Perinatal encephalopathy: causes, symptoms, consequences in adulthood
Contents:
- Symptoms of
- Causes of encephalopathy
- Treatment of
- Conclusion
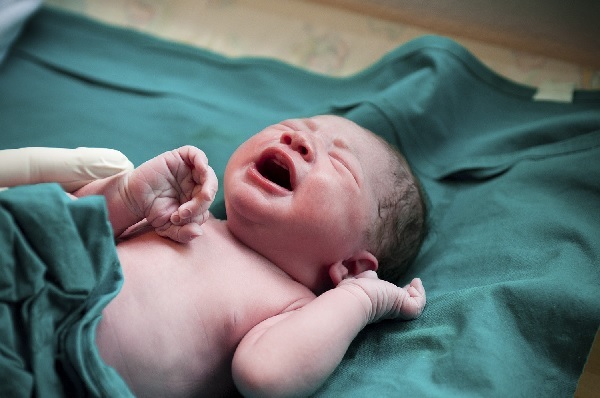 Perinatal encephalopathy is a clinical syndrome that occurs in children in the perinatal period from 28 weeks of gestation to 7 days after birth in term infants and up to 28 days in premature infants. Sometimes it ends with a lethal outcome. Perinatal encephalopathy is a serious impairment of brain function in infants, which can have consequences in adulthood.
Perinatal encephalopathy is a clinical syndrome that occurs in children in the perinatal period from 28 weeks of gestation to 7 days after birth in term infants and up to 28 days in premature infants. Sometimes it ends with a lethal outcome. Perinatal encephalopathy is a serious impairment of brain function in infants, which can have consequences in adulthood.
Symptoms of perinatal encephalopathy( code for ICD-10 G93) can be varied: - Convulsive syndrome, weakening of reflexes, muscle tone or their increase.
- Strong cries, prolonged crying crying.
- Baby does not take breast well.
- A blue face with a fit of cramps.
- Disturbance of swallowing, regurgitation.
- Heart disorder.
- The later appearance of the scream.
- A sensitive sleep, frequent awakenings.
- Irritability, increased reaction to sounds, light or lethargy, inhibition.
- Increased head size due to intracranial hypertension.
The earliest symptoms of the pathology are muscle cramps in infants - the first signs of abnormalities in the central nervous system.
 Learn about the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain: the features of the flow in children and adults.
Learn about the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain: the features of the flow in children and adults.
What is the ventriculomegaly in a child: the cause and effect.
Brain damage can cause pseudobulbar and bulbar syndromes. It manifests itself in the violation of the functions of the nerve centers located in the brain stem, the most ancient formation. The baby does not take the breast well, or the sucking, grasping reflexes are absent altogether.
In less serious disorders, a child may be choked with mother's milk, because the centers of the glossopharyngeal nerve innervating the soft palate, epiglottis, may be affected. Regurgitation can also be present. The defeat of the centers of the vagus nerve causes disturbances in cardiac activity: tachycardia, arrhythmia.
Damage to the nuclei of the oculomotor nerves causes an increase in photosensitivity and a violent reaction even to natural daylight. Difficulty with breathing and cyanosis of the skin is caused by damage to the vasomotor and respiratory centers of the medulla oblongata.
Headaches and muscle aches can interfere with sleep, frequent awakening during sleep, epileptiform seizures with salivation. When the child is growing up, such consequences of perinatal encephalopathy as
- may occur. Decreased intellect, memory impairment.
- Cerebral palsy for children.
- Muscular dystrophy.
- Syndrome of hyperactivity, attention deficit, problems with speech, writing.
- Irritability or lethargy.
- Violation of socialization, poor learning ability, inability to concentrate.
- Development delay.
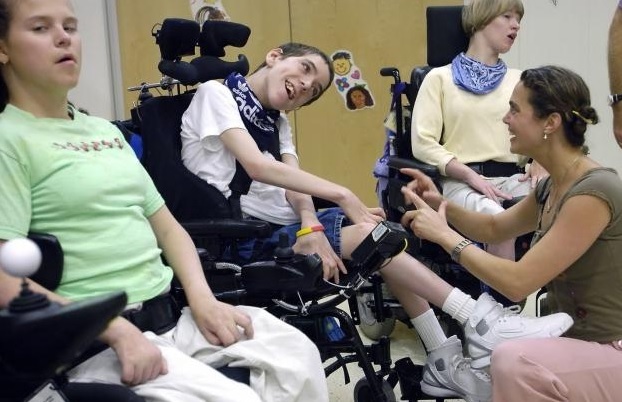 Consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in adulthood - disability, sometimes inability to serve themselves, lack of communication skills. But it is possible and gradual smoothing of the symptoms, if the damage is insignificant.
Consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in adulthood - disability, sometimes inability to serve themselves, lack of communication skills. But it is possible and gradual smoothing of the symptoms, if the damage is insignificant.
Causes of encephalopathy
Perinatal encephalopathy is usually the result of hypoxia or cerebral ischemia of the infant. The main causes of perinatal encephalopathy:
- Blood conflict during pregnancy: Rh-factor, blood group, presence of antiphospholipid syndrome, increased coagulability of blood.
- Birth injuries, umbilical cord entanglement. Prematurity of pregnancy. Intrauterine infections, as well as antiphospholipid syndrome, can cause labor before the term.
- Later delivery.
- Intrauterine infections in the mother.
- Hormonal diseases( adrenal insufficiency in a woman, progesterone deficiency).
- The presence of arterial hypertension.
- Inflammation in a pregnant woman due to the development of hepatic, renal failure.
Inflammation of the infant's brain is the result of hypoxia( oxygen starvation) and the death of the baby's neurons. This can occur with Rh-conflict. The discrepancy of the Rh factor provokes the formation of immune complexes in the blood of the placenta and the violation of microcirculation in it. Antiphospholipid syndrome has similar signs. Increased coagulability often causes fetoplacental insufficiency.
 Find out what hypoxia in newborns is: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Find out what hypoxia in newborns is: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
What mother should know about perinatal CNS lesion in a child: features of the clinical picture of pathology.
Do you know the causes of the development of oligophrenia and manifestations of the disease at various stages?
Birth injuries lead to hematomas, damage to the brain, including its trunk. The implantation of the umbilical cord of the fetus during pregnancy can signal the kicking of the fetus - this is a sign that the fetus lacks oxygen. The umbilical cord is twisted and the placental blood does not flow through the umbilical vessels.
In case of prematurity, the cause of hypoxia at birth is the underdevelopment of the lungs for breathing with atmospheric oxygen. Being born, the infant passes from the placental to the atmospheric type of breathing. The type of hemoglobin changes, old erythrocytes die, but new ones are formed more slowly. Therefore, oxygen transport deteriorates. In addition, the cardiovascular system is underdeveloped - the vasomotor and respiratory centers of the brain bulb work with overload.
Treatment of
To treat the consequences of brain damage, use reflexotherapy, massage, and exercise therapy. Therapy of intracranial hypertension includes the use of diuretics. The convulsive syndrome is corrected by anticonvulsants prescribed by the doctor. To eliminate hypoxia, Mexidol, Actovegin, and Trimetazidine are used to support the cardiovascular system.
Prevention is also important: medical supervision during pregnancy, timely treatment of sexual infections in the mother, correction of increased blood clotting. With a deficiency of progesterone designate its synthetic analogue Dyufaston. If the pregnant woman has a deficiency of hormones of the adrenal cortex, it is necessary to use GCS( Dexamethasone).This will prevent the development of lung distress syndrome.
Conclusion
Perinatal encephalopathy is a serious pathology. The prognosis of the disease depends on the extent of the lesion. Regular examination is necessary: neurosonography( ultrasound of the fontanel), dopplerography, electroencephalography, electromyography for the evaluation of muscle tone.
Warning! An Israeli clinic specialist can advise you -
write the question in the form below:
 Learn about the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain: the features of the flow in children and adults.
Learn about the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain: the features of the flow in children and adults.  Consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in adulthood - disability, sometimes inability to serve themselves, lack of communication skills. But it is possible and gradual smoothing of the symptoms, if the damage is insignificant.
Consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in adulthood - disability, sometimes inability to serve themselves, lack of communication skills. But it is possible and gradual smoothing of the symptoms, if the damage is insignificant.  Find out what hypoxia in newborns is: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Find out what hypoxia in newborns is: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. write the question in the form below:



