Vitamin D( calciferol): what is needed and in what products is contained
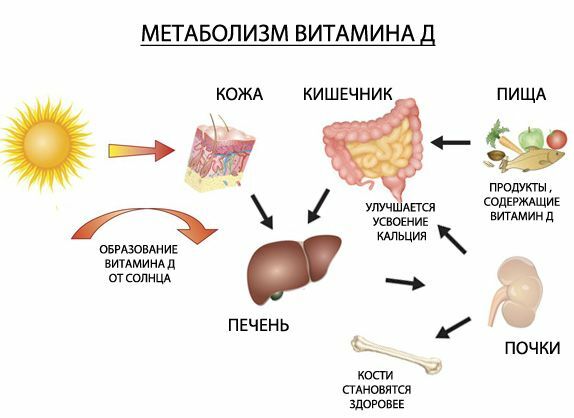
 The term "vitamin D" or "calciferol" combines several biologically active compounds that are necessary for the absorption and assimilation of such vital elements as phosphorus and calcium.These include D2( ergocalciferol), which the body receives only alimentary way, and D3( cholecalciferol), synthesized in the skin of a person under the influence of UV radiation.Also known are compounds D4, D5 and D6, which are provitamins.
The term "vitamin D" or "calciferol" combines several biologically active compounds that are necessary for the absorption and assimilation of such vital elements as phosphorus and calcium.These include D2( ergocalciferol), which the body receives only alimentary way, and D3( cholecalciferol), synthesized in the skin of a person under the influence of UV radiation.Also known are compounds D4, D5 and D6, which are provitamins.
Calciferol refers to lipid soluble substances( lipovitamins).The presence of a sufficient amount of lipids in food is an indispensable condition for the normal assimilation of vitamin D. The compound has a property to be deposited in the body.Its reserves are created mainly in the summer months due to insolation( action on the skin of the solar ultraviolet).
Contents: Why do I need vitamin D?Where is vitamin D present?Calciferol intake standards Vitamin D hypovitaminosisWhy do I need vitamin D?
Thanks to calciferol absorption of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, necessary for the formation and growth of bones.The absorption of these trace elements occurs mainly in the duodenum, and the vitamin increases the permeability of intestinal wall epithelial cells for Ca2 + and P.
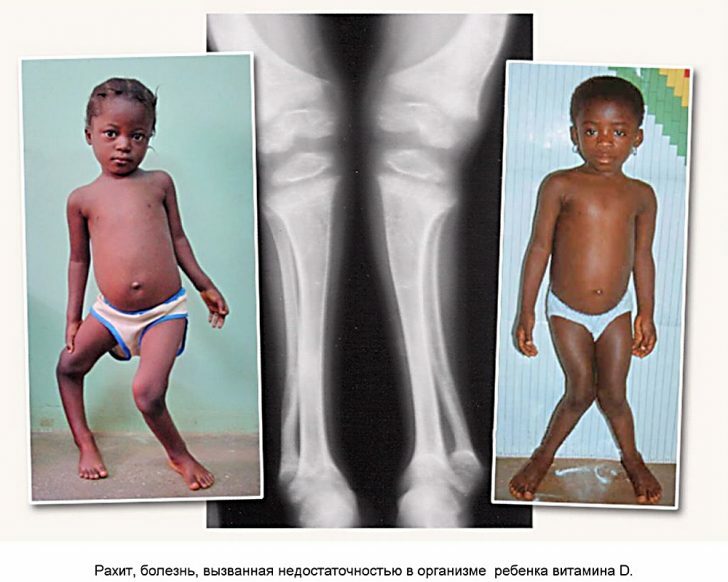
. Due to the regulation of the metabolism of minerals, calciferol prevents the development of osteoporosis in adults and rickets in children.Vitamin D is responsible for the calcification of hard tissues of the teeth( in particular - dentin).
Studies have shown that this compound takes part in a number of metabolic processes, stimulates the biosynthesis of certain hormonal compounds and regulates the process of cell division.
Cholecalciferol helps to lower blood pressure( it is especially effective in hypertension during pregnancy).
Calciferol is the only vitamin compound that can act as a hormone, increasing the reabsorption of calcium ions and taking a direct part in the production of the protein responsible for the transport of Ca2 +.
Important: activity of calciferol preparations is generally measured in IU( international units).1 μg of vitamin D corresponds to 40 IU.
The normal level of vitamin D in the liver and plasma reduces the likelihood of malignant neoplasms, cardiac, skin and joint pathologies.In regions where the products contain little calciferol, there is a higher incidence of diabetes( including adolescence) and atherosclerosis.
Vitamin D promotes an increase in resistance of the body due to the strengthening of nonspecific immunity.It normalizes the functional activity of the thyroid gland, and also prevents muscle weakness.
The stimulation of the assimilation of magnesium and calcium allows restoring the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, therefore, calciferol preparations are used as part of complex therapy of such a serious pathology as multiple sclerosis.
Where is vitamin D present?Calcium sulphate( in particular D2) is found in a number of food products of plant and animal origin.

Animals products:
- fish of fatty varieties;
- caviar;
- whole milk;
- fermented milk products;
- cheese;
- butter;
- eggs( yolk).
Note : the phosphorus present in cow's milk largely hampers the absorption of calciferol.
From natural products the most effective means for the prevention of rickets and other manifestations of hypovitaminosis is fish oil.
Absorption of calcium-supplemented calciferin occurs in the small intestine.An indispensable condition for its normal assimilation is the presence of bile, so hypovitaminosis can develop against the background of pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and ducts.
Vegetable products containing vitamin D:
- parsley( herbs);
- nettle( leaves).
Note: has a lot of vitamin D in herbs such as alfalfa and horsetail.
Cholecalciferol( D3) is produced in the skin from provitamins( sitosterol, ergosterol and stigmasterol) under the influence of UV radiation.Provitamins the organism receives with plant products or as a result of biotransformation of cholesterol.
It is established that with good insolation the body can independently produce vitamin D in a volume sufficient for normal metabolism.
The volume of synthesized cholecalciferol depends on the following factors:
- human age( in the aging skin, the level of vitamin production is significantly reduced);
- degree of skin pigmentation( in the light skin the process proceeds more actively);
- wavelength of sunlight( the optimum time for insolation is dawn and sunset);
- degree of air pollution( smoke and smog detain a significant amount of UV radiation).
Note : The incidence of rickets( a disease that is caused by a deficiency of the vitamin D) is higher among children in the industrial regions of Asia and Africa.This is due to the combination of insufficient receipt of solar ultraviolet radiation and malnutrition.
Calciferol intake standards
 Adults per day require an average of 2.5 μg of vitamin D. The need for it increases dramatically in pregnant and lactating women.To ensure normal growth and the formation of the skeleton of the fetus and the infant, they need to take 10 μg of calciferol per day.
Adults per day require an average of 2.5 μg of vitamin D. The need for it increases dramatically in pregnant and lactating women.To ensure normal growth and the formation of the skeleton of the fetus and the infant, they need to take 10 μg of calciferol per day.
Babies from birth to 3 years of age need 10 mg of vitamin D per day, and for children from 4 years the rate of consumption is the same as for adults.
The need for vitamins is significantly increased in people who do not receive enough UV radiation.
The probability of developing hypovitaminosis increases in the following categories of people:
- working in the night shift;
- patients who do not leave the enclosed premises( recumbent);
- living in areas where the atmosphere is heavily polluted;
- residents of high latitudes.
In elderly people, the ability of the skin to synthesize cholecalciferol is reduced by an average of 2 times.From vitamin Vitamin D deficiency, vegetarians and those who consume few foods containing natural lipid compounds are particularly vulnerable.
Vitamin D hypovitaminosis
The most serious manifestations of severe vitamin D deficiency are osteomalacia( softening of bone tissue due to insufficient mineralization) and rickets.
Clinical manifestations of hypovitaminosis D:
- sleep disorders;
- burning sensation in the mouth and throat;
- appetite impairment;
- weight loss;
- decreased visual acuity.
You can get more detailed information about the problems associated with vitamin D deficiency in children by viewing the video review:
Indications for taking calcitinol preparations
The intake of vitamin D is prescribed if the patient is diagnosed with:
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- rickets in children;
- Osteoporosis( including age-related);
- osteomalacia;
- bone fractures( to accelerate the splicing);
- dystrophy of bone tissue( against kidney pathology);
- gastritis against a background of disturbed synthesis of hydrochloric acid;
- syndrome of intestinal malabsorption;
- inflammation of the intestines, accompanied by osteoporosis;
- tuberculosis;
- chronic pancreatitis( with a decrease in secretory function).
It is recommended to take calciferol to improve immunity, as well as for the prevention and treatment of pollen( pollen allergies), psoriasis, joint inflammation and hemorrhagic diathesis.
Note : it is advisable to take vitamin D women during menopause.
 Future mothers are prescribed D2 in the third trimester, starting from 30-32 weeks.The duration of the course is 10 days, during which a total of 400,000-600,000 ME of vitamin is taken.During lactation it is advisable to take 500 IU of ergocalciferol from the first day of breastfeeding to the time when the baby itself can prevent the rickets.
Future mothers are prescribed D2 in the third trimester, starting from 30-32 weeks.The duration of the course is 10 days, during which a total of 400,000-600,000 ME of vitamin is taken.During lactation it is advisable to take 500 IU of ergocalciferol from the first day of breastfeeding to the time when the baby itself can prevent the rickets.
Babies D3 are usually prescribed( starting from 3 weeks) in small doses, but continuous courses.The total dose for the course is 300,000 ME.
Diagnosed rickets require the daily administration of vitamin D2 for 2000-5000 IU for 30-45 days.
Important: if necessary to treat high doses of calciferol in parallel, you need to take vitamins A, C and compounds of group B.
For the effective prevention of hypovitaminosis, 300-500 ME D3 per day is indicated.
Contraindications to vitamin therapy with calciferol preparations are:
- organic myocardial damage;
- hypercalcemia;
- ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- acute and chronic liver pathology;
- kidney failure.
Hypervitaminosis D
Because vitamin D3, like other lipovitamins, is deposited in the body, nutritional intake rarely leads to hypervitaminosis, but accumulation is possible with high doses of calciphyrol.
Vitamin D causes hypercalcemia.If a large amount of calcium accumulates in the vascular walls, then the likelihood of atherosclerotic plaques is increased.The process is aggravated when the intake of magnesium ions is insufficient.
In hypervitaminosis D the following clinical manifestations develop:
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- marked arthralgia;
- muscle pain;
- Dyspeptic disorders;
- arterial hypertension;
- dizziness;
- insomnia.
- bradycardia( reduction of heart rate);
- feverish reaction;
- convulsions.
Prolonged reception of very high doses of calciferol can cause the following complications:
- bone demineralization;
- calcification of soft tissues( including heart valves;
- calcification in the kidneys, cardiac muscle, and organs of the digestive and respiratory systems.)
Recommendations
When treating D-hypovitaminosis, you need to consume a sufficient amount of plant( preferably - andAnimals) fats

Taking vitamin D supplements is not desirable in parallel with drugs to lower cholesterol.The absorption of calciferol is adversely affected by mineral leks
Corticosteroid hormones accelerate the elimination of vitamin D from the body, in violation of calcium absorption in parallel
Calcium metabolite is poorly influenced by diphenine and barbiturate agents, which can trigger the development of osteoporosis
For a normal course of vitamin D metabolismThe liver needs a sufficiently high level of vitamin E.
Plisov Vladimir, dentist, phyto-therapeutist