Pseudomonas aeruginosa: symptoms and treatment
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative bacterium belonging to the genus pseudomonads.The microorganism lives in the soil and in open reservoirs.It actively multiplies with access to oxygen and an increased level of humidity.This bacterium can affect various organs and systems, causing a number of serious diseases.Therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is complex, since the bacillus is highly resistant to most antibiotics.This bacterium is the most common cause of so-called.Nosocomial infections( up to 20% of recorded cases).The share of this pathogen accounts for a quarter of purulent surgical pathologies and about 35% of infections of the urinary system.Pseudomonas aeruginosa is also detected in 25% of cases of primary bacteremia.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative bacterium belonging to the genus pseudomonads.The microorganism lives in the soil and in open reservoirs.It actively multiplies with access to oxygen and an increased level of humidity.This bacterium can affect various organs and systems, causing a number of serious diseases.Therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is complex, since the bacillus is highly resistant to most antibiotics.This bacterium is the most common cause of so-called.Nosocomial infections( up to 20% of recorded cases).The share of this pathogen accounts for a quarter of purulent surgical pathologies and about 35% of infections of the urinary system.Pseudomonas aeruginosa is also detected in 25% of cases of primary bacteremia.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa affects the intestines, heart, organs of the genitourinary and respiratory systems.The microorganism is often the cause of abscesses and phlegmon.
Table of contents: Pathogenicity Stages of infection development Ways of infection Risk groups Clinical signs Diagnosis Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosaPathogenicity
 The risk of development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathologies in patients with weakened immunity is especially high.The bacterium is considered opportunistic.With a sufficiently high resistance of the organism, its reproduction is competitively blocked by normal microflora.
The risk of development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathologies in patients with weakened immunity is especially high.The bacterium is considered opportunistic.With a sufficiently high resistance of the organism, its reproduction is competitively blocked by normal microflora.
The pathogenicity of the bacterium is due to factors such as its high mobility and the production of a number of toxins that lead to the disruption of the functions of blood cells( erythrocytes), the destruction of hepatocytes( liver cells), and the destruction of leukocytes that accumulate in the foci of inflammation.Resistance to many antibiotics is explained by the fact that colonies of bacteria can form around themselves a special protective capsule.
Stages of infection development
The development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa consistently goes through 3 stages:
- In the first stage, the bacterium attaches to the tissue and multiplies.Thus, the primary focus is formed.
- The second stage is the penetration of the pathogen into the deeper tissues of the body.In this case we are talking about the so-called.Local infection, which is partially restrained by the body's defenses.
- The third stage involves getting the bacterium into the systemic bloodstream and then spreading to distant organs and tissues.
Pathways of infection
The source of the causative agent of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection can be both patients and people who are carriers of the bacterium.The greatest danger from the point of view of spreading is patients with lung lesions.
The rod can be transmitted by airborne, by contact and by alimentary route.In the body, it comes with contaminated food and water.The causative agent may be present on the objects of the surrounding situation( including door handles and washstand faucets).The cause of outbreaks of nosocomial infections is often the neglect of aseptic and antiseptic rules.One of the transmission factors are poorly sterilized tools and not sufficiently well-washed hands of medical staff.
Risk groups
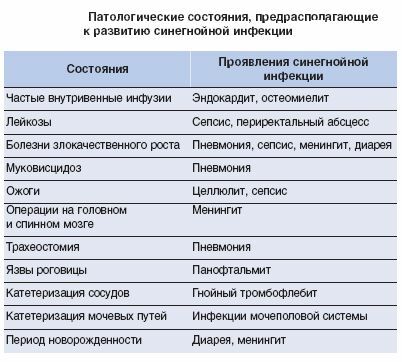
From medical institutions, at risk are purulent surgery departments, as well as burn centers and maternity hospitals.
Patients with a low level of immunity are at the greatest risk of infection.They are children, old people, and also people who already have serious illnesses.The most vulnerable category are preterm infants and toddlers of the first months of life.
In newborns, the rod can cause inflammatory damage to the membranes of the brain and digestive tract.
In burn patients, bacteria is one of the causes of sepsis development.To the same pathology can lead and the development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa against the background of leukemia.In malignant tumors, Pseudomonas aeruginosa usually leads to pneumonia.Corneal ulcers in combination with this infection cause panophthalmitis.
With regular urinary catheter installations, the risk of urinary tract infections is high, and the catheterization of the vessels when bacteria enter the body leads to purulent thrombophlebitis.After operations on the brain, complications such as meningitis and encephalitis are possible.Frequent intravenous infusions can cause endocarditis and osteomyelitis.When performing tracheostomy, Pseudomonas aeruginosa can provoke bacterial pneumonia( pneumonia).
Clinical Signs
The symptomatology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection depends on which organs the bacterium has infiltrated.
In case of defeat with Pseudomonas aeruginosa CNS, the following can develop:
- purulent meningitis( inflammation of the meninges);
- purulent meningoencephalitis( the inflammatory process affects not only the membranes, but also the substance of the brain);
- abscesses of the brain.
For these pathologies, the prognosis is generally unfavorable.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa of the respiratory system usually occurs against the background of existing respiratory tract diseases, such as:
- bronchitis;
- bronchiectatic disease;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- pneumonia.

The causative agent is often entered during endotracheal intubation.In a group of risk - patients who are on ventilation( connected to the device of artificial ventilation of the lungs).Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause pneumonia( primary or secondary), resistant to antibiotic therapy.
When entering the bacterium in the auditory canal, acute purulent otitis externa develops, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- presence of discharge from the auditory canal( pus with blood admixture);
- intense pain in the ear.
One of the most probable and most serious complications of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in this case is mastoiditis( defeat of the mastoid process of the temporal bone).
Lesion of the digestive system is accompanied by symptoms of acute inflammation of the gastric and intestinal mucosa( gastroenterocolitis), including:
- epigastric pain( i.e., in the projection of the stomach), which then spread to the entire abdomen;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- marked general malaise;
- decreased appetite;
- increase in body temperature( within subfebrile values - up to 38 ° C,
- frequent stools( with pathological impurities - mucous and bloody)
In children of early age, Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is particularly difficult.Regurgitation, diarrhea and temperature up to 39 ° C. Children are especially likely to develop acute dehydration( dehydration) and intestinal bleeding.For children of the older age group, such complications as cholecystitis( inflammation of the bileBladder) and appendicitis.The duration of the disease can be up to 4 weeks.It is accompanied by a pronounced intestinal dysbacteriosis
The lesion of the gastrointestinal tract sometimes has a few erased symptoms
Against the background of getting the pathogen in the urinary ways of the patient there is a possibility of the development of the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis( inflammation of the renal pelvis);
- Cystitis( inflammation of the walls of the bladder);
- urethritis( inflammation of the ureter's mucosa).
Pseudomonasemal infection of the urinary tract often acquires a chronic course.
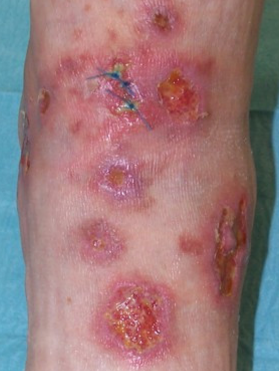
Note : An important sign of Pseudomonas infection of the skin and soft tissues is a characteristic discoloration of the color that is separated from the wound or burn surface.Pus has a blue-green color.Complication with the penetration of the rod into the tissues can become osteomyelitis.The defeat of the skin in a number of cases leads to gangrenous ecstema.
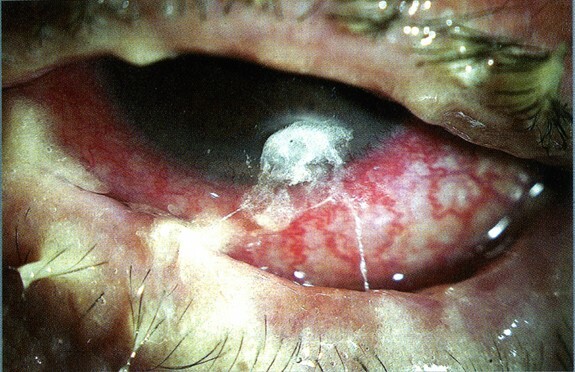
Pseudomonal infection of the eye is manifested by the following symptoms:
- vision impairment;
- feeling of "foreign body" in the eye;
- pain syndrome;
- is a purulent discharge.
Pathology can lead to purulent inflammation of the conjunctiva, keratitis and even damage to the eyeball tissue.In severe cases, the patient sometimes faces a significant reduction in visual acuity and even blindness.
Signs of bacteraemia with Pseudomonas aeruginosa are:
- tachycardia;
- rapid breathing;
- sharp drop in blood pressure;
- jaundice of the skin;
- shock( toxic origin).
Important: Pseudomonas aeruginosa can infect vessels, articular tissues, paranasal sinuses and other organs.One of the most serious manifestations of infection is sepsis, ie, generalized infection.
Diagnosis
Setting a preliminary diagnosis can cause difficulties, because the symptom specific for this pathogen is practically absent( the exception can be considered the color of the discharge in the purulent process in the wounds).
Assuming pseudomonas infection allows ineffectiveness of ongoing systemic antibiotic therapy and the association of pathology with trauma or some medical procedures.
The diagnosis of "Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection" can be confirmed only after laboratory tests of the material.
General analyzes help to clarify only the clinical form of the infectious disease.
Depending on the intended location of the focus for diagnosis, the following test methods are also used:
-
 chest X-ray;
chest X-ray; - computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound;
- lumbar puncture;
- bronchoscopy;
- thoracocentesis.
Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Patients with suspected Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection are subject to urgent hospitalization in the profile hospital.Patients are shown a strict bed rest for the entire period of clinical symptoms.
Very often there are strains resistant to antibacterial drugs.In particular, the rod is resistant to tetracyclines.
The following antibiotics are effective:
- carbapenems;
- individual preparations of cephalosporin series.
Amicacin, which belongs to the last generation of aminoglycosides, is effective in some cases.To the fluoroquinolones the stability of the strains develops very quickly, but Ciprofloxacin allows to achieve positive results.
 In practice, as a rule, designate at once not less than two means.For example, in infectious endocardial lesions, large doses of aminoglycosides are indicated in combination with penicillin preparations or a broad-spectrum antibiotic from the cephalosporin group.A similar tactic is recommended for bacteremia, but one of the remedies can be replaced with rifampicin.With purulent otitis, corticosteroids in combination with antibiotics are effective.
In practice, as a rule, designate at once not less than two means.For example, in infectious endocardial lesions, large doses of aminoglycosides are indicated in combination with penicillin preparations or a broad-spectrum antibiotic from the cephalosporin group.A similar tactic is recommended for bacteremia, but one of the remedies can be replaced with rifampicin.With purulent otitis, corticosteroids in combination with antibiotics are effective.
The duration of drug therapy can be from 2 to 6 or more weeks.
Symptomatic( postdromous) therapy is prescribed depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.
In some cases, the patient is shown surgical treatment.It is necessary to deeply treat infected wounds.Dead tissue is subject to excision.Sometimes, to save the patient's life, amputation( in particular, with pseudomonas infection against the background of the "diabetic foot") can be shown.Urgent surgery is also performed if there is a suspicion of necrosis or abscess of the intestine or the presence of perforation in the organs of the digestive tract.
Konev Alexander, internist