Actinomycosis: varieties, manifestations, diagnosis, treatment
 Actinomycosis( another name - radiate-fungal disease) is a chronic pathology, the occurrence of which provokes different types of actinomycetes.With actinomycosis, the defeat of various organs and tissues is the formation of compacted infiltrates, which after a while are inflamed with the appearance of fistulas( pathological strokes), as well as a specific lesion of the skin around them.
Actinomycosis( another name - radiate-fungal disease) is a chronic pathology, the occurrence of which provokes different types of actinomycetes.With actinomycosis, the defeat of various organs and tissues is the formation of compacted infiltrates, which after a while are inflamed with the appearance of fistulas( pathological strokes), as well as a specific lesion of the skin around them.
Etiology.Characteristics of the causative agent
The most common actinomycosis is caused by such varieties of the causative agent :
- Actinomyces Israeli;
- Actinomyces bovis;
- Actinomyces albus;
- Actinomyces violaceus.
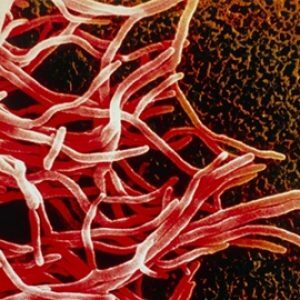 This mushroom was named radiant because it grows on a certain nutrient medium and forms peculiar colonies, often characterized by radiant margins.In the pathological material distinguish individual lumps of yellowish color, having a diameter of 1-2 mm - they are also called druses .At a microscopic examination in the middle of the lumps there are accumulations of filaments of mycelium( actually, the "body" of the fungus), which on the periphery of the druses turn into bulges that look like flasks( sometimes they are absent).
This mushroom was named radiant because it grows on a certain nutrient medium and forms peculiar colonies, often characterized by radiant margins.In the pathological material distinguish individual lumps of yellowish color, having a diameter of 1-2 mm - they are also called druses .At a microscopic examination in the middle of the lumps there are accumulations of filaments of mycelium( actually, the "body" of the fungus), which on the periphery of the druses turn into bulges that look like flasks( sometimes they are absent).
Actinomycetes are characterized by sensitivity to such antibiotics as:
- Benzylpenicillin( it is more commonly known as penicillin) - at a dose of 20 U / ml;
- streptomycin - at 20 μg / ml;
- tetracycline - at 20 μg / ml;
- levomycetin - at 10 mcg / ml;
- erythromycin - at 1.25 μg / ml.
Actinomycetes cause disease not only in humans, but also in farm animals.Nevertheless, cases of human infection from an animal, as well as from another person, were not recorded.It is interesting that actinomycetes were not once found by chance in other people when a survey was conducted to clarify another diagnosis.They were found:
- in the oral cavity;
- in plaque on the teeth;
- on palatine tonsils;
- on the mucosa of the digestive tract.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of the disease is extensive - actinomycosis is diagnosed in patients in all countries.Pathogens are widespread in nature.They were found in soil, on living plants, hay, straw and other natural structures.
Pathogenesis
With plants actinomycetes enter the body and settle on the mucous membranes in the form of saprophytes - a kind of condition where the microorganism lives in the body of the "master", but does not harm living its life.
Actinomycetes pass from saprophytic to parasitic state when a person falls ill - mainly when an inflammatory disease of mucous membranes:
- of the mouth;
- respiratory tract;
- digestive tract.
Transition of actinomycetes from saprophytic to parasitic state is facilitated by diseases of tissues and organs where these organisms live. Actinomycetes begin to actively affect the place where they live, resulting in forming a seal - an infectious granuloma that can germinate into the surrounding tissues of .Because of the mass scattering of actinomycetes, such granulomas can be scattered all over the organ that they have struck. Due to the effects of secondary infection, the granuloma undergoes the following changes, one after the other:
- is inflamed;
- is suppressed;
- appears multiple abscesses - limited small cavities filled with pus;
- wall abscesses can not withstand overflow with purulent contents and breaks, fistulous passages are formed.
Secondary infection is associated, as the body is weakened by the fight with the infectious agent.In most cases, it is staphylococci. They also contribute to suppuration of infiltration granules created by actinomycetes.The pathological process is aggravated by the fact that the antigens of radiant fungi cause a specific sensitization of the body, as a result of which it becomes more sensitive to any antigens - in particular, the microorganisms that attack it at the moment. Allergic alteration of the body is manifested:
- delayed hypersensitivity;
- by tuberculin-type hypersensitivity;
- formation of antibodies( complement-binding, agglutinins, precipitin, etc.).
Incubation period and clinical signs
The incubation period can vary very widely - from 2-3 weeks to several years.
The following clinical variants of actinomycosis are distinguished:
-
 with soft tissue damage of the head and neck;
with soft tissue damage of the head and neck; - thoracic( organs and walls of the thorax);
- abdominal( affects the abdomen);
- with damage to bones and joints;
- with skin lesions;
- with CNS lesion;
- with genitourinary damage;
- is a mycetoma, or a Madurian foot.
The disease refers to the primary chronic infections of , therefore it is characterized by:
- with a prolonged course;
- with continuous progression.
A visual picture of what changes in tissues is caused by actinomycosis gives a visual picture when skin is involved:
-
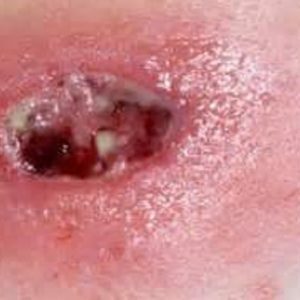 , a very firm, but painless infiltrate appears in its thickness;
, a very firm, but painless infiltrate appears in its thickness; - infiltrate develops into an abscess, which is manifested by fluctuation( softening);
- , the walls of the abscess under pressure of pus erupt, long-term non-healing fistulous passages with purulent-serous discharge are formed, with the microscopic examination of which it is possible to find drusen of whitish-yellow color.
Symptoms of maxillofacial actinomycosis
This is the most common form of actinomycosis . By the severity of the process, one can distinguish such forms:
- cutaneous, or superficial;
- subcutaneous;
- is muscular, or deep.
With the cutaneous form of actinomycosis, which is quite rare, the flow compared to other forms is rather favorable . Infiltrates are similar to balls or have a hemispherical shape, are not deep beneath the skin. Changes can capture:
- cheeks;
- one or both lips;
- language all along its length;
- amygdala;
- area of the eye sockets;
- larynx.
In the muscular variety, pathological changes concern mainly the masticatory muscles( localized under the connective tissue fascia, which covers them).Can form an infiltrate of increased density( consistency - as in cartilage) in the region of the mandibular angle. The face acquires a characteristic appearance:
- it is asymmetric;
- observed trisus( muscle spasm, which does not allow the movement of the lower jaw).
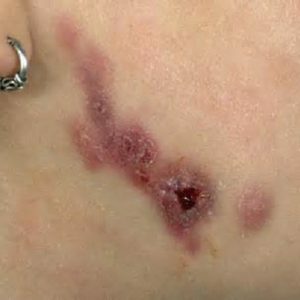 Despite the fact that the infiltrate has an increased density, soon it forms softening areas that increase and merge with each other, then randomly break through, forming fistulas.Of fistulas, a purulent fluid( or bloody purulent discharge if the process has eroded small vessels) is secreted.In the fluid, druses are sometimes observed.
Despite the fact that the infiltrate has an increased density, soon it forms softening areas that increase and merge with each other, then randomly break through, forming fistulas.Of fistulas, a purulent fluid( or bloody purulent discharge if the process has eroded small vessels) is secreted.In the fluid, druses are sometimes observed.
The skin around the fistula has a characteristic purple-cyanotic color, which indicates that these fistulas are of actinomycotic origin. Another characteristic feature - when the skin of the neck is affected, it acquires the appearance of transversely arranged ridges.
Symptoms of Thoracic Actinomycosis
The frequency among other varieties of this disease ranks second. Painting with lesions of the chest develops slowly, gradually appear:
-
 weakness;
weakness; - increase in body temperature to low-grade figures( 37.1-37.4 degrees Celsius);
- coughing, and later a full-fledged cough;First it is dry, without branches, then phlegm-purulent sputum begins to stand out, often - an admixture of blood( if the process has destroyed small vessels).There is a characteristic prognostic sign - patients note that the sputum has a taste of copper and the smell of soil( earth).
After the initial changes appear clinical picture of peribronchitis - lesions of the tissues around the bronchi. In tissues an infiltrate is formed, then it spreads further and in turn captures:
- pleura;
- chest wall;
- skin.
Skin lesion indicates that the process is prolonged. Skin characteristics:
- formed a characteristic swelling, very painful when feeling( patients complain of burning sensations with or without feeling);
- the skin acquires a characteristic bluish-purple hue;
- fistulae are formed, which communicate directly with the bronchi.In the discharge from the fistula, you can find druses.
The course of this form is severe, self-healing does not occur.
Symptoms of abdominal actinomycosis
The frequency of other forms of actinomycosis ranks third.
The primary focus is most often formed at the junction of the ileum( terminal section of the small intestine) into the blind( the initial section of the large intestine), and also in the region of the appendix. All this localization accounts for about 60% of the total abdominal form of the disease.In second place among all forms of abdominal actinomycosis is actinomycosis of other parts of the large intestine. Extremely rare primary foci are found in:
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- small intestine.
An infiltrate of primary origin originating in the abdominal cavity provokes symptoms similar to those in some surgical diseases:
- acute appendicitis;
- liver abscess;
- purulent cholecystitis;
- acute and chronic intestinal obstruction;
- local peritonitis;
- Crohn's disease
- and so on.
The infiltrate is formed in some particular area of the abdominal cavity, but then begins to build up and spreads to:
- liver;
- gallbladder and biliary tract;
- Kidney and urinary tract;
- the spine;
- anterior abdominal wall.
Often, the abdominal wall grows infiltrate, affecting the ileocecal angle. In this case, skin changes typical for actinomycosis occur:
- is a bluish-purple color;
- fistulas.
Fistulous passages communicate with the intestine, and on the skin their outer opening is most often in the groin area. By the way, primary foci directly in the abdominal wall are not formed, it is affected again, with the spread of the pathological process from neighboring sites affected by actinomycosis.
If actinomycosis has affected the terminal( terminal) parts of the colon, it rapidly spreads to the rectum and the area around it, causing inflammation of the pararectal tissue and other tissues in this localization.This inflammation is defined as a specific paraproctitis . When the paraproctitis passes into the purulent form, fistulas are formed which spontaneously open outward in the area around the anus.
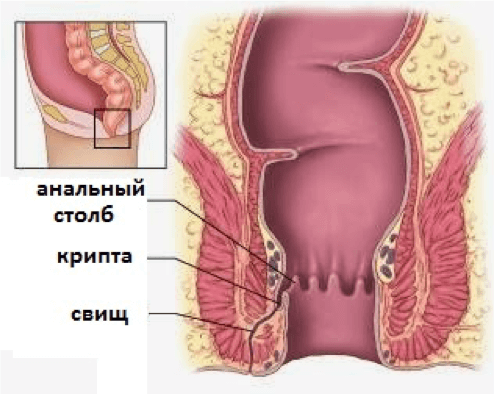
Isolations from them are typical, as with actinomycosis from fistula - purulent, with druses, determined microscopically.
Symptoms of actinomycosis of bones and joints
This form of radiation-fungal lesion is rare. It occurs:
- as a result of the dissemination of actinomycotic infiltrate from organs located in the neighborhood( for example, the hip joint can be re-affected in the actinomycosis process in the abdominal cavity);
- due to drift of actinomycetes with blood flow.
Among the actinomycosis of bones and joints causing osteomyelitis( purulent inflammation of bone tissue), lesions most often occurred:
- of the shin bone;
- of the pelvic bones;
- vertebral column;
- of the knee joint.
Often the disease is preceded by bone or joint trauma - in this case saprophytic forms of actinomycetes that have lived there for a long time without harm to bone, cartilage tissue or synovial membranes, become a parasitic infectious agent.
Osteomyelitis as a disease proceeds by itself is difficult and difficult to treat, and affection with actinomycetes further exacerbates the process. There are sequestration - limited foci of necrosis in healthy tissues, which progressively spread throughout the bone. But, despite pronounced pathological changes in bone tissues, patients retain the ability to move.When the joints are affected, their function is also not violated . In the formation of fistulous passages, characteristic changes occur on the part of the skin.
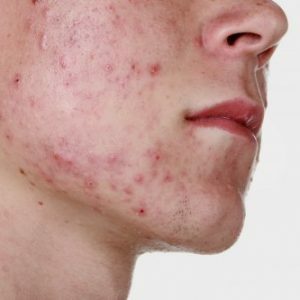
Symptoms of actinomycosis of the skin
The integument is affected, as a rule, secondarily when spreading the process from the neighboring locations:
- of the abdominal cavity organs and its walls;
- of the chest and its walls;
- bones and joints
- and so on.
The diagnosis of actinomycosis of the skin can be made already in the event that the infiltrate, moving from neighboring organs, reached the subcutaneous fat, and fistula formed.
Symptoms of actinomycosis CNS
Actinomycosis of the CNS is rare. The defeat of the structures of the brain or spinal cord manifests itself in the form of abscesses( single or
Symptoms of actinomycosis of the CNS in the initial stages are as follows:
- rise in body temperature - first to low-grade figures, then higher;
- headache thatWith time becomes more pronounced
- attacks of dizziness
With further development of the disease, there are pronounced signs of a violation of the central nervous system:
- nausea andVomiting not associated with food intake
- painful cramps
- frequent loss of consciousness
- impaired coordination( such patients may even fall)
Symptoms of actinomycosis of the genitourinary system
Urinary and urinary organs with actinomycosisAffected infrequently, and the defeat of the genitalia is generally very rare.
Primary actinomycosis of the genital organs arises as a secondary lesion in abdominal actinomycosis due to the active dissemination of the infiltrate on them and means that the primary focus should be sought in the abdominal cavity.Formed in the bladder region, the infiltrate can pass to the tissue around the prostate in men and the uterus in women, but the prostate and uterus themselves can not affect, despite the proximity of these organs to the pathological process.
Symptoms:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- purulent discharge from the urinary tract;
- in the late stages - the formation of fistulas of soft abdominal tissues in the pelvic area.
What is the mycetoma( Maduromatosis, Madura foot).Symptoms of
The mycetoma is a kind of actinomycosis that affects the foot. How nosology is known for a long time, was especially often found in patients living in tropical latitudes.
The onset of the disease is manifested by the appearance on the foot( mainly on the sole) of nodes with the characteristic features:
- dense in consistency;
- having clear boundaries;
- in sizes with a pea and more;
- coated first with unaltered skin, which then over the seal itself acquires a characteristic red-violet or brown color.
After some time, new knots appear near the primary nodes, of the foot swells, increases, looks deformed - its shape becomes ugly, like the foot of a mythical lizard with numerous warts. Nodules "mature" in abscesses, the wall of which after a while is torn, they are opened.And although the nodes are superficially-forming fistulous passages go deep, which indicates a profound infestation of the foot tissues.Out of the fistulas, purulent( sometimes with an admixture of blood) fluid with druses, often with a characteristic disgusting odor.
 A slow but steady progression of the process is observed, and with time the whole sole is covered by disfiguring its nodes.They do not subjectively subject to anxiety, since they are practically painless. Sometimes the sole is deformed so that the toes of the foot are turned upward.Filling the entire surface of the sole, knots begin to appear on the back surface of the foot. The deformation progresses to such an extent that the foot is similar not to the anatomical structure, but to the ugly mass covered with pigment spots, which reveals a number of fistulous passages and cavities of formed on the site of the nodes after the rotting of the tissues.
A slow but steady progression of the process is observed, and with time the whole sole is covered by disfiguring its nodes.They do not subjectively subject to anxiety, since they are practically painless. Sometimes the sole is deformed so that the toes of the foot are turned upward.Filling the entire surface of the sole, knots begin to appear on the back surface of the foot. The deformation progresses to such an extent that the foot is similar not to the anatomical structure, but to the ugly mass covered with pigment spots, which reveals a number of fistulous passages and cavities of formed on the site of the nodes after the rotting of the tissues.
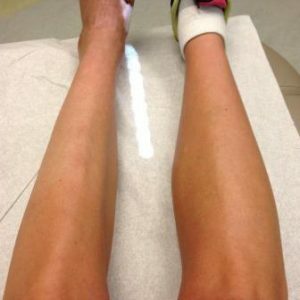
The process does not stop and can extend deep into muscle arrays, tendons and bones.In some cases, atrophic changes in the calf muscles are noted. The appearance of the limb at the Madur foot is characteristic and intimidating - a thin shin and a swollen, deformed foot.
As a rule, the mycetoma affects only one foot.The disease itself can last for long, years and even decades( an average of 10 to 20 years).
Diagnostics
If the process has gone far, up to the formation of fistulas and characteristic changes in the skin around them, the diagnosis of actinomycosis does not present any difficulties.The initial stages of the development of the disease without additional methods of investigation are much more difficult to determine.
The most reliable result in the diagnosis is the detection of the radiant fungus by the microbiological method in:
- purulent fistula;
- tissue particles taken for analysis by biopsy;
- Druses( sometimes only threads of mycelium can be found in them).
For biological bacteriological confirmation of actinomycosis, biological material is used:
- purulent discharge from fistula;
- sputum( bronchial secretion);
- biopsy material( in particular, from infiltrates).
To avoid erroneous diagnosis during sampling of biological material, care must be taken not to contaminate samples with a congenital actinomycotic saprophyte microflora from the mucous membranes. To this end, the biological material( pus or tissue) in all possible cases is obtained:
- for percutaneous puncture;
- for the diagnosis of the thoracic form of actinomycosis - through transtracheal puncture.
Such punctures bypassing congenital foci of actinomycosis are often the only way to obtain satisfactory samples of biological material for the diagnostic study of .But it should be remembered that when using a biomaterial taken from a transtracheal puncture, the diagnosis may also be unreliable, because the contents of the oral cavity in which the actinomycetes( both saprophytic and pathogenic) live can enter the bronchi.
Actinomycetes are characterized by their ability to ferment, so they are easily oxidized( although less than anaerobes).This means that to transport biological material after sampling to a bacteriological laboratory is necessary promptly, until it has undergone changes that can distort the results of the study and affect the diagnosis. If there is still a long-term transport, it is necessary to use special media designed for transportation - the type of Stewart environment.
The presence of Druses allows you to put a preliminary diagnosis of actinomycosis.They can be determined by examining, under a microscope, an actinomycotic granule placed on a cover glass with the addition of methylene blue dye. Antimycotic druses are visualized as cauliflower particles, in which:
- is not painted center;
- is painted blue in the periphery.
In these particles are visible leucocytes and filaments of mycelium( in some cases with characteristic flasks, painted in pink), which diverge from the center of the granule to its periphery.The benefit of a microbiological study is that, in addition to actinomycetes, the smear is associated with a microflora, so that the associated infectious diseases can be assessed correctly.
It is possible to single out the culture of a radiant fungus by sowing the material on the so-called Saburov medium. When sowing crops, the first results are obtained after 2-3 days.In these terms, under the microscope, it is possible to visualize the characteristic, spider-like microcolonies Actinomyces israelii or Actinomyces gerencseriae.
When detecting different types of actinomycetes in the granule, the detection of specific antibodies will help, which is carried out using immunofluorescence:
- direct;
- indirect.
This method allows you to determine the different types of pathogens even without sowing crops.
In some cases, intracutaneous form with actinolysate is used for diagnosis( it is positive in 80% of all cases). In this case, only positive and dramatically positive results should be considered - weakly positive are often noted in patients of dental clinics( for example, in alveolar pyorrhea, which manifests by the release of pus from the alveoli).On the other hand, negative test does not mean the absence of actinomycosis . It is determined in:
- patients suffering from severe forms of the disease;The negative result of the test is explained by the significant and dramatic onset of oppression of cellular immunity;
- HIV-infected( in this case, a negative result will always be observed).
In many cases, actinomycosis, developing rapidly, requires detailed elaboration in a short time. For the sake of faster diagnosis, molecular methods such as:
- are currently being developed;
- polymerase chain reaction( PCR).
In a number of cases, the diagnosis is complicated due to the fact that:
- clinical symptoms are more characteristic of other diseases than for actinomycosis;
- histological( tissue testing) and serological( definition of antibodies) studies are low-specific and low-sensitivity . In other words, they can be positive not only in actinomycosis, but also in other diseases - on the other hand, when actinomycosis yields rather weak results, and this causes us to doubt that the disease is triggered by a radiant fungus.
 Detection of drusen is not a 100% accurate method for the diagnosis of actinomycosis: druses contained only 25% of specimens excreted from fistula, their absence did not imply the absence of actinomycosis, which in these cases was confirmed by other diagnostic methods.
Detection of drusen is not a 100% accurate method for the diagnosis of actinomycosis: druses contained only 25% of specimens excreted from fistula, their absence did not imply the absence of actinomycosis, which in these cases was confirmed by other diagnostic methods.
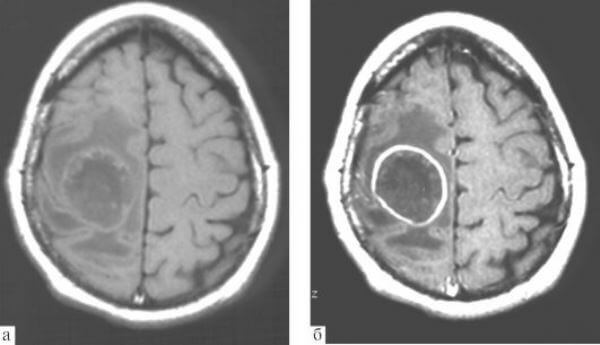
Instrumental diagnostic methods, with which you can determine the presence of ulcers, act as auxiliary, because the detection of abscesses does not mean that they are of actinomycotic origin.On the other hand, instrumental methods can prove to be an important help in diagnosis, if it is difficult to perform pus removal because of anatomical specificity or to make tissue biopsy. So , with actinomycosis of the CNS, computer tomography is performed with contrast, while the abscesses are visualized in the form of foci with the following characteristics:
- round or irregularly shaped;
- with reduced density;
- surrounded by shadows in the form of wide rings.
Differential diagnosis
Actinomycosis of the lungs must be differentiated from:
- of lung tumors;
- ulcers of the thoracic cavity;
- other mycoses( primarily aspergillosis, nocardiosis, histoplasmosis - previously rare, now more common diseases);
- for pulmonary tuberculosis.
Abdominal actinomycosis must be distinguished from surgical diseases:
- acute appendicitis;
- appendicular abscess;
- local peritonitis;
- diffuse peritonitis.
Actinomycosis of other organs and systems( joints, bones, kidneys, genitals and so on) should be distinguished from their nonspecific purulent diseases.
Treatment
For the treatment of actinomycosis, use the combination:
- etiotropic therapy - that is, aimed at the cause of the disease( antibacterial agents);
- immunotherapy.
Antibiotic therapy - long, for 1-3 months. Applied:
- penicillins;
- preparations of the tetracycline series.
These preparations have a good effect on the radiant fungus - insensitive strains of actinomycetes are not isolated.
For the purpose of immunotherapy, actinolysate is used, which :
- stimulates the phagocytic process( "eating" of phagocyte cells of foreign cells);
- enhances the production of antibodies to a wide range of microorganisms;This is valuable when the multi-infection is joined.
 Surgical treatment is used to eliminate ulcers. Abscesses and foci of empyema( diffuse purulent lesion of tissues without walls, as in abscess) are opened and drained.If actinomycosis led to a massive lesion of the lung tissue and its purulent meltdown - perform a lobectomy( removal of the affected lobe of the lung).
Surgical treatment is used to eliminate ulcers. Abscesses and foci of empyema( diffuse purulent lesion of tissues without walls, as in abscess) are opened and drained.If actinomycosis led to a massive lesion of the lung tissue and its purulent meltdown - perform a lobectomy( removal of the affected lobe of the lung).
Since relapses are possible, convalescents( cured people who no longer show signs of disease) should remain under clinical supervision for a long time - from 6 to 12 months .
Prevention
Specific prophylaxis of actinomycosis is not present, vaccines are not developed. Specific activities in the outbreak in the event of its detection are not carried out.
Nonspecific prevention includes a number of relatively simple measures that protect not only the causative agents of actinomycosis:
- thorough oral hygiene;
- timely visits to the dentist, not only with a curative, but also a preventive goal, the discovery of the smallest problems of teeth and their elimination;
- timely treatment of inflammatory changes from the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tonsils, prevention of tonsillitis.
Forecast
Without etiotropic therapy, the prognosis for health and life is unfavorable . With the development of the abdominal form of actinomycosis 50% of untreated patients died, the thoracic - 100%. Relatively easier without treatment are other types of actinomycosis.
Untimely diagnosis and late-onset treatment lead to the development of severe anatomical lesions of the tissues and organs of . It is difficult to treat fistulas caused by the disease.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician