Sialolithiasis( salivary stone disease)
Description
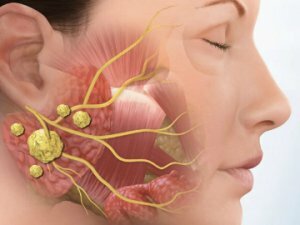
Sialolithiasis is a chronic disease that has an inflammatory nature. It flows with the formation of salivary stones( concrements) in the ducts of the glands. Much more often the submaxillary gland is affected, more rarely - parotid and very rarely - sublingual. It occurs more often in patients under the age of 45 years. Men get sick more often than women. In children, pathology develops very rarely.
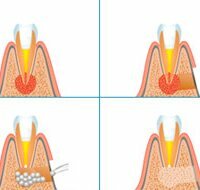
The malfunctioning of the salivary glands can slow the flow of saliva, causing it to stagnate. During the stagnation period, the salts precipitate, and stone formation takes place.
Salivary calculi consist of inorganic salts: phosphate and calcium carbonate. There is the presence of sodium, potassium, iron and magnesium.
The stones can grow at a fast pace or very slowly. Their size can reach the size of a chicken egg.
Reasons for
Science does not name exact reasons for the appearance of deposits in the salivary glands.
Only the factors contributing to the development of the disease are distinguished:
- malfunction of the salivary glands;
- violation of calcium metabolism;
- increased blood clotting;
- hypovitaminosis or vitamin A vitamin deficiency;
- trauma of the salivary glands;
- features of the anatomical structure of the jaw, in which stagnation of salivary fluid and further petrification occurs.
 The cause of sialolithiasis can be considered the impact of a foreign body on the salivary glands. This may be a toothbrush set, salt crystal or a cluster of bacteria. Foreign bodies, being in a salivary stream, around themselves collect salt layers which drop out of a saliva.
The cause of sialolithiasis can be considered the impact of a foreign body on the salivary glands. This may be a toothbrush set, salt crystal or a cluster of bacteria. Foreign bodies, being in a salivary stream, around themselves collect salt layers which drop out of a saliva.
The causes of the development of the disease include infectious diseases that are under treatment:
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- mumps;
- actinomycosis( fungus).
Symptoms of
At the initial stage of development of sialolithiasis, its clinical manifestations are absent. Sometimes there is swelling and a slight tingling pain in the glands. This is noted when eating. When palpation palpated enlarged salivary glands.
With further development of the pathology, painful sensations become more frequent. Development of purulent formation begins. The patient feels worse, the body temperature rises sharply. Particularly strong pain sensations a person experiences when chewing food.
The most pronounced symptomatology is when the stone hits the oral cavity. Cork is formed, the outflow of saliva secret is difficult.
Other symptoms of the disease include the following:
- dryness in the oral cavity;
- difficulty opening the mouth, bursting pain when swallowing and talking;
- is an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- swelling of the submandibular or parotid gland;
- chills, weakness and other signs of inflammation.
Diagnosis
Visual inspection reveals enlarged glands. Palpation reveals soreness and dense consistency of the gland.
The diagnosis is determined on the basis of laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- ultrasound of the salivary glands.
- Computerized sialotomography.
- Biochemical analysis of saliva.
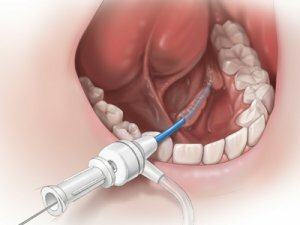 For the diagnosis, resort to the use of radiography. On X-ray images, mineralized high-density stones are clearly visible. With a weak mineralization of the stone, it is difficult to distinguish.
For the diagnosis, resort to the use of radiography. On X-ray images, mineralized high-density stones are clearly visible. With a weak mineralization of the stone, it is difficult to distinguish.
The method of contrast sialography( use of contrast medium) allows to study the structure of the ducts, their shape. The stones are fixed as voids in the contrast mass.
Concrements of the salivary glands must differentiate( differentiate) from tumors of the oral cavity, lymphadenitis, maxillary phlegmon, phlebolites( calcareous formations) and odontogenic( purulent) abscess.
Treatment of
Treatment of patients with salivary-stone disease is carried out by taking into account the stage and the presence of exacerbation.
Therapy includes:
Surgery:
- In the stage of exacerbation of sialolithiasis, a cut is made at the site of abscess formation. This increases the outflow of exudate, the stone can even stand out spontaneously.
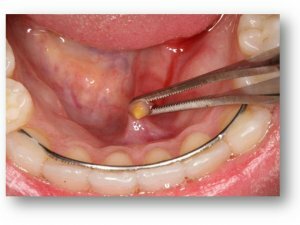
- In the chronic stage, concrements from the ducts are removed in an outpatient setting if they are located in the front of the excretory duct.
When the calculus is located in the lower jaw or upper duct of the gland, it is also removed by intraoral access. The operation is performed in a hospital environment, becauseSome equipment is required. The postoperative period is aimed at restoring the gland and removing the inflammatory postoperative process.
If it is not possible to remove the stones, an extirpation( complete removal) of the submandibular salivary gland is performed in the hospital.
Radical removal of the glands is accompanied by a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity, the destruction of teeth, which significantly reduces the quality of life of the patient.
Medication:
- Chemical dissolution of stones without disturbing the structure of the gland. In the gland ducts, 1% citric acid solution is administered daily for 14 days.
- Treatment with antibiotics. Appoints only the doctor on the basis of laboratory indicators. Streptomycin is often prescribed. Sometimes a novocaine blockade with penicillin is required.
- In combination with conservative therapy, the drug Kanefron is prescribed to treat( if required) urolithiasis.
Folk remedies
 For the treatment of sialolithiasis there are many folk recipes, they can be used at the initial stage of the disease:
For the treatment of sialolithiasis there are many folk recipes, they can be used at the initial stage of the disease:
- Therapeutic ointment. A teaspoon of honey, a Novocaine ampoule, a fresh chicken egg and a spoonful of olive oil, combine and mix thoroughly.3-4 times a day to lubricate the inflamed areas of the mouth. The course of treatment is 7 days.
- Tincture hemlock( buy at the pharmacy).Take one drop before breakfast on the first day, the second day - 2 drops, etc. To bring the reception to 30 drops. Then start reducing the intake to 1 drop.
- Soda solution. In a cup of warm water to dissolve art. Spoon of baking soda. Rinse your mouth during the day several times.
- Tincture of echinacea. Pharmacy tincture diluted with boiled water( 1: 1), make compresses on the problem site.
Complications of
With the removal of concrements from the parotid duct, a possible complication is injury of the facial nerve, as well as the formation of salivary external fistula. An abscess can occur in the soft tissues surrounding the stone.
Prognosis with timely treatment is always favorable. Relapses are very rare.
Prevention
For the prevention of disease, it is necessary to eliminate the factors contributing to stone formation:
- violation of vitamin and mineral metabolism;
- bad habits;
- abnormal development of the ducts of the salivary glands;
- to correct the medication;
- observe the hygiene of the oral cavity.
Sialolithiasis is treated by a dentist and surgeon.
Warning! Dense and painful formation in the neck can be a tumor.