Tooth Implantation: Pros and Cons
Loss of teeth entails many difficulties, because lost teeth need to be replaced. Lack of teeth in the mouth for a long period can lead to serious problems, including violation of the jaw joint, displacement of the remaining teeth, diseases of the digestive system. One of the modern methods of restoration of the dentition is implantation.
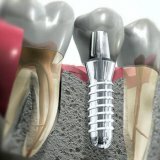
Implantation of teeth is an operation during which an artificial "root", that is, an implant, is installed. Usually it is made of zirconium, titanium or their alloys. Due to the special properties of the materials, after a while the implants "fuse" with the jaw and can be used as a support for the denture( removable or bridged prosthesis, crown).
Implantation of teeth: for and against which we will consider below, is performed under anesthesia. The operation takes 30-40 minutes, for the patient it is not tedious and painless.
Implantation of teeth: beyond
In comparison with other methods of restoring lost teeth, implantation has several advantages. It is important to note that the implant is an independent design, for which no support is needed on either side of the defect. Usually, such a support is the teeth. Due to this feature, the following problems can be solved: firstly, it is possible to prevent the grinding of adjacent teeth;Secondly, it allows not to load natural teeth with additional load during chewing food, which contributes to their preservation.
Dental implants are fixed under the gums immovably and reliably, and the crowns installed on them accurately repeat the color and shape of natural teeth. Artificial teeth are equivalent to natural perform chewing functions. No method of prosthetics can provide adequate load on the bone to retain the root of the tooth, other than implantation. In the absence of a root, the integrity of the jawbone is broken. This process often leads to a "drying up" of the bone and subsequently disrupting the proportions of the face. Replacing the natural root, implants cause the jaw bone to function.
The operation for the implantation of teeth allows you to replace various defects of the dentition, regardless of their length. This makes it possible not to install removable dentures, even if all teeth are lost.
With proper care of the oral cavity, the implants will last much longer than the crowns, removable and bridged prostheses.
Implantation of teeth: against
There are moments that can speak against carrying out this procedure. These are disadvantages and contraindications for implantation. The disadvantages are:
- early rejection, which can still happen, albeit with low probability;
- expensive implants in comparison with prosthetics;
- is a long-term method of treatment - from 1 month to 6 months, rarely up to a year, in the event that a preparatory operation is necessary.
Contraindications
There are absolute and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications manifest themselves during the implantation operation. There can be various complications that will significantly shorten the life of the implant itself:
- decompensated states of the circulatory system;
- disorders of the immune system( polymyositis, lupus erythematosus, thymic hypoplasia, severe infections, parathyroid hypoplasia);
- pathology of the bone system, reducing bone repair( congenital osteopathy, osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, dysplasia);
- disorders of the endocrine system( pathology of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, diabetes mellitus, severe hypo- and hyperthyroidism, hypo- and hyperparathyroidism);
- blood diseases( thalassemia, leukemia, hemolytic anemia, lymphogranulomatosis);
- diseases of the nervous system( paranoia, schizophrenia, psychoses, slaboumie, neuroses, drug addiction and alcoholism);
- as well as tuberculosis, malignant tumors, venereal diseases, AIDS.
Relative contraindications are related to the prescription and nature of systemic disorders. They depend on corrective treatment before surgery:
- acquired and congenital deformity of the occlusion, severe forms of periodontal disease, precancerous state of the oral cavity,
- temporomandibular joint pathology.