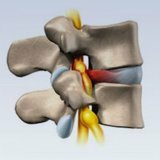
Hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm
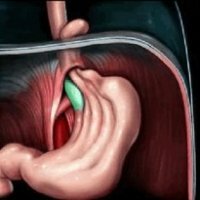
Diaphragmatic hernia( hernia affects the esophageal opening of the diaphragm).This disease refers to chronic relapsing diseases, as a result of which the abdominal esophagus, the upper stomach, cardia, and sometimes also the intestinal loops move into the chest through the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. Diaphragmatic hernia is a fairly common disease among the adult population occurs in 5%, with half the cases the disease is without symptoms, so it is impossible to diagnose.
Causes of
There are three main factors affecting the cause of diaphragmatic hernia development: increased intra-abdominal pressure, diseases of the digestive tract( esophagus as well), weakening of connective tissue structures. The only exceptions are, perhaps, only diaphragmatic hernias in children, as most often they develop this disease due to gastrointestinal pathologies of development and embryonic disorders. Diaphragmatic hernia in people of mature age occur mainly due to involutional processes occurring in the tissues of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm and in the ligamentous apparatus.
Symptoms of
In half of cases, the described disease proceeds with minor symptoms, so it is practically impossible to detect it. Most often, the disease is detected accidentally after endoscopic or radiological examination of the stomach and esophagus. In 30-35% of cases, the first symptoms are paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystole( i.e., heart rhythm disturbances) or non-coronary cardialgias( pain in the heart muscle region), such symptoms often cause unsuccessful treatment, as the disease is not diagnosed correctly.
This disease is characterized by pain syndromes, which most often stop the epigastric region, and then localize along the esophagus. In some cases, the pain gives to the interscapular region and back. Sometimes the pain is shrouded in nature, because of what is often put the wrong diagnosis - pancreatitis. In 15-20% of cases, the pain stops in the area of the heart muscle, so the diagnosis is myocardial infarction or angina, which is also not a true diagnosis. It is worth noting that in some cases the diaphragmatic hernia can be combined with coronary heart disease.
When diagnosing the pain caused by the diaphragmatic hernia, the following circumstances are taken into account: when the pain most often occurs - with physical activity, after heavy meals, with flatulence, with coughing, in a horizontal position. The pain disappears or at least decreases after vomiting, belching, change of position( from horizontal to vertical), reception of water or alkalis. Is the pain too strong, or is it often dull and mild. Whether pain increases when tilted forward.
In the clinical picture it is very important to allocate anemic syndrome, which is most often brought to the fore, hiding other symptoms of diaphragmatic hernia. The cause of anemia are repeated hidden bleeding from the lower part of the stomach and esophagus, which arise from erosive gastritis, reflux esophagitis. Sometimes the cause of bleeding are the papillary ulcers of the lower part of the esophagus. Particular attention should be paid to neurological disorders, with diaphragmatic hernia, the patient will have rapid fatigue, increased irritability, poor sleep, tearfulness, anxiety, depression. From pain in the epigastric region, the patient may develop and develop headaches. These symptoms are associated with vagasolar disorders that develop in patients with diaphragmatic hernia due to changes in the anatomical relationship of the stomach, esophagus, nerve formation and diaphragm.
Treatment
Conservative treatment is performed with uncomplicated gliding diaphragmatic hernias. The goal of treatment in such cases is to reduce gastroesophageal reflux, reduce the symptoms of esophagitis, prevent an increase in intra-abdominal pressure( for this it is necessary to change the lifestyle, diet and diet, prescribe drugs that reduce acidity).
If conservative treatment of sliding hernias was ineffective and symptoms persist, reducing the quality of life, then surgical treatment is prescribed, which is also prescribed for paraseophageal hernias.
Fracture with surgical methods for the treatment of diaphragmatic hernia has two main tasks:
- under the diaphragm to fix and hold the esophageal-gastric junction;
- to restore a constant acute cardiofundal angle.