Rational pharmacotherapy in dentistry

In dentistry, pharmacotherapy is such a direction in clinical medicine, based on a sound scientific system of principles for the use of drugs to eliminate or slow the progression of the disease. Drugs provide an opportunity to influence the causes that caused the disease and its adverse manifestations. Strictly speaking, even chemotherapy is referred to one of the directions of pharmacotherapy. It also allows you to treat diseases with drugs that work to suppress the development of pathogens in the human body. Impact action will be directed to the microflora.
Rational pharmacotherapy in dentistry is aimed at combating infections and intoxication of the body. It directly gives an opportunity to activate the defenses of the patient. The drugs will be chosen taking into account what factors have led to the disease, and support its further development. These tasks allow us to solve the use of antibiotics and immunotherapy, and the use of hormonal drugs for the correction of psychosomatic disorders.
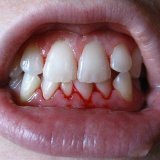
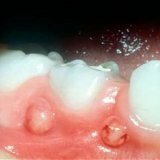
Consider the example of periodontal disease. The basis of it will be inflammation - gingivitis or periodontitis. Gingivitis is an inflammation in the tissues of the gums, in which only the surface of the tissue is affected. Periodontitis is a more serious disease, which leads to the destruction of the dentogingival joint and the progressive changes in the bone. These two diseases are related, one entails another. In this case, you can not do without complex therapy. The cause may be microbial factors, at first glance an absolute harmless accumulation of plaque.
Preferences are given to anti-inflammatory drugs that will act on the main components of pathogenesis.
The causes that lead to periodontal disease, and hence to dystrophy, the death of cells and tissues, can be different - circulatory disorders, hypoxia, infections introduced, intoxication of the body, hormonal disorders and heredity itself. Parodontosis is one of the sides of manifestation in the violation of the work of regulatory mechanisms. Rational pharmacotherapy in this case is also the use of drugs that improve metabolism in the body, hemodynamics, and drugs to stimulate regeneration processes.
With periodontal disease, the choice of medications is great. The task of pharmacotherapy will be the effect of medication on the microorganisms of the oral cavity, and simultaneously with the pathogenetic links of the periodontal process itself. The first can be conventional chemotherapy, and the second approach is more complex and aimed at local improvement of blood circulation, affecting the nervous system, enhancing the functions of regeneration. And do not interfere with preparations of general strengthening and anti-inflammatory action.
Methods and principles of drug treatment:
There are several ways to influence the pathological processes in dental diseases:
- the normalization of metabolism with the help of medications;
- normalization of the functions of the main homeostatic systems by drug exposure to them;
- is a joint hormone-metabolic therapy.
In the treatment of dental pathogens, drugs can enter the body in such ways:
- aerosol irrigation cavity;
- by inhalation;
- by means of pressure washes from a syringe;
- by rinsing;
- applications;
- application of medical dressings;
- by electrophoresis or magnetophoresis;
- for injection.
The treatment procedure is due to the peculiarities of the disease, and the way the medication is administered depends on it. From the routes of administration, for example, to the focus of inflammation, the effectiveness of treatment is determined.
Pharmacotherapy in dentistry is based on such principles:
- Refuse if possible from potent drugs such as piocid and trichloroacetic acid. They can cause tissue necrosis or irritation.
- Alternate medicinal products, as the body becomes addictive, biological balance is disturbed.
- Carry out a critical analysis of the potentialities of modern medicines.
- Study of pharmaceutical production trends.
- Knowing what side effects accompany the drugs used.
- Selection of drugs taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and tolerability, timely correction of the treatment regimen, combating the complications.
- Prognosis of the ratio of expected benefit and possible harm to health when choosing medicines.
- Minimizing the load on the patient's body with potent drugs, combining several types of therapy.
- Accurate performance by the patient of the doctor's prescription.
- A clear understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease.
- The dentist should also take into account all the characteristic features of the inflammatory process and predict possible complications in the patient.
- Introduction of strict accounting at the time of complex therapy, control of medications that the patient received.
- Immediate exclusion of prescriptions of those drugs that worsened well-being.
- When prescribing medicines, the physiological condition of the patient must be taken into account - pregnancy or lactation, concomitant diseases - diabetes, ulcer, gastritis, cholelithiasis, kidney problems and liver diseases.
- Understanding how the metabolism process proceeds and how drugs are excreted from the body to avoid complications and side effects.