Scaphoid fractures
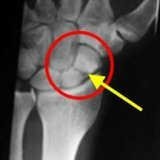
Fractures scaphoid( from Latin os scaphoideum) bones - a similar type of fracture occupies a central place in treating traumatology of the hand. Often it is compared with a fracture of the neck of the femur due to a similar pathomechanism, obstructed feeding of the proximal fragment. There is also a possible development of pseudoarthrosis. Fractures of the scaphoid bone are fused slowly. This is because, in most cases, the proximal part of the bone is supplied with blood from the terminal vessels that go from the cervix or the lower half. The second contributing factor is the presence of distraction forces between fragments. Doctors observing their patients with this disease note that many cases of fresh fractures of the scaphoid bone are fused only after a long period of time.
Fractures of limbs.
Bone fractures are most often formed in the event of a fall or radial deviation of the hand and the brush stroke in the dorsiflexion position. The styloid process also causes a fracture, striking the middle part of the bone. The fracture line is often formed at the level of constriction, has a transverse or oblique shape. Less often, the fracture line falls on the level of the upper third of the bone and the area of the tubercle.
In most cases, the primary damage is sliced bone damage. In this case, a negative result can also be given by an x-ray photograph. However, constant pain in the bend or wrist deviation makes you doubt the absence of a fracture. In this case, the radiography should be repeated after two to three weeks. And only if the result is the same it will be permissible to forget about the diagnosis of the fracture.
Complicated cases of fractures.
It is seldom possible to fix fragments( at their displacement), stretching the brush and giving it a functional position. Immobilization is carried out immediately after the diagnosis is established and does not depend on the time of establishing the fracture itself. A cast bandage is applied from the forearm to the palm of the hand, covering the cleft palmar crease and the thumb on the main phalanx. The final phalanx of the thumb and the remaining fingers of the hand remain free. They can be moved. The hands and the finger are given a functional position. Radial deviation is necessary to press the fragments against each other and prevent them from diverge when the wrist is rejected. This promotes bone splicing. The elbow joint is included in the immobilization, in order to block the rotational movements of the forearm. It is believed that rotational movements are capable of being transmitted to the scaphoid bone through the wrist band. At the same time, immobilization of fragments is disrupted. Fresh fractures often grow together in two to three months. Dates for the proximal half of the bone are increased.
Treatment of this type of fracture can be considered completed only if the radiography shows complete splicing of the fragments.
With pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid bone, patients rarely have serious complaints about this condition. Treatment in this situation is usually carried out depending on the patient's complaints and his profession. And also depending on the types of fragments and the presence of arthrosis changes in the joint. When finding arthrosis changes, it is best to perform arthrodesis of the wrist joint, if the patient has complaints. With sclerotism of the proximal fragment and absence of complaints in the patient, it is better not to perform the operation. If there is a necrotic proximal fragment and a strong soreness, it is possible to remove it. Extrusion of the proximal carpal to the number of reliable and safe does not apply. Therefore, arthrodesis of the wrist joint is preferable.
Barnard and Stubins introduced a method for treating pseudoarthrosis with styloidectomy. In this operation, a styloid process of the radius is removed. This helps to eliminate the adverse pressure in the fracture site and on the fragments. What part of the process must be truncated is determined after the brush is given the position of the maximum radial deviation. In the indicated position, the edge of the radius should not touch the fracture line. At the same time, there is no doubt about the usefulness of removing the styloid process. However, the usefulness and functionality of the styloidectomy method for splicing pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid bone has not yet been determined.
Treatment of pseudoarthrosis with osteoplasty.
It is also worth mentioning the method of treatment of pseudoarthrosis with osteoplasty. This operation was proposed by Matti in 1936. However, it has not lost its relevance even now. Often in the treatment of pseudarthrosis of the scaphoid bone, preference is given to it. However, to use this operation, it is necessary that the fragments are vital and without signs of arthrosis changes in the joints. Through the anatomical snuffbox penetrate to the bone. After excision of the styloid process, good visibility is stipulated. Through the distal fragment penetrate with the help of curette and boron. Further, both fragments are scraped and a longitudinal cavity is formed. The cavity is filled with a spongy tissue or a cortical graft. A spongiform ovoid-shaped transplant, derived from the metaphyseal radius, can be applied.
The main rule for such operations is not to violate the stability of the wreckage. Inadmissible strong scraping of the spongy tissue to reduce the size of the graft. Such scraping is justified only when the proximal fragment is sclerotic. And with pseudoarthrosis, a good fixation is more likely than an extensive transplant. Plaster dressing after the operation is superimposed as well as with fresh fractures. Immobilization after the operation lasts until the radiography has established a complete fusion of the debris.