Vitamin K: what foods are contained and what is needed for a person
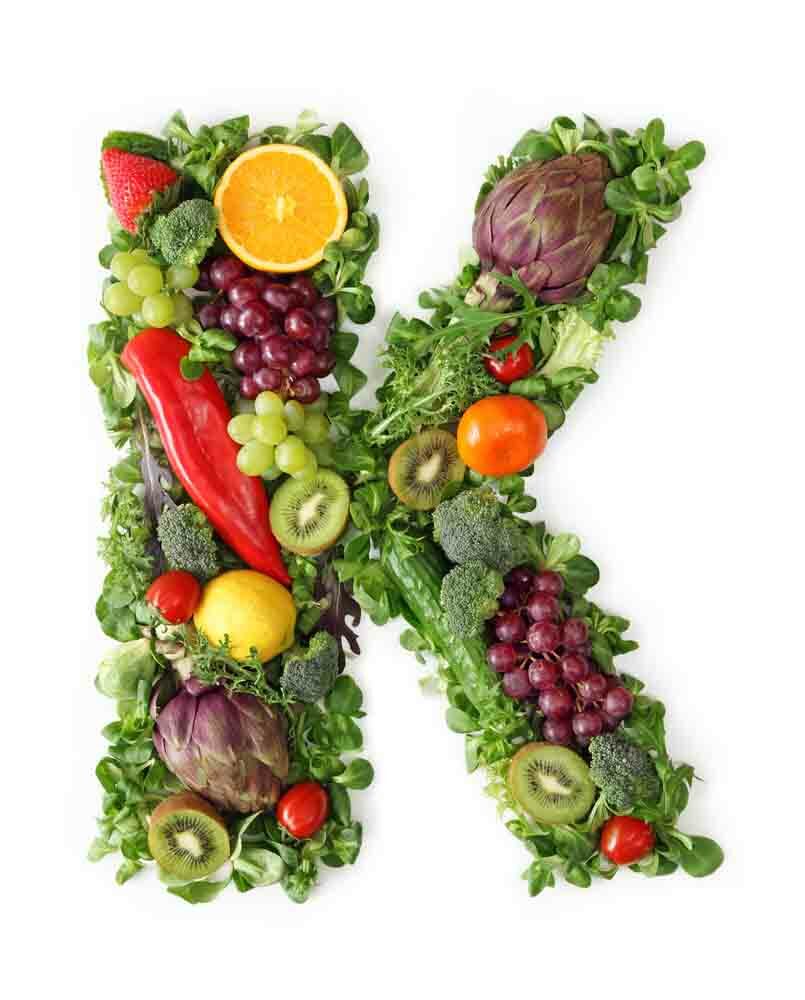
Vitamin K are several related compounds with similar properties.Vitamin K1( phylloquinone) the body receives with plant food, and somewhat less active K2( menaquinone) is produced by a normal microflora inhabiting the human intestine.Synthetic substance menadione( K3) can be transformed into K2 in the intestine.
This biologically active compound in small volumes can be deposited in the liver.Lipovitamin has the property of degrading under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, as well as in environments with alkaline pH.
Table of contents: Why does the body need vitamin K?What foods have a lot of vitamin K?Vitamin K intake norms Hypovitaminosis K Indications for the beginning of vitamin therapyWhy does the body need vitamin K?
The main purpose of vitamin K is the normalization of the blood coagulation process.Due to this substance in the liver, biosynthesis of prothrombin - protein, which is the most important component of the coagulation system - is realized.Coagulation properties can prevent hemorrhage( bleeding).
Lipovitamin is able to neutralize the action of toxins( in particular - coumarin), which are present in spoiled products.It also minimizes the negative effect of aflatoxins similar to coumarin, which have carcinogenic properties.
Vitamin K is essential for the formation of bone tissue.He takes a direct part in the process of biosynthesis of osteocalcin, a protein that provides precipitation and crystallization of calcium.A sufficiently high level of vitamin in the body makes it possible to prevent the development of osteoporosis.Naphthoquinones also regulate a number of oxidation-reduction reactions.
Important: Absorption of lipovitamin obtained by alimentary route occurs in the presence of bile, therefore, in pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and ducts, hypovitaminosis may develop.In which products are there many vitamins of vitamin K?
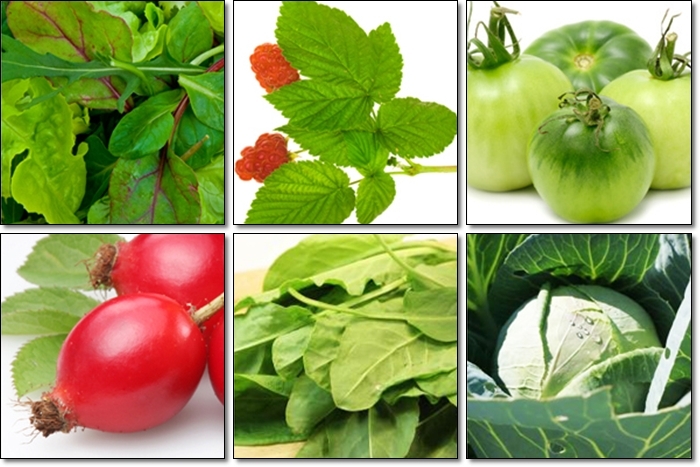

Vegetable products:
- green leafy vegetables;
- immature tomatoes;
- cabbage( mainly - color and Brussels);
- soybeans;
- walnuts;
- cereals( wheat, oats, rye);
- spinach;
- sea kale;
- rose hips.
In fruits and roots, the content of the biologically active compound is significantly lower than in green leaves.
Please note : for the preparation of salads and drinks useful for K-hypovitaminosis, you can use nettle leaves, alfalfa grass, and also needles.
Animal products rich in vitamin K:
- eggs;
- veal;
- pork liver.

Regardless of the way vitamin K( with food or synthesized by intestinal saprophytes) entered the body, lipids are required for its normal assimilation.Therefore, in the diet must certainly be present products containing vegetable and animal fats.Against the background of some types of limiting diets, it is possible to develop K-hypovitaminosis.
Vitamin K intake rates
A healthy adult in normal conditions requires 1 μg of vitamin per kg of body weight per day.In the conditions of insufficient intake of vitamin K with food, the volume of this substance is sufficient for normal vital activity and is produced by microflora.
Men need to get 65-80 micrograms of vitamin with food, and women - 55-60 micrograms.The need for a vitamin increases during pregnancy, so the daily rate should be increased to 65 mcg.
In newborns, there is a relatively high risk of developing K-hypovitaminosis, since this vitamin in the mother's milk is rather small, and the process of colonization of the intestinal bacteria synthesizing menaquinone has not yet been completed.
In the very first days of life, the baby's need for vitamin K is 10-12 μg per day.The first six months of life require 5 micrograms of life a day, and children between the ages of 6 and 12 months need 10 micrograms.At the age of 1 to 3 years, the need rises to 15 mcg, and from 4 to 6 years - up to 20 mcg.Children from 7 to 10 need 30 micrograms of vitamin K per day.
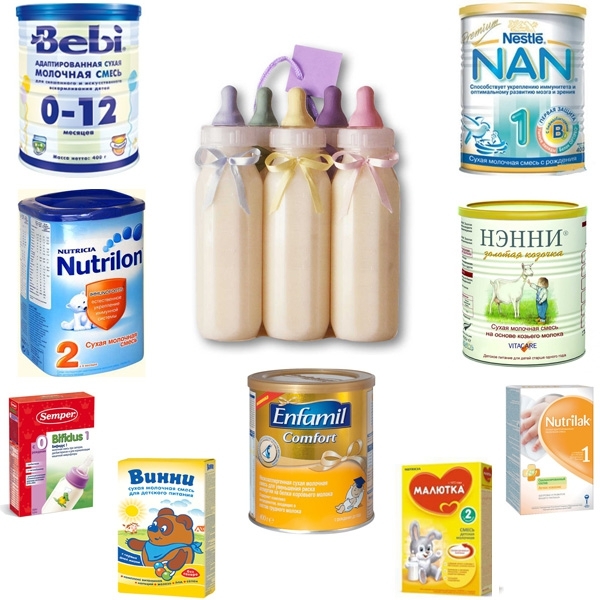

Important: in most infant formulas for artificial feeding contains about 4 μg of vitamin K per 100 calories.Normally, this is quite enough for the prevention of vitamin deficiency.
Hypovitaminosis TO
 Hypovitaminosis for compounds of group K is a phenomenon that is rarely encountered in clinical practice.Deficiency is possible with a sharp restriction of nutrition.Normally, an adequate amount of menaquinone( K2) is produced by intestinal bacteria, but this process is disrupted by prolonged course intake of salicylic acid derivatives and agents from the sulfanilamide group, as well as against antibiotic therapy.Assimilation of vitamin K is hampered by the lack of fat in the diet, so one of the possible causes of hypovitaminosis may be a restrictive diet.
Hypovitaminosis for compounds of group K is a phenomenon that is rarely encountered in clinical practice.Deficiency is possible with a sharp restriction of nutrition.Normally, an adequate amount of menaquinone( K2) is produced by intestinal bacteria, but this process is disrupted by prolonged course intake of salicylic acid derivatives and agents from the sulfanilamide group, as well as against antibiotic therapy.Assimilation of vitamin K is hampered by the lack of fat in the diet, so one of the possible causes of hypovitaminosis may be a restrictive diet.
Possible causes of K-hypovitaminosis:
- prolonged receipt of food by intravenous route;
- cholelithiasis( obstruction of the duct by concrement);
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- dyskinesia of the bile duct;
- neoplasms in the pancreas;
- irrational antibiotic therapy;
- reception of anticoagulants( in particular - Warfarin);
- chemotherapy for oncological diseases;
- use of some anticonvulsants;
- expressed intestinal dysbiosis;
- ulcerative bowel disease;
- enterocolitis;
- is a syndrome of intestinal malabsorption.
Calcium production in quantities in which the calcium-phosphorus ratio is greater than 2: 1 inhibits the synthesis of vitamin K and prevents its absorption.The administration of excessively high doses of tocopherol also affects negatively.
Note : one of the early symptoms of vitamin K deficiency is hypoprothrombinemia, which is detected in a laboratory blood test.When the prothrombin level drops to 35% of the norm, the probability of hemorrhages increases with minor injuries.The fall in the content of this protein to 20% threatens bleeding, posing a danger to life.
The most important clinical manifestation of vitamin K deficiency is hemorrhagic syndrome.
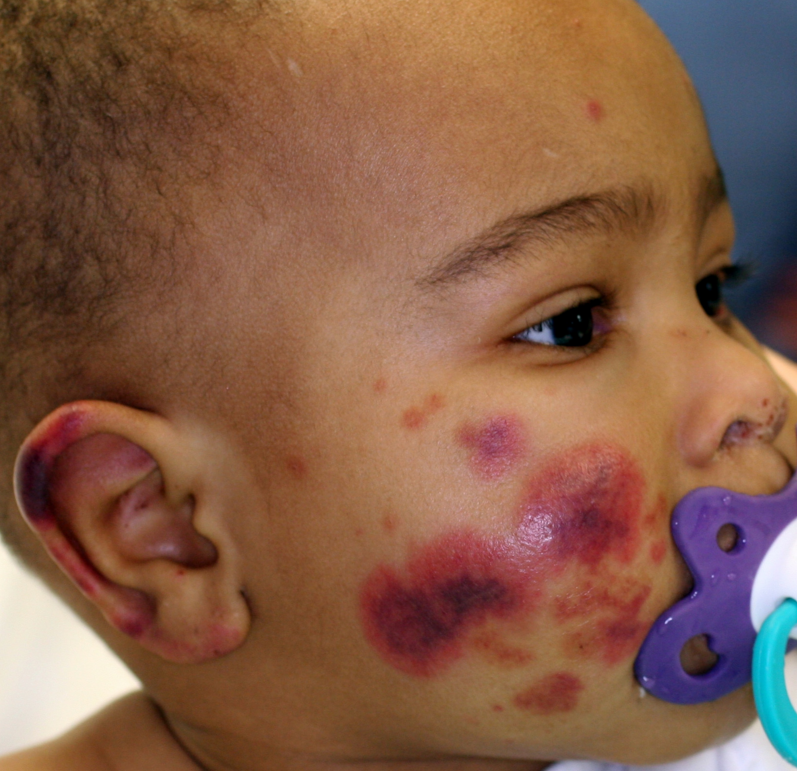
In newborn babies, the signs of hemorrhagic syndrome are:
- vomiting with blood;
- tarry( black) stool;
- hemorrhage( subcutaneous and intradermal);
- bleeding( intestinal, from the urinary tract and umbilical wound).
Manifestations of hypovitaminosis K in adults:
- increased gingival hemorrhage;
- formation of conspicuous subcutaneous hematomas with minimal mechanical stress;
- bleeding from the nose;
- bleeding in the organs of the digestive tract.
Important: suggests the development of gastrointestinal bleeding can occur if the stool becomes black or an impurity is detected in it.
The development of osteoporosis and the slow union of bone fractures can also be signs of a deficiency of naphthoquinones( vitamin K).
Indications for the beginning of vitamin therapy
Vitamin K is often prescribed to pregnant women in order to prevent the development of bleeding during childbirth.For the same purpose, the compound can be administered before routine surgical operations.
Indications for the beginning of the intake of synthetic preparations of vitamin K( menadione) are:
- low serum prothrombin;
- bleeding after injury;
- hemorrhagic syndrome;
- hepatitis;
- jaundice due to blockage of the bile duct;
- pulmonary hemorrhage due to tuberculous lesion;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased motility or intestinal atony;
- fragility of the walls of blood vessels;
- bleeding on the background of radiation exposure;
- overdose of anticoagulants.
 Important: if bleeding is caused by hemophilia, vitamin K preparations are ineffective.
Important: if bleeding is caused by hemophilia, vitamin K preparations are ineffective.
Contraindications to the prescription of vitamin K3 preparations( Vikasol, etc.) are individual hypersensitivity, increased blood coagulability and a tendency to thrombogenesis.
Why does a person need vitamin K, who can be diagnosed with a deficiency and what causes hypovitaminosis?These questions are answered in a personal video blog by a doctor:
Vladimir Plisov, phyto-therapeutist, dentist