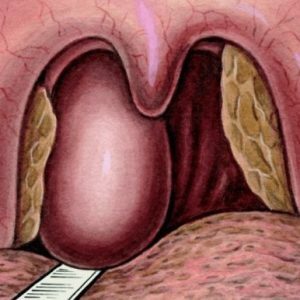
Hypertrophic abscess is purulent inflammation of soft tissues, which are literally behind the throat - lymph nodes and loose tissue .Restriction of inflammation of the fascia( thin, but strong film) of the pharyngeal muscles and the pre-invertebrate fascia.The terminologically pharyngeal abscess also appears as a retrofaringual abscess.
Table of contents:Etiology of the disease
Suppuration is provoked most often by Group A streptococci, which are pus-forming organisms, a little less often staphylococci. But an abscessed abscess can also provoke:
- klebsiella, causing pneumonia;
- E. coli;
- pathogenic fungi.
Having penetrated into the pharyngeal space, pathogens begin their destructive activity, provoking tissue suppuration.
Who and why is sick more often
Most often, young children are affected.
Approximately up to 4-5 years of age in the pharynx:
- well developed lymph nodes;
- fatty tissue is loose.
 Both these conditions contribute to the formation of suppuration.
Both these conditions contribute to the formation of suppuration.
Adults may also have pharyngeal abscesses, but they are usually "coming in" - due to the accumulation of pus from other sources.
Pathogenesis( development) of the disease
In children, pathogens that provoke the retropharyngeal abscess, enter the retropharyngeal space as a result of the development of other infectious diseases, both local and generalized:
- angina;
- pharyngitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx;
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- purulent inflammation of the tympanum and auditory tube.
The clinic describes cases when the pharyngeal abscess developed after the back wall of the pharynx was injured, as well as after the removal of the tonsils - this gave the impetus to activation of the "sleeping" infection.Common factors are also important for the development of a child's pharyngeal abscess in children.
So, children are more often ill with:
-
 weakened immunity( often suffering from catarrhal diseases);
weakened immunity( often suffering from catarrhal diseases); - poor nutrition( due to low social level of the family);
- metabolic disorders;
- general weakening of the body( children who are not characterized by physical activity, which mothers are fed, not hardened, wrapped up in any weather, stuffed with unhealthy food).
In a number of cases, the children are not "guilty" - in infants, the retropharyngeal abscess may occur because of problems with the mother:
- nipple cracks;
- of beginning mastitis, when the mother has not yet orientated and continues to breast-feed the child.
The reasons for the development of the retropharyngeal abscess in adult patients are more scarce.Of the prevalent:
- is the so-called tuberculous retention;
- purulent lesion of cervical vertebrae of syphilitic nature.
Symptoms of a pharyngeal abscess
When a disease is distinguished:
- general symptoms;
- local signs.
The general symptomatology, being characteristic of all infectious( and in particular purulent) diseases, can serve as an auxiliary criterion for the diagnosis of "Hugo abscess".These are:
-
 marked hyperthermia( body temperature increase) - up to 38-39 degrees Celsius;
marked hyperthermia( body temperature increase) - up to 38-39 degrees Celsius; - weakness;
- feeling is broken;Sweating( not always); ;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- dizziness.
Local signs are more informative for diagnosing.They even help to determine the location( location) of the ulcer.
If the abscess develops in the upper space of the peropharyngeal space, then there are observed:
- difficulty in trying to breathe through the nose;
- the voice of the voice;
- in infants - a violation of sucking my mother's breast.
If the disease affects the space of the oral space at the level of the oral cavity - clearly diagnosed:
- difficulty in swallowing, with further development of the process - difficulty swallowing liquid food, and then the inability to swallow even a small piece;
- stridor - wheezing noisy breathing, it is provoked because inflamed tissues press on the pharynx, its lumen narrows, there is a logical sound effect due to the rapid passage of airflow through a narrow space.
If the process touched the occlusion space in its lower part, the signs are as follows:
-
 simultaneous difficulty in breathing and swallowing - due to the compression of both the esophagus and the larynx;
simultaneous difficulty in breathing and swallowing - due to the compression of both the esophagus and the larynx; - breathing difficulty is more pronounced if the child is in a horizontal position( even if it concerns the upper half of the trunk - for example, when the child is playing, flexing);
- in some cases - "adult" hoarseness of voice.
A characteristic feature that can be observed in different localizations of the abscess is the inclination of the head to the sore side due to the fact that the lymph nodes swell and become painful . The inclination of the head to the sick side reduces their soreness, because the "stretching" of soft tissues decreases.
An experienced doctor will immediately "compute" a child with a typical retropharyngeal abscess - along a tilted head, strained wheezing, a large, like berry, cervical lymph node.
Due to the fact that "blistering" abscesses of the aperture space in adults are not local, as in children, but more pronounced, it is more difficult to determine the exact location of the ulcer.But the symptoms are the same:
- difficulty swallowing;
- difficulty breathing;
- tenderness in the occipital and submandibular areas due to increased occipital and submandibular lymph nodes;
- common symptoms - weakness, hyperthermia, indifference to food intake.
Diagnostics
 In addition to the patient's complaints, the doctor is guided by the data of rhino, laryngo- and pharyngoscopy - instrumental examination of the lower nasal passage( posterior segment), pharynx and larynx, if there is a suspicion of a pharyngeal abscess.
In addition to the patient's complaints, the doctor is guided by the data of rhino, laryngo- and pharyngoscopy - instrumental examination of the lower nasal passage( posterior segment), pharynx and larynx, if there is a suspicion of a pharyngeal abscess.
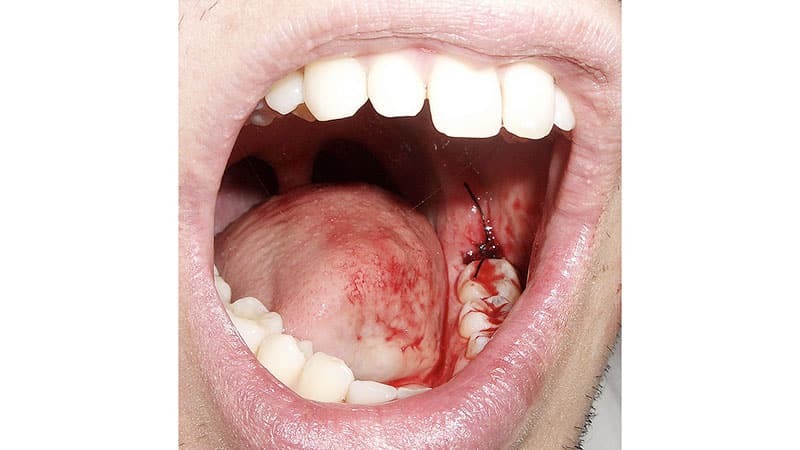
In this case, a characteristic hyperemic( with reddening) protrusion of the pharyngeal mucosa - its posterior wall) is observed.If the protrusion is in the upper parts, and you can feel it - it feels soft to the touch, fluttering( fingers feel the movement of pus in the cavity), sharply painful( on examination, the patient cries and shakes his head to avoid pressure of the doctor's fingers on the swelling). In some cases, pus is seen in the external auditory canal - this is indicative of the otogenic nature of the abscess, that is, triggered by a pathological process in the structures of the ear.
The development of a purulent process is also affected by blood counts - in particular, changes in the general blood test will be recorded:
- increase in the number of leukocytes;
- significant increase in ESR - up to 40-50 mm per hour.
In the contents obtained by puncturing the site of the alleged abscess, microbiological examination reveals infectious pathogens that provoke suppuration.
If the focus is deep in the tissues, and rhino, laryngo-, pharyngoscopy will not be informative, computer tomography and roentgenography of the pharynx can help in diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
Hyphalic abscess should be distinguished from some other pathologies similar in symptomatology to :
- from paratonsillar abscess( abscess around the tonsils) - with the retropharyngeal abscess, no changes in the tonsils characteristic of paratonsillar abscess;
- from edematous laryngitis - with it the mucous larynx is affected at a wider extent, there is no fluctuation of pus;
- from neoplasm of posterior pharyngeal wall - with it there are no signs of inflammation in the form of sharp soreness, redness, fever;
- from an aneurysm of an ascending pharyngeal artery - with it the process is limited, there is no swift increase in swelling and signs of inflammation( pain, redness, hyperthermia).
Treatment of peroretic abscess
Patients with a zagrugal abscess should be immediately hospitalized in the ENT or surgical department. Due to the fact that the intraluminal space is limited in size and pus continues to be produced, the process quickly spreads to nearby areas, while the ulcer itself can open up in the respiratory tract and cause asphyxia( airway overlap) with a fatal outcome. Therefore, the ruptured abscess should be immediately opened, its cavity should be cleaned from purulent contents as much as possible.In case of surgery, it is necessary to ensure that there is no aspiration of pus in the respiratory tract, otherwise death may occur.
In the postoperative period, designate:
- dressings;
- antibiotics depending on the sensitivity of the infectious agent that triggered the onset of the retropharyngeal abscess;
- vitamin therapy;
- desensitizing drugs, reducing possible side effects of antibiotics.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician