Technique for performing spinal anesthesia
A bit of history.
Spinal anesthesia was first performed in 1897 with ankle resection. Soon, the progressive method attracted the attention of a large number of surgeons who began to use it widely in their medical practice. In obstetric practice, spinal anesthesia was first used in 1900.
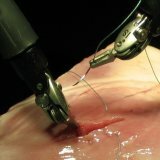
For spinal anesthesia a set of tools is used, consisting of needles of various types and sizes( for example, the Quincke needle).
For spinal anesthesia 2% solutions of trimecaine, 0.5% of marcaine, 2% of lidocaine, 1% of dicaine are used. Local anesthetics are found in the epidural space. Thus, the roots of the spinal nerves are blocked. The action of anesthetics should be reduced to a decrease in the ability of cellular membranes to be excited. Thus, the effect of anesthetics on the myocardium should be reduced to a decrease in excitability, intracardiac conduction and a weakening of the influence of mediators. Due to the influence of anesthesia, the blood vessels expand, which in turn leads to an increase in the capacity of the vascular bed. With stable hemodynamics, epidural anesthesia does not have any adverse effect on external breathing. At the general anesthesia, in connection with its centralized action, oppression of cardiovascular activity and respiration is marked.
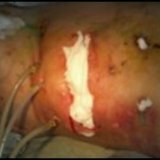
The main damage during spinal anesthesia can be considered an unnoticed puncture of the dense dura mater and the penetration of the entire anesthetic( or its significant amount) into the subarachnoid cavity. As a result of such damage, the sympathetic innervation is blocked in the greater part of the body, the tone of the vessels decreases, the volume of the vascular bed increases, which can quickly lead to the development of a deep collapse. As a result, when performing the technique of spinal anesthesia, you need to carefully identify epidural space.
The technique of performing spinal anesthesia involves several methods of .
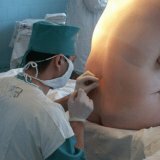
With the median method, after you have processed the puncture site with alcohol, you need to identify an interstitial gap. After this, a spinal needle with mandril is inserted into the interval between the spinous processes through the interstitial and adnate ligament.
If the physician does not have enough experience in carrying out this technique of spinal anesthesia, it is most convenient to puncture the area of L7-S1.It is here that the lumbosacral opening is more pronounced than the interstitial holes of other levels. The direction of the needle should depend on the angle of inclination of the spinous processes. After passing through the needle of the yellow ligament, the sensation of the "failure" of the tip of the needle takes place, "signs of loss of resistance" are revealed.
If during the procedure the tip of the needle interferes with the arc of the spine, you need to pull the needle back and, slightly changing the angle, try to enter it again.
After a puncture of the epidural space, a "test dose" of the anesthetic solution should be introduced to exclude allergic reactions.
With the paramedical method in the technique of performing anesthesia, the skin puncture is performed at a depth of 0.5-2 centimeters, depending on the weight of the patient, laterally the median line. The needle is aimed at an angle of no more than 20 degrees.to the medial plane. In this case, the interstitial ligaments stay apart, and only the yellow ligament has to be overcome.
In medicine, numerous methods and techniques have been developed to identify the epidural space. They are divided into visual, tactile, combined. Combined methods of identification use various devices. The easiest tactile symptom is the sensation of "loss of resistance" when the tip of the needle penetrates the epidural space. To perform this method, a small air bubble is left in the syringe with the solution attached to the puncture needle. With periodic and frequent pressure on the piston, when the needle passes through the hard ligaments, the bubble contracts, and after expansion of the pressure again expands. When the vesicle enters the epidural space, its springing effect disappears, because the solution can pass without resistance through the needle. At this point, the progress of the needle should be suspended. This method of identifying epidural space is the most common.
A sign of a "suspended" drop.
The symptom of a "hanging" or "suspended" drop is visual and is defined as follows. At the moment when the point of the needle is in the yellow ligament, a drop of the solution used for anesthesia is hung from the pavilion of the needle, then the needle is gently pushed forward. At the moment when the needle enters the epidural space, after which the drop is drawn into it because of the negative pressure in the epidural space.
Another method of finding epidural space is known. It consists in the fact that the puncture is carried out from two points, with two needles, in two nestled interstitial spaces. If the needles are in the epidural space, an anesthetic solution starts to be injected through one needle and immediately outward through the second needle. This is a guarantee of finding the needles in the epidural space.
The technique of spinal anesthesia should be carried out with great care to prevent puncture of the dura mater, which can lead to unpleasant consequences.