Reduction of the thyroid gland, causes of the disease, symptoms and treatment
Various kinds of thyroid lesions in endocrinology are among the most common diseases( naturally, after diabetes mellitus).Such a situation is fully explained by the rather bad environmental situation in the vast majority of countries, but especially such diseases are found in the territories where radioactive substances were emitted.
The vast majority of thyroid diseases sooner or later lead to a noticeable even naked eye enlargement of the organ, which entails, among other things, deformation of the neck.However, not all diseases of the thyroid gland lead to its reduction.
Diseases leading to a decrease in the thyroid gland, although much less common than leading to an increase in the thyroid gland, can also occur.In most cases, a decrease in the size of the body is caused either by congenital maldevelopment or by the fact that the pathological process simply destroys the thyroid tissue.
content:
- Hypoplasia thyroid
- diagnosis and treatment of congenital hypoplasia shchitovidki
- Atrophic embodiment autoimmune thyroiditis
- Clinical manifestations and methods of treating autoimmune thyroiditis
- Subacute thyroiditis
Manifestations hypoplasia thyroid
One possible diseases, In which the size of the thyroid gland is substantially lower than normal, is the thyroid gland hypoplasia.With this disease, the factor that led to the underdevelopment of the gland operated during the period of intrauterine development, and the pathology is most often detected in early childhood( if the disease is not identified, then in the future it threatens with cretinism).
Congenital thyroid reduction is more common in women, the causes of hypoplasia of the thyroid gland are:
- Thyroid disease in the mother during pregnancy, lack of iodine.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Use of hormonal drugs during pregnancy.
- Exposure to certain chemicals, as well as to ionizing radiation.
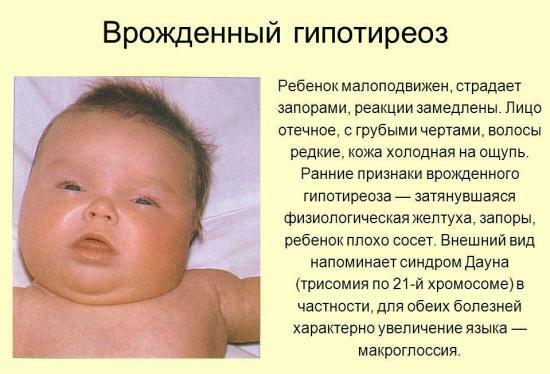
The manifestations of hypoplasia of the gland in early childhood will be:
- Poor appetite, low rate of body mass gain, or even its reduction.
- Delayed response to various stimuli.
- Constipation often occurs in the absence of gastrointestinal tract diseases.
- Explicit lag of the child in psychomotor development.
If the disease is not diagnosed at an early age, then in the absence of hormone replacement therapy, hypothyroidism leads to mental retardation and infertility.
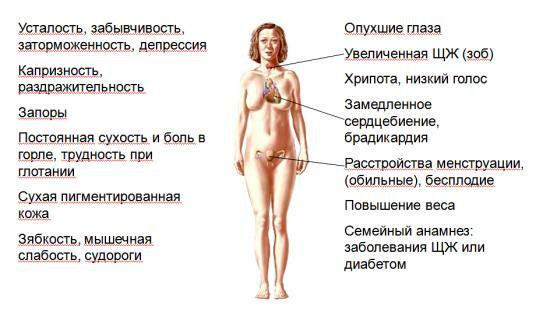
At the older age, the following manifestations are noteworthy:
- Low height, as well as a disproportionate physique.
- Skin in these patients is thick and rough.
- Macroglossia( too large a tongue), the organ in this case often does not fit in the mouth.
- Sexual organs are underdeveloped.
- Different severity of mental development disorders.
- In severe cases, the presence of myxedema edema is possible.
Features of diagnostics and treatment of thyroid hypoplasia
In the case of congenital underdevelopment of the thyroid gland, early diagnosis is extremely important, since if treatment is begun no later than 21 days of the child's life, then there is no intellectual or physical development gap from peerswill be.
There are screening systems that detect the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood.Determination of the content of this hormone makes it possible to judge the function of the thyroid gland - in case the test shows an elevated level, additional tests should be performed, but previously such data indicate hypoplasia of the thyroid gland.
For more accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the content of the thyroid hormone thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the blood.Also perform an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, which allows you to determine whether it is hypoplasia, or whether the iron is completely absent.
Treatment consists of lifelong hormone replacement therapy with synthetic analogues of thyroid hormones, for example, Levothyroxine.Timely diagnosis and treatment prescription provides normal growth and development of body tissues, normalizes the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and also avoids the delay of physical and mental development.
Children with hypothyroidism, whose treatment was started up to 21 days after birth, later with regular intake of the drug are no different from healthy.
Atrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis is an inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland with chronic course and autoimmune development mechanism.With this pathology, antibodies produced by immune cells, the systems begin to take thyroid tissue for foreign.This leads to the destruction of hormone-producing cells of the thyroid gland, which subsequently leads to hypothyroidism.
However, a low level of thyroid hormones is observed not all the time of the disease - at first the aggression of the immune system, with a sufficiently high activity of the process may develop the opposite, hyperthyroidism up to thyrotoxic crisis.Such a situation can arise due to mass death of thyroid cells and the ingestion of hormones contained in the bloodstream.
Autoimmune thyroiditis can be considered a hereditary disease, or a disease with hereditary addiction, as close relatives are more likely to suffer than genetically unrelated patients.Also in such patients often there are other autoimmune diseases - myasthenia gravis, Sjogren's syndrome, ophthalmopathy.
Any factor that traumatizes thyroid tissue can provoke the development of the disease( this leads to the ingress of antigens into the bloodstream) - it can be infectious lesions, inflammatory processes, injuries, and surgical interventions on the thyroid gland.Push the development of the disease can also unfavorable environmental conditions, exposure to radioactive materials, excess, or vice versa, lack of iodine.
The researchers also noted the role of selenium in the development of the disease - in regions where the content of selenium is low in the soil, autoimmune thyroiditis is more common.
Features of the clinic, as well as the treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis
In autoimmune thyroiditis, the thyroid gland firstly attracts itself, it can be either diffuse or affect only a part of the gland, with the seal being most often symmetrical.
Also to manifestations of autoimmune thyroiditis can be attributed:
- Difficulties in swallowing, as well as breathing problems.
- Pain can be felt in the projection of the gland.
- The size of the thyroid gland may change - in hypertrophic form it increases in size, while atrophic form, on the contrary, there is a decrease in the thyroid gland.
- There is also a marked decrease in the number of thyroid hormones produced, which will lead to manifestations of hypothyroidism.
There are several options for autoimmune thyroiditis:
- Hypertrophic form, also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis.The gland is enlarged and compacted.Depending on the stage of the disease, both thyrotoxicosis( caused by mass destruction of thyroid cells) and hypothyroidism are possible.
- Atrophic variant of autoimmune thyroiditis.For such a disease is characterized by a pronounced decrease in the thyroid gland, as well as hypothyroidism.
- Sometimes there is a so-called postpartum thyroiditis.
Treatment of the disease depends on the prevailing manifestations.When expressed hypothyroidism, patients need hormone replacement therapy, in the case of thyrotoxicosis, respectively, use drugs that reduce the secretory function of the gland( for example, Mercazolil).
Surgical treatment is indicated in individual cases - with a fast rate of goitre growth, and also if the enlarged gland begins to squeeze the vital structures of the neck.As an additional therapy, it is also possible to use selenium preparations.With the appropriate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Subacute thyroiditis - a characteristic manifestation of the disease
Subacute thyroiditis is an extremely poorly understood disease.It is assumed that an important role in the development of this pathology is played by viral pathogens, since the disease in the overwhelming majority of cases can be associated with viral diseases in the anamnesis.It is also assumed that, despite the association with viral damage, autoimmune processes play an important role in the pathogenesis of subacute thyroiditis.
Specific for the disease the virus is not defined, suggest that it can be adenoviruses, influenza viruses, measles, mumps and Coxsackie viruses.
The disease can begin with a rise in body temperature, while attracting attention to the increase in the thyroid gland in size, but the pain is much less pronounced than with an acute variant of the disease.Possible decrease in the thyroid gland in size with subacute thyroiditis can be explained by the fact that the gland, destroyed by the pathological process, is replaced by a connective tissue - such a thyroid gland may have smaller dimensions and a greater density upon palpation than a healthy organ.
Treatment for high activity of the inflammatory process consists in the introduction of glucocorticoids.Also, symptomatic treatment is applied depending on the prevailing manifestations - it can be pain relievers or antipyretic drugs.
Also in the hypothyroid stage of the disease, hormone replacement therapy with levothyroxine may be prescribed.When receiving appropriate treatment, the prognosis is favorable - in most patients the function of the gland is completely restored.
A decrease in the thyroid gland in size can also be a manifestation of serious diseases of this body.And although it is basically a slightly less dangerous disease than accompanied by an increase in thyroid gland malignant neoplasms, however, timely examination and treatment with such a symptom is also necessary.
More details about thyroid diseases and their treatment - on the video: