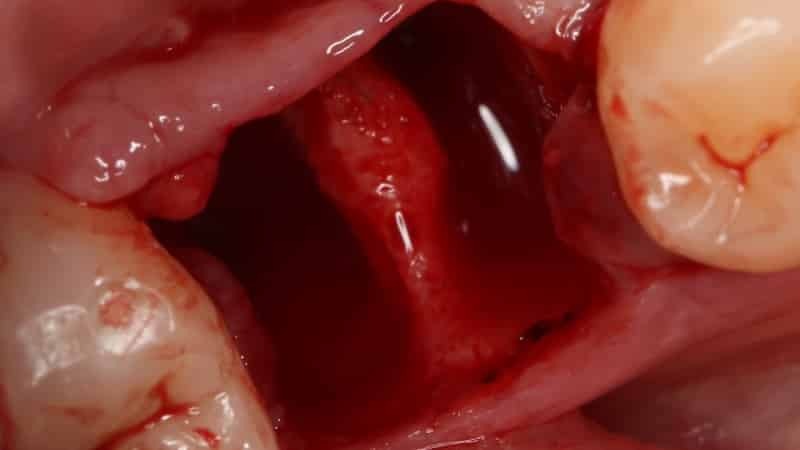
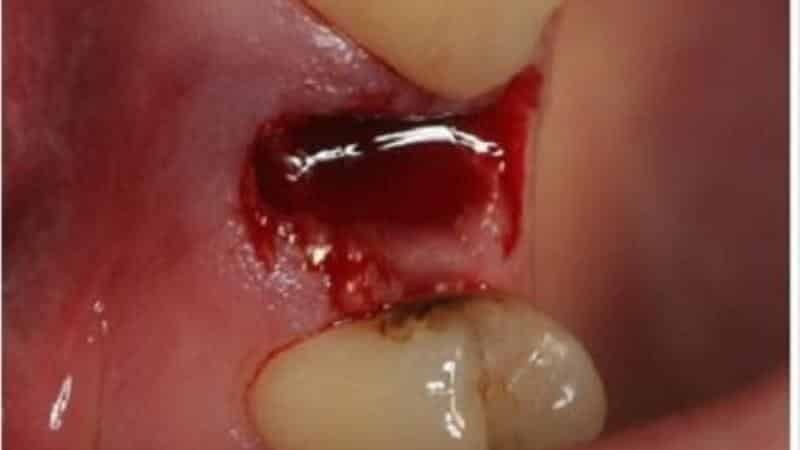
Treatment of purulent and necrotic wounds
The outcome of the treatment depends to a large extent on the duration of the wound, the treatment methods prior to the application of preservative therapy, and the presence of polyresistant flora in the wound.
Treatment of purulent and necrotic wounds in the 1st stage of the wound process of different etiology is successful with Baneocin. The form of the drug is a powder, applied externally.
This drug was tested in 2008 on 54 patients, middle-aged 64 years. Patients were divided into three groups:
- trophic ulcers due varicosity and post-thrombotic syndrome
- Burns II-nd and III-th stage
- Decubitus sacro-lumbar region
following results were obtained after regular application of the drug:
- first group: average duration ofUlcers - 2.5 months
- For the second group: the average duration of ulceration is 21 days
- For the third group: the average duration of the existence of wounds is 15 days
All studiesmye patients prior to placement in a hospital and the drug treated repeatedly with no apparent success. Necrotic wounds were in 30% of patients. Purulent in 60%.10% had both kinds of wounds. After the treatment, all wounds were localized on the surface of the skin without penetrating deep into the muscle tissue. Unsuccessful treatment of patients lasted about 2 months, the area of wounds about 10 cm2.
More than 90% of patients were previously treated with gauze dressings using water-soluble ointments, antiseptics. Some patients used antibiotics.
Treatment of purulent wounds is carried out by two methods - local treatment and general. Choose the form of treatment, based on the phase of the wound process.
The first method. Local treatment.
In this case the task to destroy microorganisms in the wound, the use of the normal drainage of exudate, wound cleansing from necrotic tissue residues, reduce potential inflammation. Apply methods of both physical antiseptic and biological and chemical.
If a purulent wound is formed in the postoperative period, then open the edges of the wound sufficiently wide. Secondary surgical intervention( VCB) is performed if these methods are insufficient.
Such VCB is carried out if there is a large purulent focus, the presence of necrotic wounds, the absence of outflow of pus, zateka. Contraindication to HBV will be only an extremely serious condition of the patient, in this case, limited to the introduction of drainage into the wound.
What should be done when the surgeon HCS:
- Open the purulent wound
- Pruning dead tissue
- normal drainage of purulent wounds
Before use HCS, should first of all to identify the boundaries of the purulent center, localized areas of suppuration, determine the route of transmission suppuration. This study is done both with the help of palpation, and computer and X-ray equipment.
VCV as the first surgical intervention is conducted by a team of surgeons in the operating room, with the use of painkillers. Only the use of anesthesia will allow to fulfill all the planned operations with VCB.
During HCS with dead tissue and amputation of purulent necrotic wounds it is worth remembering that close wounds or herself may be blood vessels and / or nerves. At the end of the operation, the wound is rinsed with antiseptic solutions until completely cleansed, soaked with gauze napkins and drainage installed.
treatment of purulent and necrotic wounds after HCS
After HCS is a daily( or more often, according to the state of the patient) opening and washing the wound. The doctor examines the wound, assesses her condition and the progress of the wound development. The edges are treated with alcohol, the wound cavity is cleaned with a cotton swab dipped in an antiseptic solution. After that, draining and tamponing is performed.
In the initial period of healing of purulent and necrotic wounds, ointments can not be used. These drugs create a barrier to the outflow of pus, proteolysis products. Also, ointments prevent the separation of necrotic tissues. The bandage applied to the wound in the first phase of healing should be as hygroscopic as possible and be impregnated with antiseptics.
An important tool in the treatment of purulent wounds is "chemical necrosis".Proteolytic enzymes are used. Of the known drugs can be called - trypsin and chymopsin. Powdered drugs are poured into the wound or dissolved in the antiseptic. To effectively remove pus from the wound, sorbents, such as polyphepan, are used.
After the first stage of healing of necrotic wounds, the second phase - regeneration - begins. During this period, the wound cleared from dead tissues, the inflammation has passed. The primary role in the second phase is played by the formation of granulation tissue. This tissue performs a protective role, but do not forget about a possible repeated outbreak of inflammation. And already during this period, it is reasonable to use drugs on an ointment basis, which prevent mechanical damage to newly formed tissues. These ointments include local action antibiotics.
Multicomponent ointments are widely used. Such as "Levometikotid", "Oksiktsiklos".
For quick regeneration and healing, the method of applying secondary seams is applied. Both "late" and "early".The method of tightening the edges of the wound with an adhesive plaster is also considered safe.
The third stage of wound healing involves the acceleration of epithelialization of the wound. During this period, the wound is protected from trauma. Apply ointments based on stimulation and indifference, as well as use physiotherapy procedures.
The treatment period for purulent and necrotic wounds can last from 7 days to one year.