Caries of milk teeth
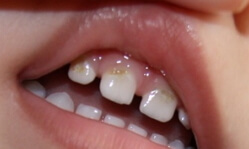 Caries of infant teeth in children is a multifactorial disease of the teeth, with a tendency to chronization, in the pathogenetic basis, which has a decrease in the mineralization( demineralization) of the enamel-dentine layer, which provokes the destruction of the underlying constituents of the tooth.
Caries of infant teeth in children is a multifactorial disease of the teeth, with a tendency to chronization, in the pathogenetic basis, which has a decrease in the mineralization( demineralization) of the enamel-dentine layer, which provokes the destruction of the underlying constituents of the tooth.
Caries of baby teeth in children is an intractable and urgent task of dentistry. A child is rarely seen, whose teeth are intact to caries. The destruction of teeth is diagnosed even in toddlers who have not reached the year. The cavities formed by the carious process form an infectious focus, which is the primary cause of chronosepsis. Infection from the mouth spreads hematogenously, along the tropic organs, where it becomes an etiotropic factor of inflammation. Before children's doctors there are many difficult tasks, such as: methods of prevention, methods of therapy and diagnosis of caries, monitoring of complications and their prevention. The dentistry of childhood has a number of separate characteristics due to the morphology of the child's teeth and the psyche of the growing organism, the inability to use individual therapy techniques, the variety of causative factors and the symptoms of temporary tooth diseases.
Causes of caries of infant teeth
Caries of infant teeth, most often, occurs already from the time of the appearance of the first tooth. To this predispose some features of the morphology of the infant teeth, namely:
- solid constituents of the teeth( enamel, dentin) have incomplete mineralization;
- dentin and enamel thin;
- the enamel is almost completely represented by an organic matrix;
is a pronounced pulp chamber;
- limited pulp capacity to form dentine;
- dentinal tubules are pronounced, caries of milk teeth spread faster;
- the roots of the teeth have a stage of development( formation, resorption).
In dentistry there is the term "cariogenic situation" of the oral cavity. This is a combination of factors contributing to a combination of conditions, the beginning of carious lesions of the teeth. To such cariogenic factors include:
- genetic predisposition, causing resistance to caries;
- the quality of mineralization of the enamel layer in areas most prone to damage( fissures, dental touch points to each other, cervical region);
- abnormalities of bite and palate, gums and jaws, teeth;
- location density and localization in the dental arch;
- the nature and thoroughness of hygienic measures, the formation of plaque, the presence of food residues;
- features of nutrition and the quality of products consumed by the child, excessive use of refined carbohydrates, eating micronutrients in food, predominance of soft in consistency of food;
- features of salivation and saliva: the number of lactobacilli, the viscosity of saliva, the degree of salivation;
- the presence of infection Streptococcus mutans, the infectious agent, is mainly transmitted by parents;
- the nature and frequency of the emergence of infectious diseases, the presence of chronic somatic diseases, the reduction of body defenses.
Theories of the pathogenesis of dental caries are numerous, according to the most common of them, the pathological process begins when there are predisposing factors, against which there is an imbalance in the mechanisms of mineralization of solid tissues( the predominance of demineralization over the process of remineralization).At the sites of demineralization, a plaque is formed, consisting of pathological microorganisms. In the process of their life they split carbohydrates, the final product of their metabolism - organic acids. These acids exacerbate the dimineralization. The result is a more intense penetration of the pathogen into the thickness of the tooth and its destruction.
Infants often have a "bottle" tooth decay of their teeth. It occurs as a consequence of the fact that some children receive sweet milk formulas, milk, gruel at night, after the procedure for cleaning teeth. The lactose contained in these beverages is a substrate for the reproduction of the cariogenic bacterial flora. The whole front teeth of the baby are affected. But importantly, the "bottle" tooth decay of the baby teeth does not develop in all children receiving sugar-containing drinks at night, as this is facilitated by a combination of cariogenic factors.
Symptoms of caries of infant teeth
Caries of baby teeth in children often occurs without any clinical symptoms. Typical for him torpid, symmetric distribution, simultaneous damage to several sites.
A child may complain of:
- pain, intermittent or persistent;
- a feeling of discomfort after contacting hot, cold or sweet food;
- small children unmotivated refuse food, saliva, capriciousness.
- parents pay attention to the appearance of whitish rough spots on the teeth, the loss of shine. Yellow, brown areas appear on the enamel layer.
For children's teeth, the staging in the development of the root system is characteristic, therefore clinical manifestations can differ at each stage.
For the caries of the baby teeth, in the period when the root system is formed, it is characteristic that the basis for its formation is a failure in the maturation of the enamel-dentine layer. This occurs during the period of intrauterine development, under the influence of unfavorable pregnancy. Earlier, caries lesions occur more often in preterm babies, in the initial months after suffering any diseases. During this period, the clinic for dental caries is characterized by:
- acute manifestation, with rapid progression;
- damage to the upper incisors in the neck( cervical caries of the baby teeth), in the indentations of the first molars;
- rapid destruction of dentin, due to its immaturity;
- multiple tooth lesions, symmetrical;
- proceeds practically without symptoms, which undoubtedly complicates its detection until the moment of complications development;
- rapid transformation into complication( pulpitis and periodontitis);
- predominance of deep caries;
- the area of carious destruction is unlimited, the walls of the cavity are light, the enamel layer is thin, the dentin is moist, it leaves the layers.
For caries with already formed roots is characteristic:
- asymptomatic flow;
- caries spots are formed in typical areas( cervical and proximal areas, fissures);
- the lesions are covered with a coating, after cleansing, dull, rough areas are identified.
During the root resorption, the carious lesion also has the characteristic features:
- manifests with fang lesions;
- is diagnosed already in the phase of complication;
- process timing;
- affects deep structures;
- has a course without symptoms.
For temporary teeth, some types of caries are typical, for example, circular caries of infant teeth. Localized damage in the neck and surrounds the tooth around the perimeter. Frequently ill, weakened children, mainly, are subject to such carious destruction. It occurs more often with teething, which occurs before time. Carious destruction rapidly penetrates into the pulp area, but the inflammatory process does not develop. Due to the activation of the pulp, a substitute dentin is abundantly formed, sometimes until the root canals are completely filled. The outcome of this caries is the fracture of the dental crown.
Another type of tooth decay typical for baby teeth is planar caries. It appears on the surface of molars with a chewing side. With a planar carious lesion, the whole surface is completely affected. In addition to the fact that planar caries affects children weakened, the tooth hypoplasia plays an important role in its development. A distinctive feature of this caries is the rapidity of the development of the process and the rapid destruction of the deep structures of the tooth.
Caries phases of infant teeth
The carious process is characterized by a staged flow. Damage to the teeth begins with the onset of the plaque, which also goes through several stages:
- during the first two days, the accumulation of micromolecules of food remnants and bacteria accumulates on the gingival margin;
- then within 3-4 days the layer of plaque noticeably thickens and is covered with Gram-positive cocci;
- the next few days the plaque penetrates the gum. Bacteria and products, synthesized as a result of their vital activity, begin to circulate in the furrow between the gum and the tooth;
- on the 7-11th day a secondary bacterial flora is attached, which produces organic acids that destroy tooth tissues.
The stages of development of caries of the baby teeth are similar to the process of permanent teeth damage, but the difference is that in the childhood period the destruction of the tooth tissues is rapid, from one stage to another there is little time. In modern dentistry, the following stages of the carious process in the milk tooth are distinguished:
- Spot stage. Under the influence of cariogenic provoking factors, the enamel area is demineralized, practically without affecting its outer layer. If you dry the surface of the tooth, you can notice a whitish or yellowish area with no natural shine. Clinically, this stage can be manifested by a slight reaction to sweet or sour food.
- The stage of caries of the enamel of the milk tooth. In the absence of treatment, with repeated demineralization processes, a dark zone appears, the lesion penetrates the entire thickness of the enamel. On the tooth appears a hole where the remains of food can accumulate. At this stage, there may be soreness when chewing food.
- Stage of medium deep caries of infant teeth. The lesion extends to the dentin tissue. There is a clear pain reaction to food irritants, food clogs the carious cavity, the putrefactive processes begin and there is a smell from the mouth.
- The stage of deep perforated caries. If treatment measures are not started in a timely manner, then the tissues around the tooth and / or pulp are destroyed, complications develop.
Surface caries of infant teeth
The form of a carious lesion in which a defect in the enamel layer does not reach the dentin layer is superficial. In this process, several zones of enamel destruction are distinguished:
- sites where complete destruction and invasion of bacteria occurred;
- total demineralization;
- areas of incomplete demineralization;
- places of visually undamaged enamel.
Areas of carious destruction in typical places are localized. Children do not make any complaints. Subjective sensations in children are not noted, although there may be discomfort when contacting the tooth with various stimuli coming in with food. At an objective stomatologic survey the site of caries is rough, in the center its fragile enamel. This form is characterized as a rapid and acute process. Chronicization of superficial caries occurs extremely rarely.
Deep caries of infant teeth
In case of deep caries, the dentine layer is damaged. In the process of its destruction, a number of pathomorphological zones can be identified:
- replacing the destroyed dentin;
is a normal layer where there are dentinal tubules without crystals and bacterial agent;
- translucent dentin. Thin crystals form in the tubules, but bacteria do not yet exist;
is a transparent dentin. The crystals in the tubules become larger, there are no bacteria. This damaged dentin, unlike the healthy one, is softer;
- sites of the damaged tissue structure. The tubules are expanded and changed, filled with microorganisms;
is an infected area. Abundant bacterial flora, the dentine structure is completely destroyed.
In the deep caries of milk teeth, the lesion focuses on the dentine layer around the pulp. The course of this type of carious destruction is acute. At him, the children complain of periodically arising soreness, discomfort in the tooth, when contacting with thermal and mechanical agents. With deep caries, there is always an indirect effect on the tissue of the pulp. Before the start of therapeutic treatment, it is worth making sure that there is no complication.
In some cases, deep caries of baby teeth in children can have a chronic course. This process is characterized by lethargy, the formation of sclerotized dentin, due to the activation of the pulp. The carious lesion cavity with a wide entrance, the dentin brown, is poorly separated by an excavator.
If deep caries remains untreated, complications that can lead to the progression of the infection and spread to nearby tissues and throughout the body inevitably develop. It also leads to a possible loss of the tooth and, accordingly, a place for the eruption of the future permanent tooth. The process of decay in the milk tooth can damage and located deeper, permanent teeth.
Diagnosis of tooth decay of infant teeth
When children have any complaints from the teeth, an infant dentist should be immediately examined. There are certain diagnostic techniques and methods that allow to make an unmistakable diagnosis. Methods for diagnosing the carious process in children include:
- Analysis of anamnesis data. When parents contact the child, you should carefully conduct a survey, find out the time of the onset of the disease, its possible cause, ask about subjective feelings, find out the general condition of the child, allergic anamnesis, drug intolerance, identify possible negative behavioral and somatic reactions to examination and treatment. During the conversation with the child, the wording of the questions asked should be clear and mutually exclusive.
- Visual objective examination of the oral cavity. It is carried out with the help of dental mirrors, with sufficient light. The surface of the tooth is then dried and protected from saliva.
- Sounding. Should be carried out as carefully as possible. With the help of this method, the state of the enamel is determined in the area of the spots, in the case of a deep tooth caries, the depth of the lesion can be estimated.
- Technique of "silk thread".A thin thread of silk is held in the interdental space, then, pressing the thread to the surface, where it is supposed to have a cavity, pull it up. If there is damage, the thread breaks. Thus, check the surfaces of adjacent teeth, to avoid false diagnosis.
- Coloring of tooth enamel. The method is based on the fact that the damaged areas of the enamel layer are stained with a dye( methylene blue).It is used as a method of differential diagnosis with pathologies of non-carious teeth, such as fluorosis and hypoplasia of the enamel layer.
- Painting of dentin. After the cavity of the caries of the milk tooth is opened, to determine the extent of the therapeutic intervention, the affected dentin is stained with fuchsin on propylene glycol. In this case, only the infected areas will be painted.
- Method of "trial preparation".This method of diagnosis is used in determining the lesion of the pulp. With viable pulp, when the preparation is in the place of the enamel-dentine border, sensitivity is retained when contacting with chemical and mechanical stimuli. If the pulp is "dead", then this region becomes intact to stimuli of any nature.
- Laser diagnostics. A modern technique that is based on fixing different wavelengths reflected from an intact and damaged area of the enamel. It allows to determine the presence of a carious focus on hard-to-reach surfaces.
- Diagnosis by ultraviolet radiation. Healthy teeth, under the influence of ultraviolet, have a glow with a bluish tinge. The study is conducted in a darkened office, a special apparatus. Affected areas lose luminescence, which allows to identify the localization and extent of damage.
- Radiographic study. It can be done both with the help of an X-ray apparatus, and with the help of a computer. The second method is preferable, since it takes less time, the picture is transferred to the computer screen, the image can be enlarged and reduced, the dose of the radiation load is reduced. Allows you to evaluate not only the crown of the tooth, but also its root system.
Treatment of caries of infant teeth
There is an opinion that caries of milk teeth does not need therapy. In addition to the fact that caries delivers aesthetic and physical discomfort, dental caries can become a causal factor in serious complications, diseases of permanent teeth and other organs.
Therapeutic treatment is always best to start at the stain stage. This treatment takes less time and, most importantly, does not require painful manipulation.
Important fact is that children, especially those of young age, are extremely negative about medical manipulation, so parents should take care in advance of choosing a place where the therapy will be performed.
Depending on material well-being, parents have the right to choose a clinic equipped especially for children, where the classrooms are equipped with colorful equipment and interior, a TV where the child feels comfortable and treatment is performed in a playful form.
An important component in therapy is the psycho-emotional mood of the child. Particular attention should be given to methods of sedation, anesthesia and reduced salivation. On how the visit to the dentist for the first time will take place, the further success of treatment depends.
Therapeutic treatment of dental caries caries occurs in two stages - it is the treatment of the cavity and sealing.
For the opening of carious areas, various methods are used:
- Chemico-mechanical. Refers to a non-invasive method of treatment. An acid or special solution is applied to the damaged tissue site, then after a short period of time, the softened tissues are removed using an excavator without using a drill.
- Air abrasion method. With this technique, the carious cavity of the milk tooth is opened and processed using an aerosol spray consisting of water and abrasive. The technique allows for more precise and fine processing, by adjusting the water supply.
- Ultrasonic method. When ultrasonic waves are used, microvibrations and vibration are created in the affected cavity, which facilitates the rupture of molecular bonds and the easy removal of the treated tissues.
- Laser method. The method is carried out in a non-contact way. The surface to be treated is always sterile. By means of laser radiation, any surface can be treated. When using a laser installation, there is practically no thermal impact, which reduces the soreness of the procedure.
- Opened cavities with a drill. The method is based on the removal of tissues through the rapid rotation of microbes of various sizes. The disadvantage of this method is that when using boron there is a specific smell and sound, and also a strong enough pressure that causes discomfort.
Therapy of superficial and middle teeth caries is most often done by grinding the affected tissues and applying remineralizing preparations( silver nitrate, fluorine lacquer) to these areas. This technique stops the progressing development of the carious process for six months. The appearance of enlightenment in impregnated areas is an indication for repeated application of the drug.
If necessary, caries cavity opening, this is done very carefully, creating additional grounds for strengthening the seals. If necessary, the therapeutic treatment can be performed in several sessions. In this case, a gasket with a medicine or remineralizing agent is placed in the cavity.
The materials for seals used in children's practice are presented with a number of requirements:
- moisture resistance and resistance to various chemical irritants;
- radiopacity;
- hardness close to the hardness of the enamel;
- low thermal conductivity, to protect the pulp;
- high adhesive ability to the tooth tissues;
- a color close to the tooth tissues;
- they should not give, even minimal, shrinkage after hardening;
- abrasion resistance;
- antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties.
In some cases, atraumatic restorative dentistry is used. In this case, the caries section of the milk tooth is removed with a sharp excavator, it is necessarily dried and a freshly made glass ionomer cement is applied to this place.
In the therapeutic treatment of deep caries lesions, the softened dentin is carefully and carefully removed, then the cavity is treated with an antiseptic and a therapeutic paste is applied, and the next step is the application of a permanent seal.
In the treatment of infant teeth, complications and errors sometimes occur, such as:
- a secondary carious lesion that occurs some time after treatment, which indicates a violation of the technique of opening the cavity, applying and preparing a seal;
- opening the pulp cavity with inaccurate preparation;
- development of pulpit due to the use of toxic materials without insulation;
- loss or cleavage of a seal, due to a violation of the technique of its application;
- development of inflammation of the interdental papilla( papillitis) due to tissue trauma in the absence of the use of isolating agents;
- the seal changed color due to a violation of the technique of its preparation and application.
Prevention of caries of infant teeth
Caries prevention is divided into primary and secondary measures. Primary prevention begins at the stage of development in the womb and consists in:
- the use of foods rich in microelements( calcium and fluorine, phosphorus, etc.) by a pregnant woman, the use of complex vitamins, minerals, frequent and long walks, rational physical activity;
- prevention and prevention of pregnancy pathologies that cause fetal development retardation and hypoxic conditions;
- the baby of the first six months should be breastfed, lures should be introduced by age and be diverse;
- timely initiated prevention of rickets, daily and long walks, preferably in a forest park area;
- with artificial, mixed feeding try to reduce the number of night feeds to prevent bottle caries of baby teeth;
- minimization of the child's use of sweets, foods rich in easily assimilated carbohydrates;
- to organize a diet so that to cover all the needs for vitamins, micronutrients and minerals. The diet should be dominated by solid food, which contributes to the mechanical cleaning of the teeth;
- providing the child with individual dishes, cutlery. Parents should not lick the baby's nipples and spoons;
- with endemic deficiency in fluoride drinking water, use additional fluoride enrichment of drinking water, special nutritional supplements enriched with this element.
A separate point in the prevention of dental caries is hygiene of the oral cavity. The beginning of oral care should be combined with the moment of eruption of the first tooth. For cleaning use gauze moistened in the cooled boiled water or special napkins. Wipe the teeth after any meal. You can use a special children's brush, which is put on the finger of an adult. The first toothbrush is purchased at the age of one and a half years. Toothbrush and children's paste should be appropriate to the age of the child and be as safe as possible. In the form of a game, parents should show the child the correct movements while brushing their teeth, by their example they can instill oral hygiene skills.
To the methods of secondary prevention, with the already developed caries, to prevent the progression of the process and the damage to intact teeth are:
- regular examinations of a children's dentist or a hygienist doctor;
- if necessary, complete and timely treatment;
- application of remineralizing coatings( fluorinated coating, silvering);
- treatment of chronic somatic diseases, diseases of the oral cavity, prevention of infections;
- timely orthodontic therapy.
Caries of baby teeth in children is a very common and acute problem, which should be addressed not only by dentists, but also by pediatricians. But nevertheless parents, are the main link, in prevention of tooth lesions in children. Adhering to simple hygienic rules for the care of teeth, mouth, vaccinating their child, loving parents make a huge contribution to the future health of the baby. And timely preventive examinations and, if necessary, treatment, ensure the prevention of odontogenic complications of both the structures of the oral cavity and other organs, and contribute to the formation of healthy permanent teeth.



