Bury-Berry disease
 Bari-Beri disease is a disease caused by a deficiency in the human body of thiamine( vitamin B1), which promotes the normal course of fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency of thiamine leads to the fact that pyruvic acid begins to accumulate in the blood of a person with a noticeable increase in its concentration in the nervous system. The consequence of the ongoing biochemical metabolic disturbance is acute damage to the midbrain( Wernicke's encephalopathy) or nervous system damage( polyneuritis).Bery-Beri's disease predominantly develops in people whose daily diet is dominated by shell-deprived rice and some other types of cereal crops.
Bari-Beri disease is a disease caused by a deficiency in the human body of thiamine( vitamin B1), which promotes the normal course of fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency of thiamine leads to the fact that pyruvic acid begins to accumulate in the blood of a person with a noticeable increase in its concentration in the nervous system. The consequence of the ongoing biochemical metabolic disturbance is acute damage to the midbrain( Wernicke's encephalopathy) or nervous system damage( polyneuritis).Bery-Beri's disease predominantly develops in people whose daily diet is dominated by shell-deprived rice and some other types of cereal crops.
At present, this disease is quite a rare phenomenon, but until quite recently whole families or even villages where the main food product was ground white rice were subjected to this rapidly progressing severe disease. However, despite the fact that in the niches of the days, the disease of Bury-Beri is rare, the consequences of this disease are very serious. Therefore, you should closely monitor the adequate intake of food thiamine( vitamin B1).
Causes of Bery-Beri development - inadequate intake of vitamin B1 and disruption of the body's absorption of vitamin B1
Bery-Beri disease - symptoms of
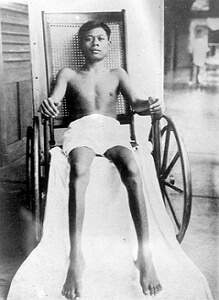
Symptoms of this disease differ and directly depend on which of the systems the human body has been affected: nervous or cardiovascular. There are two types of this disease: wet and dry Bury-Beri. Wet form is accompanied by edema and affects the cardiovascular system, dry Beri-Berry often leads to exhaustion and affects the nervous system.
Symptoms of wet Beri-Beri - shortness of breath, swelling of the pleura area, increased heart rate, fatigue, pain and swelling in the legs.
Symptoms dry Beri-Beri - vomiting, nystagmus( uncontrolled eye movements), slurred speech, discomfort and pain, paralysis, problems with logical thinking and memory, loss of sensitivity, tingling and other unusual sensations in hands and feet, loss of coordination of movement, difficultyWhen walking
Bery-Beri disease - treatment
Treatment of this disease is necessarily under the supervision of a doctor and is to bring the level of vitamin B1( thiamine) in the body to normal.
2-3 r. Intramuscular injection of 5% p-thiamine chloride is shown per day. Intramuscular administration of amidopyrine, analgin, 1% of nicotinic acid( for a course of 125-150 ml), 1 ml of 0.05% of prozerine solution( 20-25 injections) is also shown.
In addition to medicines, a vitaminized diet is shown, physiotherapy( physiotherapy, massage, coniferous-salt baths, ultraviolet irradiation, Bernard currents).Along with this treatment measures are applied that eliminate the symptoms of the defeat of the food canal.
Possible complications of Bury-Beri disease: psychotic conditions, neurological problems, loss of consciousness, coma, heart failure.
To minimize the likelihood of developing this disease, it is necessary to eat foods with a high thiamine content and to exclude alcohol as much as possible. Namely chronic alcohol intoxication contributes to the development of vitamin B1
More articles on the topic:
1. Neurosis
2. Pincering of the sciatic nerve
3. Dizziness