Vitamin R: where is contained and for what it is needed by man

The term "Vitamin R" unites a number of biologically active water-soluble substances( bioflavonoids), which are present in large quantities in the leaves and fruits of many plants in the form of glycosides.
Table of contents: Functions of vitamin P Where is vitamin P contained?Vitamin R intake norms Indications for vitamin P-hypovitaminosisFunctions of vitamin P
For the first time bioflavonoids were obtained from lemon peel.To date, over one hundred and fifty joints with similar properties have been discovered.
The most common bioflavonoids are:
- routine;
- naringidine;
- quercetin;
- citrine;
- catechins;
- Eriodictiol;
- cyanidine;
- eskulin;
- anthocyane.
Note: vitamin P can partially cover the human need for ascorbic acid.In this connection, in the medical literature, bioflavonoids are often referred to as "vitamin C2".
Bioflavonoids are rather unstable compounds.They have the property of breaking down when cooking food products under the influence of high temperatures and water.In addition, they are inactivated by UV-radiation( including - solar ultraviolet).
Bioflavonoids( in particular - catechin) are powerful antioxidants that protect the body from the negative effects of free radicals at the cellular level.Due to this they are able to slow down the natural process of aging, substantially strengthen nonspecific( general) immunity and prevent the emergence and development of a number of diseases.
Note: contains the highest amount of antioxidant-catechin found in green tea.
Vitamin P increases the resistance of the body to the effects of unfavorable exogenous factors.
Vitamin R is called "capillary permeability factor".It has been experimentally established that in combination with ascorbic acid it helps to strengthen the walls of small blood vessels-increase their elasticity and decrease the degree of permeability.Bioflavonoids prevent vascular sclerosis and promote their expansion.
A person who receives enough vitamin P with his food will normalize blood pressure and heart rate, and the edema of tissues will decrease or disappear.Rutin, gesperedin and quercetin are effective agents for combating varicose veins, scurvy and hemorrhagic diathesis.Active compounds prevent the appearance of intradermal and subcutaneous hematomas( "bruises").
Bioflavonoid compounds increase the uptake of ascorbic acid, potentiate and prolong its action.Catechins strengthen protective forces, increasing the body's resistance to the effects of infectious agents of bacterial and viral nature.
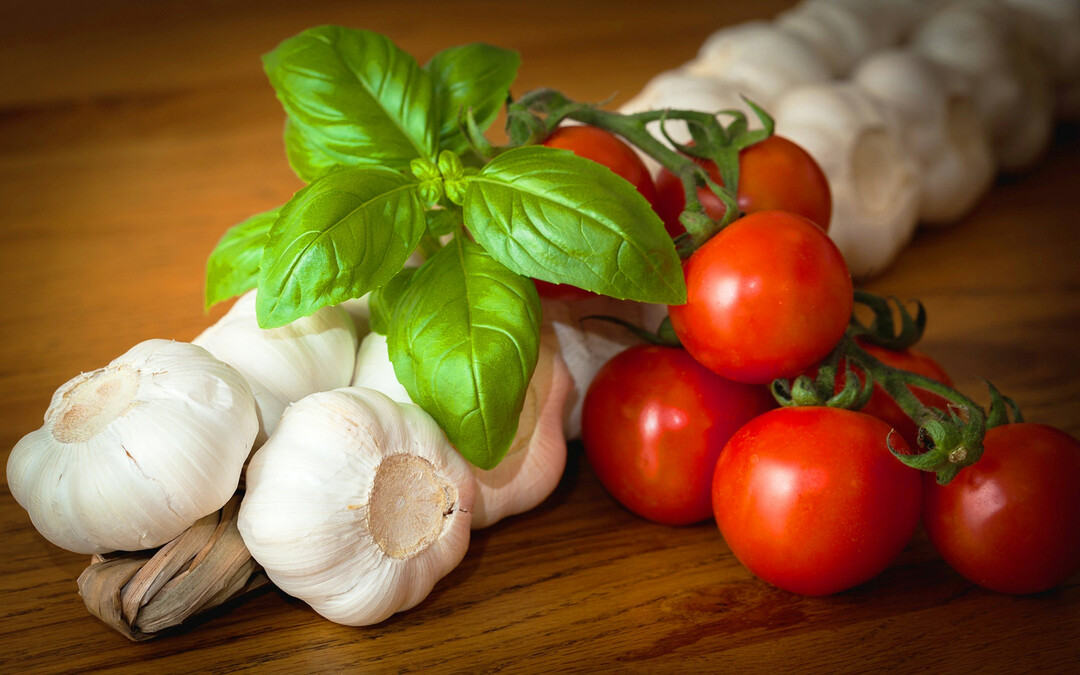
Important: antioxidant activity of quercetin inhibits the growth of malignant tumors.Especially noticeable is its effectiveness in the complex therapy of leukemia and breast cancer!The greatest amount of quercetin is found in garlic, tomatoes and sweet pepper.
 Bioflavonoids have the ability to slightly stimulate the functional activity of the adrenal cortex, thereby increasing the production of glucocorticoid hormones.
Bioflavonoids have the ability to slightly stimulate the functional activity of the adrenal cortex, thereby increasing the production of glucocorticoid hormones.
Hesperidin, quercetin and catechin inhibit biosynthesis and release of the main mediators of allergic reactions.In addition, these bioflavonoids can reduce swelling of tissues and have analgesic effects.Thus, they reduce the severity of hypersensitivity reactions and facilitate the course of diseases with an allergic component( in particular - bronchial asthma).
It is established that one of the bioflavonoids( quercetin) is able to protect the heart and blood vessels from excess cholesterol, thus preventing the development of atherosclerotic lesions and their severe complications( hypertension, heart attacks and strokes).
Vitamin P is able to regulate daily diuresis( volume of urine being separated) and takes part in the formation of bile.
Where is vitamin P contained?
Vitamin P is not synthesized by our body;He can act only alimentary way( that is, with food).Since bioflavonoids are not deposited, a person needs to regularly receive them from the outside.

These biologically active compounds are present in the same products that are the main sources of vitamin C.
Foods high in vitamin P:
- chokeberry( berries, juice);
- Citrus( lemon, grapefruit, etc.);
-
 salad;
salad; - green tea;
- sorrel;
- parsley greens;
- black currant( berries);
- blueberries;
- blackberry;
- rose hips( fruits);
- apples;
- apricots;
- plums;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- pepper( sweet "Bulgarian");
- garlic
- cabbage( all kinds);
- grapes;
- buckwheat groats.
Note: the main source of bioflavonoids for the pharmaceutical industry are two kinds of larch - Dahur and Siberian.
Vitamin P intake rates
Vitamin P should be present in the daily diet. Norms for the consumption of bioflavonoids for the average adult are:
- hesperidin - 100 mg;
- Routine - 30 mg;
- quercetin - 15 mg.
Note: in 100 ml of chokeberry juice contains about 2000 mg of bioflavonoids.This product is the best source of vitamin P!
It has been established that the need for vitamin P increases significantly in people who smoke, since the products of tobacco combustion reduce the concentration of bioflavonoids in the body.
Indications for vitamin therapy
Clinical studies have shown that vitamin P helps with hypertension, stomach ulcer and rheumatism.It is also included in the complex therapy of atherosclerosis and certain oncological diseases.
The use of quercetin and rutin is indicated if the following pathologies are diagnosed in the patient:
- glomerulonephritis;
- septic endocarditis;
- autoimmune inflammation of the arachnoid's cobweb( arachnoiditis);
- radiation sickness;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- infectious diseases( typhus, scarlet fever, measles).
Vitamin P is prescribed for the prevention and therapy of small vessel lesions caused by the intake of salicylates and anticoagulants.
P-hypovitaminosis
In the absence of routine and other bioflavonoids, the following clinical manifestations of may occur:
- spontaneous subcutaneous and intradermal point hemorrhages;
- increased fatigue;
- reduced mental and physical performance;
- muscle pain;
- joint pain;
- acne( blackheads);
- alopecia( hair loss);
- bleeding gums.
Note : hypovitaminosis most often develops in the winter-spring period, when the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits is reduced, and in the harvested plant products, the vitamin P content decreases.
Hypervitaminosis
Excess intake of vitamin P into the body does not pose the slightest danger, as excesses are very quickly excreted naturally( excreted by the kidneys).
Konev Alexander, Therapeutist