Methods of prevention of adhesions
Short information about adhesions.
All organs of the pelvis and abdominal cavity are covered externally with the peritoneum. This is a very thin and shiny shell, on the smoothness and evenness of which depends the bias of the loops of the uterus, intestine and fallopian tubes. Thanks to this film and lubricant during pregnancy, during the operation of the stomach other organs continue to function normally.
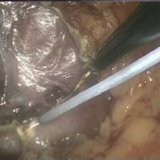
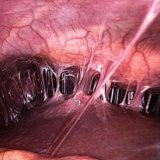
Inflammation of the peritoneum or peritonitis is a serious disease. The larger the area of damage, the more dangerous the situation. But, the human body has found a way to prevent this dangerous disease through the formation of adhesions. During the inflammation of the abdominal region, all organs swell, and on the peritoneum an adhesive substance is formed, namely, fibrin. When the peritoneum of one organ touches the peritoneum of the other, thanks to fibrin they stick together and thus prevent the spread of the inflammatory process. After recovery, these adhesions do not disappear anywhere, on the contrary they can grow together in the form of transparent whitish films. It is these films that are called spikes. Spikes by their nature protect the abdominal cavity from the spread of purulent-inflammatory processes.
The inflammatory process of the abdominal cavity does not always lead to the formation of adhesions. If treatment is started on time and carried out correctly, then there should be no problems. Basically, they appear only during a chronic illness or a long healing.
Spikes can adversely affect the functioning of the body as a whole: they disrupt the functioning of various organs, so they can cause intestinal obstruction or infertility in gynecology and many other diseases. Therefore, the prevention of this disease is very important, especially if the patient underwent surgery.
Basic methods of prevention of adhesions.
If after the operation there are symptoms of intestinal obstruction, then it's time to start the prevention of adhesions. Today, there are many treatments for adhesions, but they are not very effective. Therefore, it is very important to take preventive measures on time.
Prevention of an adhesion disease consists of the following:
- timely treatment and surgical intervention for inflammation in the abdominal cavity without the use of rough tampons and drains;
- use of various anticoagulants( like heparin or fractiparin), as well as prednisolone with novocaine;
- timely stimulation of intestinal motility with the help of proserin;
- rinsing, and sometimes peritoneal dialysis;
- use of drugs that dissolve fibrin, because of which spikes are formed. To do this, usually use - urokinase, chymotrypsin, fibrinolysin, streptokinase or trypsin;
- to conduct therapy both after the operation and before it with the help of such groups of antibiotics as tetracycline, cephalosporin or sulfonamide.
But, in order to proceed with the prevention of this disease, it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis. It is reconciled when receiving anamnestic data, and on these instrumental studies( laparoscopy, x-ray, nuclear magnetic resonance).In addition, laparoscopy not only reveals the presence of adhesions and the severity of the process itself, but also treats this disease.
For the diagnosis of the intestine, the electrogastroenterography method is also often used. With it, you can measure electrical signals that come from the stomach and other parts of the intestine. This method can be performed only with the help of such a device as "Gastroscan-GEM".
New methods of prevention of adhesions.
Modern methods of preventing disease associated with the appearance of adhesions are not very effective. Therefore, scientists are constantly searching for new methods and methods of prevention. The root cause of commissural disease is considered to be inflammation of the peritoneum, postoperative intestinal paresis or surgical trauma.
It is very useful in the post-operative period to undergo treatment with corticosteroids - they reduce reparative processes in the wound and may well affect the inconsistency of intestinal anastomoses.
Prednisolone is very helpful in this disease. For proof of harmlessness of this drug, even carried out tests on dogs. After passing the tests, it became clear that this drug does not reduce the strength of the suture joints and does not slow the healing of the wound of the intestinal wall in comparison with other similar prednisolone preparations.
To prevent the formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity after the transfer of the operation in the first place, everything must be done in order to restore intestinal motility. Without the use of stimulating agents, the intestinal peristalsis is restored within 3-4 days, which leads to the appearance of adhesions. Therefore, the use of stimulants is mandatory.
Another effective method of prevention is to remove the peritonitis, drain the abdominal cavity and inject into it a mixture consisting of 50 ml of 0.25% solution of novocaine, 30 mg of prednisolone and 500 thousand units of antibiotic. Enter all this with a rubber irrigator once a day for 3-4 days after the operation, depending on the situation. Also, except for this three times a day, the patient must be injected intramuscularly with 1 ml of a 1% solution of dimecoline.
No less effective method of prevention of adhesive intestinal obstruction, especially in patients who have not been operated on for this for the first time, is intubation of the small intestine. It is carried out with the help of a special probe with the laying of its loops in a certain order. Intestinal loops are fixed by fusions on this skeleton in a functionally advantageous position.
In practice, the following methods are also used for the prevention of adhesions: large gland seal, abdominal suture, qualitative sanitization of the abdominal cavity and restoration of the natural location of the small intestine loops.