Gingivitis Clinic: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment
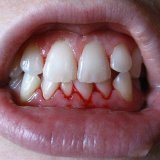 Some people suffer from inflammation of the gum tissue, which is accompanied by bleeding and soreness of the gums, as well as the appearance of bad breath - this disease is called gingivitis( gum - lat. gingiva ).G Ingivit, a clinic, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of which is described below, a disease that today affects about half of all patients seeking help from specialists.
Some people suffer from inflammation of the gum tissue, which is accompanied by bleeding and soreness of the gums, as well as the appearance of bad breath - this disease is called gingivitis( gum - lat. gingiva ).G Ingivit, a clinic, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of which is described below, a disease that today affects about half of all patients seeking help from specialists.
Causes of the appearance and development of gingivitis.
- Non-compliance with oral hygiene;
- Some medications;
- Chemical or thermal burns;
- Smoking;
- Absence of the necessary amount of vitamins in the consumed foods;
- Gastritis;
- Presence of some infectious diseases;
- Ulcerative processes in the digestive system;
- Caries.
There are quite a few reasons, and they are all divided into two groups: internal and external causes.
Internal causes.
This group can include, first, an unbalanced diet, diseases of the digestive system and insufficient functioning of the immune system, including local immunity in the oral cavity.
It follows that the internal causes of gingivitis are due to the presence of chronic diseases and the general condition of the whole organism.
External causes.
- Mechanical injuries of gum tissue;
- Chemical and thermal burns;
- Allergic reactions resulting from the administration of certain medications;
- Smoking and other bad habits;
- Improper filling and / or dental prosthetics.
The main cause of gingivitis is the presence of tartar and plaque. Harmful microorganisms are able to accumulate on the surface of teeth and gums, forming a special film, which, with time, hardens into tartar.
This process occurs about four to six months, for this reason, dentists advise cleaning teeth from the formed stone at least every six months.
The main symptoms of gingivitis.
The symptomatology of the disease is as follows:
- Pain sensations in the area of inflamed gingival tissue;
- Puffiness of gum tissues;
- Non-gingival tissue color - bright red;
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- Pain when eating;
- Rapidly accumulating on the surface of gums and teeth plaque.
By the way, gingivitis does not necessarily indicate the presence of any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, it can also act as an independent disease.
Gingivitis: a clinic.
Different not only symptoms of gingivitis, but also the course of the disease, in connection with which the acute and chronic forms of inflammation of the gums are isolated.
The symptomatology in the acute form of the disease is traditional: reddening of the gum tissue, bleeding and swelling.
For chronic gingivitis, there is no visible symptoms and a calm course of the disease, but this form of the disease can lead to hyperplasia, that is, tissue overgrowth. Over time, tissues can grow to such an extent that they are able to cover( in whole or in part) the surface of the crown of the tooth.
In addition, dentists also distinguish several types of the disease: catarrhal gingivitis, ulcerative, hypertrophic and mixed gingivitis.
Inflammation of the gums, in which a tissue consisting of leukocytes and proteins is slowly released from the tissues, is called catarrhal gingivitis. This disease occurs differently, in connection with which catarrhalic gingivitis is distinguished in the following forms: mild, moderate and severe. Symptomatology of the disease: a burning sensation in the gums, the formation of a large amount of plaque, puffiness of the papillae of the gum and their transformation into a dome-like shape from a normal ostoid.
In hypertrophic gingivitis, the inflammatory process leads to an increase in the gingival papilla due to fibrous dysplasia and swelling. The mild form of hypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the papillae by one-third of the dental crown, the middle one by half the crown of the tooth, with a severe form of the disease, the papillae increase by more than ½ the size of the crown of the tooth.
Ulcerative gingivitis is also called necrotic. For him, the appearance of pathological changes in the periodontal tissues is characteristic. With this type of disease, the classic symptoms persist, but they are added to the increased body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes and headache. When untimely treatment or in the absence of such necrotic processes can spread to the mucous membranes of the tonsils and cheeks. In addition, ulcerative gingivitis is one of the causes of blood diseases.
Gingivitis: Diagnosis.
Diagnose this disease on the basis of the above symptoms.
Gingivitis: treatment.
If you have this disease, do not self-medicate! Do not help you and traditional medicine. At the first sign of gingivitis, you should consult a qualified dentist. Treat the disease by affecting the dental plaques, eliminating common and local predisposing factors.
In case of gingivitis, first of all it is necessary to pay attention to the rules of hygiene of the oral cavity.
Special preparations can slow down the development of the disease and prevent complications in the acute and chronic stage of gingivitis, including some antibiotics, immunocorrectors for topical use, and various anti-inflammatory drugs.
Often it is necessary to resort to such types of dental intervention as removal of calculus, replacement of badly selected seals and their grinding. Today, the tooth stone is removed not only mechanically, but also ultrasound.
Sometimes treatment requires surgical intervention. In this case, the curettage is carried out, the essence of which is that the deposits are removed with the help of special devices - curettes, excavators, hooks. Sometimes for this purpose it is necessary to cut the gum tissue. In the first case, the procedure is called closed curettage, in the second - open curettage.
In the presence of chronic gingivitis, the oral cavity is treated with a solution of sodium bicarbonate and various anti-inflammatory drugs.
If gingivitis is caused by infectious diseases, then the source of the disease should be eliminated - for this the doctor will recommend antifungal or antibacterial drugs.
Often, gingivitis is a consequence of decreased immunity, so treatment includes the use of such agents as immunocorrectors, which contribute to improving the protective properties of the oral cavity. Immunocorrectors help to increase the activity of the phagocytosis process( i.e., neutralize pathogenic bacteria) and increase the amount of lysozyme that has bactericidal action in saliva.
Gingivitis: prevention.
- Regular dental visits and professional dental cleaning;
- Daily cleaning of teeth from dental plaques( using dental floss and paste).