Gas gangrene: symptoms and treatment, risks
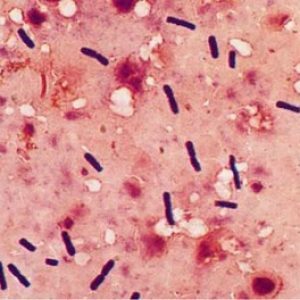
Gas gangrene is one of the most unpleasant diseases of , from which patients suffer and with whom physicians should be engaged in order to save the patient not only health, but life.
Contents:The disease is very closely related to the fact of injury. Experienced physicians diagnose gas gangrene( or are warned of a high possibility of getting sick with it), even with initial, not very expressive clinical manifestations, if they are delivered to a patient with a wound that is characterized by extensive crushing of tissues heavily contaminated with earth, sand, scraps of clothing. Most often this happens when obtaining wounds such as:
- gunshot;
- torn;
- is ripped-bruised.
The stronger the injuring tool damaged the tissues:
- the greater the risk of gas gangrene;
- and if it is sick - the more pronounced manifestations.
Especially favorable conditions for the pathogen are created if the muscular arrays of are destroyed( it does not matter which location).
Etiology.Characteristics of the causative agent
Gas gangrene is provoked by an anaerobic infection, one that requires a medium that does not contain oxygen for development. The most common disease is caused by the following varieties of anaerobes:
- Clostridium perfringens;
- Clostridium septicum;
- Clostridium oedematiens;
- Clostridium histolitycum.
Clostridia persistently live in the intestines of domestic herbivores.They are also found on the skin and in the feces of healthy people who have not previously complained about the diseases caused by clostridia.
In order for the causative agent of gas gangrene to multiply( for the start of the disease it is necessary to have a certain amount of an infectious agent, otherwise it will not arise), it needs a nutrient medium - first of all, particles of dead muscles. For "nutrition" other biological tissues that are in the wound are suitable:
- scraps of connective tissue structures;
- fragments of muscle aponeuroses;
- blood;
- tissue exudate, formed in the wound due to pathological processes that triggered the wound in the tissues.
Another condition for the successful reproduction of anaerobes is an oxygen-free environment. In this process, in the process of rapid life activity, most varieties of pathogens themselves form a gas( not oxygen).
Characteristic of clostridia as a pathogenic factor:
-
 is a feature of their pathological activity - the production of toxins.Gas gangrene on this basis is classified as a toxicoinfection;
is a feature of their pathological activity - the production of toxins.Gas gangrene on this basis is classified as a toxicoinfection; - high invasiveness - ability to easily spread in tissues due to their damage;Is achieved through the development of so-called aggression factors - proteolytic( destroying tissue structures) enzymes.So, Clostridium perfringens produces proteinase( cleaves proteins), collagenase( cleaves collagen, which provides strength and elasticity of connective tissue), hyaluronidase( a part of connective, nervous and epithelial tissue).
The toxins released by the causative agents of gas gangrene are one of the most powerful biological poisons. They act extremely destructively and are characterized by:
- hematotoxicity( destroying blood cells - in particular, red blood cells and leukocytes);
- necrotoxicity( cause tissue necrosis);
- by neurotoxicity( acting destructively on nerve cells);It is less expressed in comparison with the neurotoxicity of clostridia poisons that cause other clostridiosis, but it is enough to cause significant disturbances from the nervous system.
-
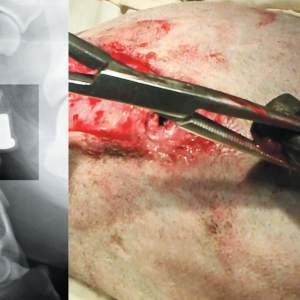
traumatic detachment of the upper and lower limbs;
- injuries to any of the large intestine( with injuries of the abdomen, less often with atypical sexual ways of satisfying with the use of the rectum, when sexual pleasures were held in natural conditions without hygiene);
- hit foreign bodies in tissues( both in military field conditions, and in domestic);
- crushed wounds( shallow, but extensive violations of the integrity of tissues, when from those remains in the literal sense of tissue "porridge").
- within the first 24 hours from the moment of injury;
- in some cases - even in the first hours;
- less often - for 2-3 days.
- necrosis( necrosis) of tissues;
- fibrinolytic course( blood clotting level decreases);
- marked hemolysis( destruction) of blood cells( the causative agent releases a large amount of hemolytic toxin);
- marked intoxication of the body.
- bloody-serous swelling of tissues;
- release of gas in a small amount( but not always);
- erythrocyte destruction;
- hypotension;
- severe heart rhythm disturbances - they are especially dangerous if changes in the heart muscle are already diagnosed.
- swelling of the tissues, which rapidly increases in the affected tissues and quickly seizes new tissue massifs;

- allocation of a large amount of gas;
- mass destruction of erythrocytes.
- "Dissolution" of living tissues( they remain amorphous tissue "porridge");
- "melting" of muscles( their structures are thinned, muscles atrophy);
- "melting" of connective tissue.
- emphysematous( classical);
- edematous-toxic;
- phlegmonous;
- is a putrid( or putrefactive).
- it becomes dry;
- there are extensive areas of necrosis;
- the crushed muscular massifs in the wound quickly necrosis;
- muscle remnants acquire a greyish-green color;
- after a while there is a cadaveric smell, which indicates a total decomposition of muscles;
- granulations, which usually indicate the start of the healing process, are not observed;
- if you press on the tissue around the wound - from it begins to flow fluid with a trace of blood, gas is released, but there is no pus.
- pale;
- cold to the touch;
- are stained with brownish-brown spots.
- after a while, the pulse on its peripheral vessels disappears;
- skin becomes brownish;
- sharply reduced tactile, painful, temperature sensitivity up to complete disappearance;
- begins to necrosis all over.
-
 no gas or very small amount of formation( its bubbles can be seen in small amounts during radiography);
no gas or very small amount of formation( its bubbles can be seen in small amounts during radiography); - pus is not observed;
- , a selection of the color of meat slops appears( like water that turned pinkish red after the meat was washed in it);
- the muscles are raised above the wound surface, due to the fact that they are pressured by swollen tissues, they acquire a characteristic pale color;
- the subcutaneous fat becomes like a jelly, acquires a greenish shade.
- pale;
- with a distinctive shiny tint;
- tight;
- with palpation - cold.
- the pulse disappears;
- rapidly progressing, the necrosis of the entire limb develops.
- the wound surface is covered with purulent discharge;
- there are gas bubbles;
- tissues are drawn into the process in a limited way, on some extent, it is possible to estimate the depth of the process( in contrast to the two above described forms, in which the changes so far absorb the tissues until they absorb the entire array), and deep and surface formsTissue destruction;
- muscles that are visible in the wound are preserved to a greater extent than in the previous forms of gas gangrene - they are not completely melted, but have necrosis areas, are characterized by a pink tinge.
- is pale but not pronounced:
- feels warm to the touch( with phlegmonous form the temperature of the tissues is generally not reduced);
- swelling around the wound is not total and unrestrained, but limited, moderate;
- skin patch is not observed, it is possible to separate the indistinguishable spots, scattered over the skin mass near the lesion.
- , there are observed putrefactive discharges mixed with scraps of dead tissue and gas bubbles, having a sharp putrefactive, very unpleasant smell, which is felt even a few meters away from the patient;
- muscles that are visible in the wound, a characteristic dirty-gray color;
- there is a very rapid necrosis of connective tissue fascia of muscles, the muscles remain without a natural individual "wrapper" and seem to merge with each other.
- heart palpitations( up to 120-140 beats per minute);
- rapid breathing, in some cases superficial;
- hypotension( decreased both systolic and diastolic pressure);
-
 Hyperthermia, beginning with the onset of the disease;If the elevated body temperature is maintained at 38-39 degrees Celsius, this is considered a poor prognostic sign;
Hyperthermia, beginning with the onset of the disease;If the elevated body temperature is maintained at 38-39 degrees Celsius, this is considered a poor prognostic sign; - because of kidney damage by the toxin of an infectious agent their excretory function is severely impaired.This is manifested by oliguria( less urine than normal), which, if the disease progresses, can develop into anuria( urine is not produced at all).In especially severe cases, because of the involvement of the glomeruli of the kidneys, hematuria may arise-blood in the urine of . It is detected both in small quantities, determined only with the help of laboratory analysis, and in large ones, when the color of urine from straw-yellow changes to the color of meat slops.
- the skin becomes dry to the touch;
- lips dry up and crack;
- in the mouth dries up( up to difficulty and inability to swallow);
- develops a feeling of excruciating thirst;
- reduces sweating;
- dark circles appear under the eyes;
- the skin becomes dry and flabby, as in the elderly( in older people with age-related skin changes this symptom is less noticeable), an attempt to take it into the fold fails, as the elasticity of the skin is lost;
- dries out the conjunctiva, which can not be got rid of, even blinking often;The eyes appear hollow at the same time;
- expressed a feeling of general weakness;
- in the dehydrated cases of dehydration the patient is disturbed consciousness up to a semi-rare state.
- excited state;In a number of cases, such patients are on the contrary depressed, withdrawn;The condition depends on which centers of the brain were affected by toxins released by the causative agent of gas gangrene;
- in an excited state there is a logarithm( excessive talk), in a depressed - silence, down to unwillingness to answer questions of close and medical personnel;
- severe insomnia.
- the fact of massive injury;
- characteristic wound appearance;
- signs of general intoxication;
- rapid development of the disease.
- X-ray study( due to gas bubbles in the muscle tissues, they seem porous, in some cases similar to honeycombs);
- microscopic examination of excretions from the wound( they reveal clostridia in the form of sticks that acquire a characteristic blue-violet color when staining the smear according to Gram).Crops are not relevant, looking at the rapid development of the disease: the patient can die even before the growth of colonies of microorganisms;
- laboratory blood test.
-
 decrease in hemoglobin level to 70-100 g / l;
decrease in hemoglobin level to 70-100 g / l; - decrease in the number of red blood cells to 1-1.5 * 1012 / l;
- increase in the number of leukocytes to 15-20 * 1012 / l, the shift of the leukocyte formula to the left( due to the fact that the number of rod-nuclear neutrophils increases, young forms appear, eosinophils are absent).Despite the destructive effect of clostridial toxin on leukocytes, at first their number increases as an activation of the body's immune system.
- fascial gas-forming phlegmon( it does not develop muscle damage);
- is a putrid( putrefactive) infection( characterized by the fact that there is no gassing, the development of symptoms is more moderate, there is no mass destruction of tissues).
- for surgical treatment;
- vigorous common activities.
- excision of all compromised tissues( dead and nonviable);There is no question of sparing surgical intervention - all suspicious areas should be treated;
- dissection into the entire possible depth of tissue and fascia around the wound( since anaerobic infection kills when exposed to oxygen).Such cuts are called lamp-like.Relatively large surgical interventions can be served only by large vessels and nerve trunks, but in case of a life threatened by a patient created by gas gangrene, they prefer to open the tissue radically with stopping bleeding if necessary);
- maximum drainage for adequate outflow from the wound;It is necessary to drain each "pocket" in the tissues;
- is extremely important: the dressing is not superimposed, the wounds should be open ;
- bottom and wound edges must be treated with antibiotics;
- if limb tissues have been compromised, and the diagnosis of the disease has been confirmed, then with the further spread of gas gangrene in urgent order, amputation of the limb or exarticulation( amputation at the joint level) is necessary.The wound can not be stitched after such an operation.
- Intensive infusion therapy( intravenously drip albumin, plasma, solutions of electrolytes and proteins);
- with severe anemia and worsening of red blood - transfusion of whole blood or erythrocyte mass;
- parenteral administration of high doses of antibiotics( important: performed intravenously or intraarterially);
- intravenous injection of anti-gangrenous sera in a dose of 150 000 AE( initially the serum should be dissolved in isotonic sodium chloride solution and heated to a temperature of 37-37 degrees Celsius). If the pathogen is identified, monovalent sera are injected, if not - polyvalent, that affect all kinds of clostridia that cause gas gangrene.
- in a hot-air oven( air sterilization method) where it is exposed to a temperature of 1500 degrees Celsius;
- in a steam sterilizer at a pressure of 2-2.5 atmosphere.
- antitoxin;
- anti-enzyme antibodies.
- is not produced in sufficient quantity;
- does not have protective properties to prevent clostridia from multiplying.
- with conductive anesthesia;
- anesthesia.
- local( antibiotic treatment of the wound surface);
- general( parenteral administration).
- Wound dressings, oral and skin care should be carried out in undamaged rubber gloves.After each, even the slightest manipulation, during which tactile contact with the patient occurred, the gloves should be disinfected( using chloramine, a solution of carbolic acid, lysol and other solutions,
- dressings must be collected in separate medical containers and burned immediately after dressing, And the containers used under it are thoroughly disinfected.
ASD1001ASD Pathogenesis
One of the features of anaerobic infection, due to which the disease is classified as heavy, is a very rapid spread in the tissues of the , which, in turn, quickly leads to intoxication of the whole organism.
Infection "seeps" into tissues, using a violation of their integrity.This is most common when:
Gas gangrene can develop even because of the smallest wound. The causative agent searches for the oxygen-free environment, adapts very quickly to the tissues and then begins to multiply rapidly, the amount of it increases rapidly. Classically, the disease develops:
The main pathogenetic feature of the action of clostridia is the predominance of necrotic processes in the tissues over the inflammatory( the latter may not be manifested at all).
Symptoms of gas gangrene depending on the causative agent
The clinical symptoms of gas gangrene depend on which particular representative of anaerobic infection caused the disease.In a number of cases, even without crops and microbiological research, a variety of pathogens can be identified.
In the defeat of Clostridium perfringens, the following are observed:
For Clostridium septicum are characterized by:
Clostridium oedematiens provokes:
Clostridium histolitycum is characterized by such pathological action as:
Clostridium histolitycum, acting with proteolytic toxins, extremely actively corrodes tissues.In 10-12 hours they are destroyed to such an extent that bones are visible - as if they are not biological tissues, but wax that melts under the influence of high temperature.
Gas gangrene is equally pronounced as local changes, at the tissue level, and common signs. Depending on what symptoms prevail, four types of disease are distinguished:
Clinical signs of emphysema
In the wound area, there is swelling, which quickly spreads to surrounding tissues, then further and further.From the very beginning of living in the human body, microorganisms secrete toxins that accumulate, lead to the necrosis of tissues.In the same time, pronounced gas formation is observed.Subjectively, the patient complains of severe pain in the wound.
Wound characteristics:
Skin around the wound:
If the limb is affected:
Clinical signs of edematous form
The edema observed around the wound becomes very generalized very quickly - it spreads far from the wound itself. The build-up of the edema is so strong that the tissues swell just before our eyes.
Wound characteristics:
Skin around the wound:
If the process develops on the limbs:
Clinical features of the phlegmonous form
The phlegmonous form, in comparison with other clinical forms of gas gangrene, does not develop so rapidly and affects a limited area of the body.
Wound description:
Skin:
With this form, there are signs of inflammation that can spread through the intermuscular spaces.Since the puffiness of the tissues is moderate, when the limbs are affected, the pulse on the peripheral vessels remains.
Clinical signs of the putrid( putrefactive) form
Characterized by rapid development and almost lightning decay.All the changes are mainly related to subcutaneous fat and intermuscular spaces.
Injury characteristic:
 Festering changes occur due to the fact that putrefactive bacteria join the anaerobic infection - a kind of symbiosis is formed, which explains such a rapid attack on the tissue. Toxic substances released by these microorganisms are universal in their destructive ability: they can destroy proteins of any tissues - including vascular walls, which explains the occurrence of secondary erosive bleeding.
Festering changes occur due to the fact that putrefactive bacteria join the anaerobic infection - a kind of symbiosis is formed, which explains such a rapid attack on the tissue. Toxic substances released by these microorganisms are universal in their destructive ability: they can destroy proteins of any tissues - including vascular walls, which explains the occurrence of secondary erosive bleeding.
Another important difference of this variety of gas gangrene from other forms is the tendency to damage the perineal tissues( especially in the rectum) and the mediastinum.While emphysema, edematous and phlegmonous forms affect mainly limbs( equally high and low).
General clinical features common to all forms of gas gangrene
Despite the fact that the clinical period of gas gangrene can be different in time - from 1-2 days to several hours - the incubation period( the period from the moment when microorganisms hit theTissue and the development of their pathological activity) is approximately the same and is 2-3 days . Compared to the incubation period of other infections, it is considered to be short.In some cases there is a lightning development, when several hours pass from the moment of infection and until the appearance of violent symptoms.
Common symptoms in all forms are the same:
With gas gangrene, signs of dehydration develop rapidly, which is another dangerous prognostic sign:
Characteristics of the central nervous system are also characteristic:
If you do not start treatment in time, then due to severe intoxication of the whole body within 2-3 days, there is a lethal outcome.
Diagnosis of gas gangrene
Symptoms of gas gangrene are so distinct that it is almost impossible to make a mistake in making the right diagnosis on the basis of clinical data.The main help is the combination of such signs as:
The diagnosis can be confirmed with the help of:
The following changes in the blood are observed:
The clinical picture is not similar to the manifestation of other infectious diseases, but in some cases the differential diagnosis is carried out with:
Treatment of gas gangrene
For symptoms of gas gangrene or suspected occurrence, one should resort to:
Surgical treatment includes:
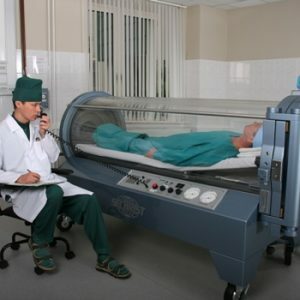 As an addition to the surgical intervention, hyperbaric oxygenation is shown - saturation of an organism of the patient with oxygen . For this, the patient is placed in a chamber in which pressure is increased to 3 atmospheres.Sessions last 2-2.5 hours - on the first day at least 3 times, more than 1 time per day.Hyperbaric oxygenation should in no case be regarded as an alternative method, which should be used instead of surgical intervention.
As an addition to the surgical intervention, hyperbaric oxygenation is shown - saturation of an organism of the patient with oxygen . For this, the patient is placed in a chamber in which pressure is increased to 3 atmospheres.Sessions last 2-2.5 hours - on the first day at least 3 times, more than 1 time per day.Hyperbaric oxygenation should in no case be regarded as an alternative method, which should be used instead of surgical intervention.
Please note! As the wounds remain open, in order to avoid intercurrent infection, a thorough sanitization of the patient's premises should be carried out with the help of disinfectants and using quartz lamps.
General treatment:
Patients with gas gangrene should be isolated in a separate room. For them it is necessary to allocate a separate nursing post.
All items that concerned such a patient( underwear, household items, utensils, surgical instruments) should be carefully treated according to instructions specifically designed for the case of a patient with gas gangrene in the clinic.
Vegetative forms of bacteria( actually, pathogens) die by boiling.But clostridia are able to form so-called exospores, which can withstand a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius and die only with repeated( fractional) boiling.
The instrumentation should be processed:
During development of the infectious process, antitoxins are formed in the human body, and antitoxic immunity is formed. It can be assessed by determining in the blood serum level:
But the tension of such immunity is low - both antimicrobial and antitoxic.Anti-infectious bodies:
Therefore, the level of such immunity is not enough to cope with gas gangrene, if its pathogens re-entered the body of a person who had previously had gas gangrene.Therefore, with repeated infection, the risks remain the same, the clinic and medical tactics do not change.
Prevention
If the clostridium is heavily wounded during extensive wounds, its simple washing, although modern antiseptics will be used, is not 100% able to protect a person from the disease by gas gangrene.Therefore, performs initial wound treatment - as soon as possible after the injury. Perform surgical excision of tissues - but not only removal of dead, but also non-viable within the tissues of healthy.Especially carefully clean the bottom of the wound. Such deep cleansing results in a pronounced pain response, therefore, surgical treatment of the wound should be performed under:
In the arsenal of preventive methods - anti-gangrenous sera. But, as practice shows, they do not justify the preventive hopes placed on them - not to mention the fact that the introduction of such serum often leads to serious complications( in particular, development of severe anaphylactic shock).
Despite its virulence, vitality and aggressiveness, anaerobes are microorganisms sensitive to the action of antibiotics. Therefore, after performing primary surgical treatment of the wound, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy should be performed:
Medical personnel who treat patients with gas gangrene( operating surgeons, assistants, treating doctors), perform medical appointments( nurses on duty, nurses dressing) and take care of them( nurses, nurses), must especially observe the rules of personal hygiene:
Forecast
Forecast for gas gangrene is complex
Due to the massive,After the recovery, the patients recover after prolonged recovery The health is restored for a long time, after the transfer of severe forms of the disease - not completely
In many cases, the limb is affected by disability - due to amputation or exarticulation of the affected arm or legLife indications.
If untimely started treatment( even with a delay of several hours), the forecast is unfavorable for life.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, medical adviser