Antibiotics: classification, rules and application
 Antibiotics are a huge group of bactericidal preparations, each of which is characterized by its spectrum of action, indications for use and the presence of various consequences.
Antibiotics are a huge group of bactericidal preparations, each of which is characterized by its spectrum of action, indications for use and the presence of various consequences.
Antibiotics are substances that can suppress the growth of microorganisms or destroy them.According to the definition of GOST, antibiotics include substances of plant, animal or microbial origin.At present, this definition is somewhat outdated, since a huge number of synthetic drugs are created, but the prototype for their creation was served by natural antibiotics.

The history of antimicrobial agents begins in 1928, when A. Fleming first discovered penicillin .This substance was just open, and not created, because it always existed in nature.In the wildlife it produces microscopic fungi of the genus Penicillium, protecting itself from other microorganisms.
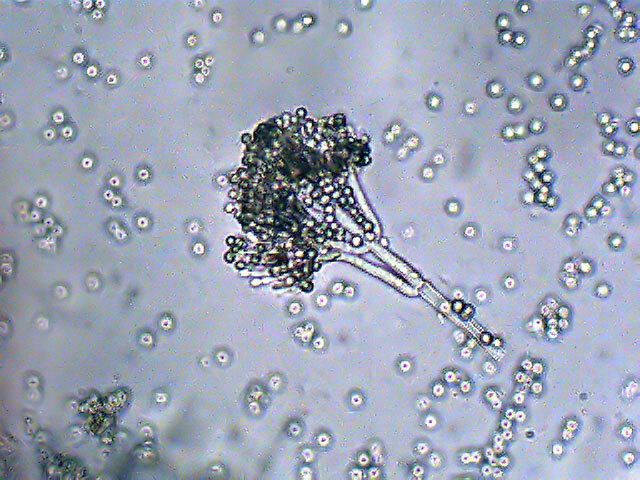
Penicillium fungus
In less than 100 years, more than a hundred different antibacterial agents have been developed.Some of them are already obsolete and are not used in treatment, and some are just being introduced into clinical practice.

We recommend you to watch a video that describes in detail the history of the struggle of mankind with microbes and the history of the creation of the first antibiotics:
How antibiotics
work We recommend to read:All antibacterial drugs for effect of action on microorganisms can be divided intoTwo large groups:
- bactericidal - directly cause death of microbes;
- bacteriostatic - prevent the reproduction of microorganisms.Unable to grow and multiply, bacteria are destroyed by the immune system of the sick person.
Antibiotic effects are realized in a number of ways: some of them interfere with the synthesis of nucleic acids of microbes;Others interfere with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, others disrupt the synthesis of proteins, and the fourth block the functions of respiratory enzymes.
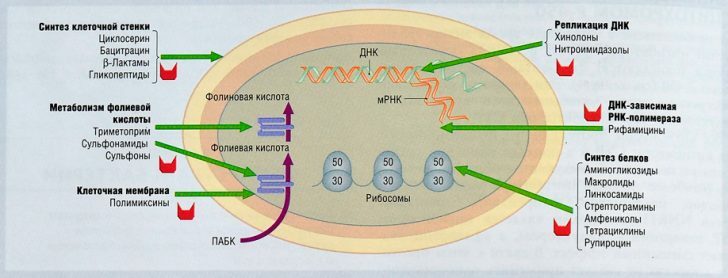
Mechanism of action of antibiotics
Groups of antibiotics
Despite the diversity of this group of drugs, all of them can be attributed to several main types.This classification is based on the chemical structure - drugs from one group have a similar chemical formula, differing from each other by the presence or absence of certain fragments of molecules.
The classification of antibiotics implies the presence of groups:
- Derived penicillin.This includes all drugs created on the basis of the very first antibiotic.In this group, the following subgroups or generations of penicillin preparations are distinguished:
- Natural benzylpenicillin, which is synthesized by fungi, and semisynthetic drugs: methicillin, nafcillin.
- Synthetic preparations: carbpenicillin and ticarcillin, which have a wider range of effects.
- Mecilli and azlocillin, which have an even wider range of action.
- Cephalosporins are the closest relatives of penicillins.The very first antibiotic of this group, cefazolin C, is produced by the fungi of the genus Cephalosporium.Preparations of this group in the majority have bactericidal action, that is, they kill microorganisms.There are several generations of cephalosporins:
- I generation: cefazolin, cephalexin, cefradine, etc.
- 2nd generation: cefsulodin, cefamandol, cefuroxime.
- III generation: cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefodizim.
- IV generation: cephpie.
- V generation: ceftolozane, ceftofibrol.
The differences between the different groups are mainly in their effectiveness - later generations have a larger spectrum of action and are more effective.Cephalosporins 1 and 2 generations in clinical practice are now used extremely rarely, most of them are not even produced.
- Macrolides are preparations with a complex chemical structure that exert bacteriostatic action on a wide range of microbes.Representatives: azithromycin, rovamycin, josamycin, leucomycin and a number of others. Macrolides are considered one of the safest antibacterial drugs - they can be used even for pregnant women. Azalides and ketolides are varieties of makorlids that have differences in the structure of active molecules.

Another advantage of this group of drugs is that they can penetrate the cells of the human body, which makes them effective in the treatment of intracellular infections: chlamydia, mycoplasmosis.
- Aminoglycosides.Representatives: gentamicin, amikacin, kanamycin.Effective against a large number of aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms.These drugs are considered the most toxic, can lead to quite serious complications.They are used to treat infections of the urinary tract, furunculosis.
- Tetracyclines.Basically, this semisynthetic and synthetic drugs, which include: tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline.Effective against many bacteria.The disadvantage of these drugs is cross-resistance, that is, microorganisms that have developed resistance to one drug will be insensitive to others in this group.
- Fluoroquinolones.These are completely synthetic drugs that do not have their own natural counterpart.All drugs of this group are divided into the first generation( pefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin) and the second( levofloxacin, moxifloxacin).They are most often used to treat infections of the ENT organs( otitis, sinusitis) and respiratory tract( bronchitis, pneumonia).
- Lincosamides.This group includes the natural antibiotic lincomycin and its clindamycin derivative.They have bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects, the effect depends on the concentration.
- Carbapenems.This is one of the most modern antibiotics, acting on a large number of microorganisms.Preparations of this group refer to reserve antibiotics, that is, they are used in the most difficult cases, when other drugs are ineffective.Representatives: imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem.
- Polymyxin.These are highly specialized drugs used to treat infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Polymyxins include polymyxin M and B. The lack of these drugs is a toxic effect on the nervous system and kidneys.
- Anti-tuberculosis drugs.This is a separate group of drugs that have a pronounced effect on the tubercle bacillus.These include rifampicin, isoniazid and PASC.Other antibiotics are also used for the treatment of tuberculosis, but only if the drugs have developed resistance.
- Antifungal means.This group includes drugs used to treat mycoses - fungal lesions: amphotirecin B, nystatin, fluconazole.
Methods of using antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are available in various forms: tablets, powder, from which the solution for injection, ointments, drops, spray, syrup, candles are prepared. The main ways of using antibiotics:
- Oral - reception through the mouth.Take the medicine can be in the form of a pill, capsule, syrup or powder.The frequency of reception depends on the type of antibiotics, for example, azithromycin is taken once a day, and tetracycline - 4 times a day.For each type of antibiotic, there are recommendations that indicate when it should be taken - before meals, during or after.This affects the effectiveness of treatment and the severity of side effects.For young children, antibiotics are sometimes prescribed as a syrup - it is easier for children to drink liquid than swallow a pill or capsule.In addition, the syrup can be sweetened to get rid of the unpleasant or bitter taste of the medicine itself.
- Injection - in the form of intramuscular or intravenous injection.With this method, the drug quickly enters the focus of the infection and is more active.The disadvantage of this method of administration is soreness in pricking.Apply injections for moderate and severe disease.
Important: to do nyxes must be exclusively by a nurse in a clinic or hospital!At home, antibiotics are not strongly recommended to prick.
- Local - applying ointments or creams directly to the source of infection.This method of delivery of the drug is mainly used for skin infections - erysipelas, as well as in ophthalmology - for infection of the eye, for example, tetracycline ointment with conjunctivitis.
The route of administration is determined only by the physician.At the same time, many factors are taken into account: the absorption of the drug in the digestive tract, the state of the digestive system as a whole( in some diseases, the rate of absorption decreases, and the effectiveness of treatment decreases).Some drugs can be administered in only one way.
With an injection, you need to know how to dissolve the powder.For example, Abaktal can be diluted only with glucose, as when sodium chloride is used it is destroyed, which means that the treatment will be ineffective.
Sensitivity to antibiotics
Any organism sooner or later gets used to the harshest conditions.This statement is true also in relation to microorganisms - in response to the prolonged exposure to antibiotics, microbes develop resistance to them.In medical practice, the concept of sensitivity to antibiotics was introduced - with what effectiveness is affected this or that drug on the pathogen.
Any prescription of antibiotics should be based on knowledge of the sensitivity of the pathogen.Ideally, before prescribing the drug, the physician should conduct an analysis for sensitivity, and prescribe the most effective drug.But the time of such an analysis at the best is several days, and during this time the infection can lead to the most sad result.
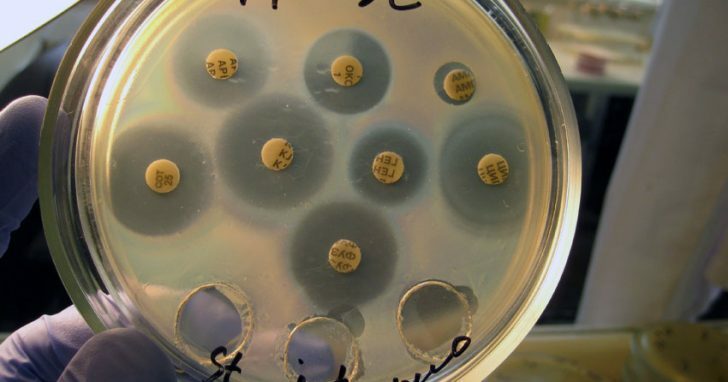
Petri dish for antibiotic susceptibility determination
Therefore, for an infection with an unknown pathogen, doctors prescribe drugs empirically - taking into account the most likely pathogen, with knowledge of the epidemiological situation in a particular region and medical institution.To do this, antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action are used.
After performing the sensitivity analysis, the doctor has the opportunity to change the drug to a more effective one.Replacement of the drug can be made and in the absence of the effect of treatment for 3-5 days.
More effective etiotropic( targeted) use of antibiotics.At the same time it becomes clear what causes the disease - with the help of bacteriological study, the type of pathogen is established.Then the doctor selects a specific drug to which the microbe lacks resistance( stability).
Do antibiotics always work
Antibiotics only work on bacteria and fungi!Bacteria are considered unicellular microorganisms.There are several thousand kinds of bacteria, some of which quite normally coexist with humans - more than 20 species of bacteria live in the large intestine.Part of the bacteria is conditionally-pathogenic - they become the cause of the disease only under certain conditions, for example, if they fall into an untypical habitat.For example, very often the prostatitis causes an E. coli, which goes up the prostate to the prostate from the rectum.
Please note: is absolutely ineffective antibiotics for viral diseases.Viruses are many times smaller than bacteria, and antibiotics simply do not have a point of application of their ability.Therefore, antibiotics for colds have no effect, since the common cold in 99% of cases is caused by viruses.
Antibiotics for cough and bronchitis can be effective if these phenomena are caused by bacteria.Understand what causes the disease only a doctor - for this, he appoints blood tests, if necessary - examination of sputum, if she departs.
Important: should not prescribe antibiotics!This will only lead to the fact that part of the pathogens will develop resistance, and next time the disease will be cured much more difficult.
Certainly, antibiotics are effective in angina - this disease is extremely bacterial in nature, cause its streptococci or staphylococci.To treat sore throats use the simplest antibiotics - penicillin, erythromycin.The most important in the treatment of angina is compliance with the frequency of medication and the duration of treatment - at least 7 days.Do not stop taking the medication immediately after the onset of the condition, which is usually observed on day 3-4.Do not confuse the true sore throat with tonsillitis, which can be of viral origin.
Note: untreated tonsillitis can cause acute rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis!
Inflammation of the lungs( pneumonia) can have both bacterial and viral origin.Bacteria cause pneumonia in 80% of cases, so even with an empirical appointment, antibiotics for pneumonia have a good effect.In viral pneumonia, antibiotics do not have a therapeutic effect, although they interfere with the attachment of the bacterial flora to the inflammatory process.
Antibiotics and alcohol
Simultaneous intake of alcohol and antibiotics in a short period of time does not lead to anything good.Some drugs are destroyed in the liver, like alcohol.The presence of antibiotic and alcohol in the blood gives a strong load on the liver - it simply does not have time to neutralize the ethyl alcohol.As a result, the likelihood of developing unpleasant symptoms increases: nausea, vomiting, intestinal disorders.
Important: a number of drugs interact with alcohol at the chemical level, as a result of which the therapeutic effect is directly reduced.These drugs include metronidazole, levomycetin, cefoperazone and a number of others.Simultaneous intake of alcohol and these drugs can not only reduce the therapeutic effect, but also lead to shortness of breath, convulsions and death.
Of course, some antibiotics can be taken against the background of alcohol consumption, but why risk your health?It is better to refrain from alcohol for a short while - the course of antibiotic therapy rarely exceeds 1.5-2 weeks.
Antibiotics for pregnancy
 Pregnant women suffer from infectious diseases at no less than all the rest.But the treatment of pregnant antibiotics is very difficult.In the body of a pregnant woman, a fetus grows and develops - a future child, highly sensitive to many chemical substances.The ingestion of antibiotics into the developing organism can provoke the development of fetal malformations, toxic damage to the central nervous system of the fetus.
Pregnant women suffer from infectious diseases at no less than all the rest.But the treatment of pregnant antibiotics is very difficult.In the body of a pregnant woman, a fetus grows and develops - a future child, highly sensitive to many chemical substances.The ingestion of antibiotics into the developing organism can provoke the development of fetal malformations, toxic damage to the central nervous system of the fetus.
In the first trimester it is desirable to avoid the use of antibiotics in general.In the second and third trimesters, their appointment is safer, but also, if possible, should be limited.
It is not possible to discontinue antibiotic prescribing to a pregnant woman in the following diseases:
- Pneumonia;
- sore throat;
- pyelonephritis;
- infected wounds;
- sepsis;
- specific infections: brucellosis, boreilliosis;
- Sexual infections: syphilis, gonorrhea.
What antibiotics can be prescribed for pregnant women?
There is almost no effect on the fetus penicillin, cefalosporin series, erythromycin, josamycin.Penicillin, though passes through the placenta, does not adversely affect the fetus.Cephalosporin and other named drugs penetrate the placenta in extremely low concentration and are not capable of harming the future child.
Conventional safe drugs include metronidazole, gentamicin and azithromycin.They are prescribed only for life indications, when the benefit for a woman outweighs the risk to the child.These situations include severe pneumonia, sepsis, other severe infections, in which a woman can simply die without antibiotics.
Which of the drugs can not be prescribed during pregnancy
Do not use in pregnant women the following drugs:
- aminoglycosides - can lead to congenital deafness( exception - gentamicin);
- clarithromycin, roxithromycin - in the experiments had a toxic effect on the embryos of animals;
- fluoroquinolones;
- tetracycline - disrupts the formation of the osseous system and teeth;
- levomitsetin - is dangerous in late pregnancy due to oppression of bone marrow functions in a child.
For some antibacterial drugs, there is no evidence of adverse effects on the fetus.This is explained simply - on pregnant women do not conduct experiments to find out the toxicity of drugs.Experiments on animals do not allow 100% certainty to exclude all negative effects, since the metabolism of drugs in humans and animals can differ significantly.
It should be noted that before the planned pregnancy should also refuse to take antibiotics or change plans for conception.Some drugs have a cumulative effect - women are able to accumulate in the body, and for some time after the end of the course of treatment are gradually metabolized and withdrawn.Pregnant should not be earlier than 2-3 weeks after the end of taking antibiotics.
Consequences of taking antibiotics
The ingestion of antibiotics into the human body leads not only to the destruction of pathogenic bacteria.Like all foreign chemical preparations, antibiotics have a systemic effect - in one way or another affect all the systems of the body.
Several groups of side effects of antibiotics can be distinguished:
Allergic reactions
Almost any antibiotic can cause allergies.The severity of the reaction varies: a rash on the body, angioedema( angioedema), anaphylactic shock.If an allergic rash is practically not dangerous, anaphylactic shock can lead to death.The risk of shock is much higher with injections of antibiotics, which is why injections should be done only in medical institutions - there may be rendered emergency care.
Antibiotics and other antimicrobial drugs that cause cross-allergic reactions:

Toxic reactions
Antibiotics can damage many organs, but the liver is most affected by them - against the background of antibacterial therapy, toxic hepatitis can occur.Some drugs have a selective toxic effect on other organs: aminoglycosides - on the hearing aid( cause deafness);Tetracyclines depress the growth of bone tissue in children.
Note: toxicity of the drug usually depends on its dose, but with individual intolerance, sometimes smaller doses are sufficient to have an effect.
Exposure to the gastrointestinal tract
When taking certain antibiotics, patients often complain of stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, stool disorders( diarrhea).These reactions are most often caused by the local irritant effect of the drugs.The specific effect of antibiotics on the flora of the intestine leads to functional disorders of its activity, which is accompanied most often by diarrhea.This condition is called antibiotic-associated diarrhea, which is more popular among people under the term dysbacteriosis after antibiotics.
Other side effects of
Other side effects include:
- suppression of immunity;
- appearance of antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms;
- superinfection is a condition in which microbes resistant to this antibiotic activate, leading to the onset of a new disease;
- a violation of the exchange of vitamins - is due to the inhibition of the natural flora of the colon, which synthesizes some B vitamins;
- bacterialysis of Jarisch-Gerxheimer is a reaction that occurs when bactericidal preparations are used, when a large number of toxins are released into the blood as a result of the simultaneous death of a large number of bacteria.The reaction is similar in the clinic to shock.
Can antibiotics be used for the prophylactic purpose of
Self-education in the field of treatment has led to the fact that many patients, especially young moms, try to prescribe an antibiotic for themselves( or their child) at the slightest sign of a cold.Antibiotics do not have a preventive effect - they treat the cause of the disease, that is, eliminate microorganisms, and in the absence of manifest only side effects of drugs.
There is a limited number of situations in which antibiotics are administered prior to clinical manifestations of the infection, with a view to preventing it:
- surgery - in this case, the antibiotic, which is in the blood and tissues, prevents the development of infection.As a rule, a single dose of the drug administered 30-40 minutes before the intervention is sufficient.Sometimes even after appendectomy in the postoperative period, antibiotics are not pricked.After "pure" surgical operations, antibiotics are not prescribed at all.
- major injuries or wounds( open fractures, soil contamination of the wound).In this case it is absolutely obvious that an infection has entered the wound and it should be "crushed" before it appears;
- Emergency prevention of syphilis is carried out with unprotected sexual contact with a potentially sick person, as well as with health workers who have been infected by blood of an infected person or other biological fluid on the mucous membrane;
- Penicillin can be prescribed to children for the prevention of rheumatic fever, a complication of angina.
Antibiotics for children
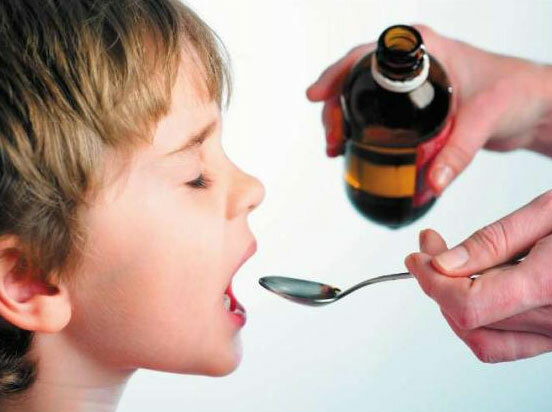 The use of antibiotics in children in general does not differ from their use in other groups of people.Children of small age pediatricians are most often prescribed antibiotics in syrup.This dosage form is more convenient for taking, unlike injections, completely painless.Older children may be prescribed antibiotics in tablets and capsules.In severe infection, they switch to the parenteral route of injection - injections.
The use of antibiotics in children in general does not differ from their use in other groups of people.Children of small age pediatricians are most often prescribed antibiotics in syrup.This dosage form is more convenient for taking, unlike injections, completely painless.Older children may be prescribed antibiotics in tablets and capsules.In severe infection, they switch to the parenteral route of injection - injections.
Important : The main feature in the use of antibiotics in pediatrics is the dosage - children are prescribed smaller doses, since the calculation of the drug is carried out in terms of kilograms of body weight.
Antibiotics are very effective drugs with at the same time a large number of side effects.To heal with their help and not cause harm to your body, they should be taken only according to the doctor's prescription.
What are the antibiotics?In what cases is antibiotics needed, and in which is dangerous?The main rules of antibiotic treatment are told by the pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky:
Gudkov Roman, resuscitator